Hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell carcinoma syndrome-associated renal cell carcinoma
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell carcinoma syndrome-associated renal cell carcinoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
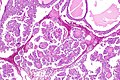
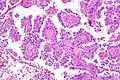
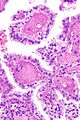
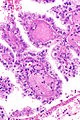
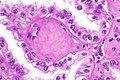
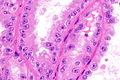
 Hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell carcinoma syndrome-associated renal cell carcinoma showing the characteristic hyalinized papillary cores. H&E stain. (WC/Nephron) | |
|
| |
| LM | large eosinophilic nucleolus with perinucleolar clearing (may be focal), variable architecture: papillary (classic description) +/-hyaline material within the fibrovascular cores (characteristic), tubulopapillary, tubular, solid, sieve-like pattern/cribriform |
| LM DDx | papillary renal cell carcinoma (type 2), tubulocystic carcinoma of the kidney, collecting duct carcinoma, renal medullary carcinoma |
| IHC | FH -ve, 2SC +ve, CK7 -ve, TFE3 -ve, CK20 -ve, CD10 -ve, UEA-1 -ve |
| Molecular | FH mutation |
| Grossing notes | total nephrectomy for tumour grossing, partial nephrectomy grossing |
| Staging | kidney cancer staging |
| Site | kidney - see kidney tumours |
|
| |
| Associated Dx | uterine leiomyomas (women), skin leiomyomas |
| Syndromes | hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell carcinoma syndrome |
|
| |
| Clinical history | +/-family history of kidney cancer |
| Signs | +/-skin rash |
| Prevalence | rare |
| Prognosis | poor |
| Clin. DDx | other kidney tumours |
| Treatment | resection |
Hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell carcinoma syndrome-associated renal cell carcinoma is a malignant epithelial tumour of the kidney associated with the hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell carcinoma syndrome.
General
- Often aggressive - significant cause of mortality.[1]
Microscopic
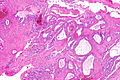
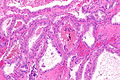
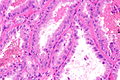
Features - renal cell carcinoma:[1]
- Large eosinophilic nucleolus with perinucleolar clearing - proposed hallmark - important.
- May be focal.
- Variable architecture:
- Papillary - classic description.
- Hyaline material within the fibrovascular cores - characteristic.
- Tubulopapillary.
- Tubular.
- Solid.
- Sieve-like pattern/cribriform.
- Papillary - classic description.
Notes:
- Not common: psammoma bodies, foamy macrophages.[2]
DDx:
- Papillary renal cell carcinoma (type 2).
- Tubulocystic carcinoma of the kidney.
- Collecting duct carcinoma.[3]
- Renal medullary carcinoma - cells also have a prominent nucleolus.
Images
RCC
HLRCC - TC-like - low mag.
www
IHC
- Fumarate hydratase (FH) -ve.
- 2SC +ve -- cytoplasmic,[4] cytoplasmic and nuclear.[1]
- 2SC = S-(2-succino)-cysteine.
Others:
- CK7 -ve (0 +ve/38 cases[5]).
- CD10 -ve.
- May be positive in clear cell RCC-like areas.
- CK20 -ve (0 +ve/38 cases[5]).
- UEA-1 -ve.[5]
- TFE3 -ve (0 +ve/38 cases[5]).
- CK34betaE12 -ve (0 +ve/38 cases[5]).
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Chen, YB.; Brannon, AR.; Toubaji, A.; Dudas, ME.; Won, HH.; Al-Ahmadie, HA.; Fine, SW.; Gopalan, A. et al. (May 2014). "Hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell carcinoma syndrome-associated renal cancer: recognition of the syndrome by pathologic features and the utility of detecting aberrant succination by immunohistochemistry.". Am J Surg Pathol 38 (5): 627-37. doi:10.1097/PAS.0000000000000163. PMID 24441663.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Launonen, V.; Vierimaa, O.; Kiuru, M.; Isola, J.; Roth, S.; Pukkala, E.; Sistonen, P.; Herva, R. et al. (Mar 2001). "Inherited susceptibility to uterine leiomyomas and renal cell cancer.". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98 (6): 3387-92. doi:10.1073/pnas.051633798. PMID 11248088.
- ↑ Pithukpakorn, M.; Wei, MH.; Toure, O.; Steinbach, PJ.; Glenn, GM.; Zbar, B.; Linehan, WM.; Toro, JR. (Sep 2006). "Fumarate hydratase enzyme activity in lymphoblastoid cells and fibroblasts of individuals in families with hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell cancer.". J Med Genet 43 (9): 755-62. doi:10.1136/jmg.2006.041087. PMID 16597677.
- ↑ Reyes, C.; Karamurzin, Y.; Frizzell, N.; Garg, K.; Nonaka, D.; Chen, YB.; Soslow, RA. (Jul 2014). "Uterine smooth muscle tumors with features suggesting fumarate hydratase aberration: detailed morphologic analysis and correlation with S-(2-succino)-cysteine immunohistochemistry.". Mod Pathol 27 (7): 1020-7. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2013.215. PMID 24309325.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 Merino, MJ.; Torres-Cabala, C.; Pinto, P.; Linehan, WM. (Oct 2007). "The morphologic spectrum of kidney tumors in hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell carcinoma (HLRCC) syndrome.". Am J Surg Pathol 31 (10): 1578-85. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e31804375b8. PMID 17895761.