Difference between revisions of "Glioblastoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→Images: tweak) |
(→IHC: more) |
||
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
*[http://cancerres.aacrjournals.org/content/64/3/920/F7.expansion.html Pseudopalisading necrosis in GBM (aacrjournals.org)]. | *[http://cancerres.aacrjournals.org/content/64/3/920/F7.expansion.html Pseudopalisading necrosis in GBM (aacrjournals.org)]. | ||
==IHC== | |||
*GFAP +ve (cytoplasm). | *GFAP +ve (cytoplasm). | ||
*IDH-1 -ve. | *IDH-1 -ve. | ||
Revision as of 23:36, 23 July 2013
| Glioblastoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
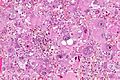
 Glioblastoma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | astrocytic differentiation, nuclear atypia, necrosis, microvascular proliferation, +/-pseudopalisading necrosis |
| LM DDx | anaplastic astrocytoma |
| IHC | GFAP +ve, IDH-1 -ve/+ve |
| Site | brain, spinal cord |
|
| |
| Radiology | intra-axial |
| Prognosis | very poor |
| Clin. DDx | metastatic carcinoma |
Glioblastoma a very common malignant primary brain tumour in adults. It has a very poor prognosis.
It was previously known as glioblastoma multiforme, abbreviated GBM.
General
- Median survival is measured in months.[1]
- Only about 5% can expect to survive more than three years.[2]
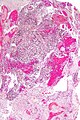
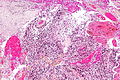
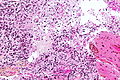
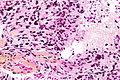
Microscopic
Features:
- Astrocytic tumour with:
- Nuclear atypia.
- Necrosis.
- Endothelial proliferation (AKA microvascular proliferation).
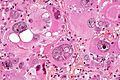
- +/-"Pseudopalisading necrosis" - tumour cells lined-up like a picket fence around necrotic areas.
Images
www:
- Microvascular proliferation in a GBM (ouhsc.edu).
- Pseudopalisading necrosis in GBM (aacrjournals.org).
IHC
- GFAP +ve (cytoplasm).
- IDH-1 -ve.
- +ve if developed from lower grade astrocytoma. (???)
See also
References
- ↑ Jubelirer, SJ.. "A review of the treatment and survival rates of 138 patients with glioblastoma multiforme.". W V Med J 92 (4): 186-90. PMID 8772403.
- ↑ Krex, D.; Klink, B.; Hartmann, C.; von Deimling, A.; Pietsch, T.; Simon, M.; Sabel, M.; Steinbach, JP. et al. (Oct 2007). "Long-term survival with glioblastoma multiforme.". Brain 130 (Pt 10): 2596-606. doi:10.1093/brain/awm204. PMID 17785346.