Difference between revisions of "Basal cell hyperplasia of the prostate"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
*No nuclear hyperchromasia. | *No nuclear hyperchromasia. | ||
*Two cell populations (as in normal prostate glands). | *Two cell populations (as in normal prostate glands). | ||
*Basal cells may have nucleoli. | *Basal cells may have [[nucleoli]]. | ||
DDx: | DDx: | ||
Revision as of 14:10, 30 June 2016
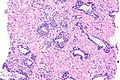
Basal cell hyperplasia of the prostate, also known as basal cell hyperplasia, is a benign change of the prostate gland that may be misdiagnosed as prostate carcinoma.
General
- Benign lesion that can be misdiagnosed as cancer.[1]
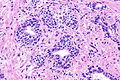
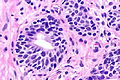
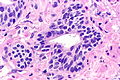
Microscopic
Features:[2]
- Low power gland architecture near normal.[3][4]
- Glands not as small as cancer.
- Folds in gland lumina.
- No nuclear hyperchromasia.
- Two cell populations (as in normal prostate glands).
- Basal cells may have nucleoli.
DDx:
- High-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia - has nuclear hyperchromasia, architecture usually different (micropapillary, tufted, cribriform or flat).
- Prostatic adenocarcinoma.
- Adenoid cystic/basal cell carcinoma of the prostate - for the adenoid cystic-like pattern of BCH.[5]
- Urothelial metaplasia of the prostate - larger cells, cell borders seen.
Images
www
Sign out
- Usually not reported.
See also
References
- ↑ Cleary, KR.; Choi, HY.; Ayala, AG. (Dec 1983). "Basal cell hyperplasia of the prostate.". Am J Clin Pathol 80 (6): 850-4. PMID 6195916.
- ↑ URL: http://pathologyoutlines.com/prostate.html#bch. Accessed on: 28 June 2010.
- ↑ URL: http://www.nature.com/modpathol/journal/v16/n6/fig_tab/3880810f1.html. Accessed on: 28 June 2010.
- ↑ URL: http://www.nature.com/modpathol/journal/v16/n6/fig_tab/3880810f2.html. Accessed on: 28 June 2010.
- ↑ McKenney, JK.; Amin, MB.; Srigley, JR.; Jimenez, RE.; Ro, JY.; Grignon, DJ.; Young, RH. (Oct 2004). "Basal cell proliferations of the prostate other than usual basal cell hyperplasia: a clinicopathologic study of 23 cases, including four carcinomas, with a proposed classification.". Am J Surg Pathol 28 (10): 1289-98. PMID 15371944.