Difference between revisions of "Aneurysmal bone cyst"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(+cat.) |
m |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ Infobox diagnosis | |||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | |||
| Image = Aneurysmal_bone_cyst_-_intermed_mag.jpg | |||
| Width = | |||
| Caption = Aneurysmal bone cyst. [[H&E stain]]. | |||
| Synonyms = | |||
| Micro = | |||
| Subtypes = | |||
| LMDDx = [[giant cell tumour of bone]], [[telangiectatic osteosarcoma]], other [[giant cell lesions]] | |||
| Stains = | |||
| IHC = | |||
| EM = | |||
| Molecular = | |||
| IF = | |||
| Gross = | |||
| Grossing = | |||
| Site = [[bone]] | |||
| Assdx = | |||
| Syndromes = | |||
| Clinicalhx = | |||
| Signs = | |||
| Symptoms = | |||
| Prevalence = common | |||
| Bloodwork = | |||
| Rads = | |||
| Endoscopy = | |||
| Prognosis = benign | |||
| Other = | |||
| ClinDDx = | |||
| Tx = | |||
}} | |||
'''Aneurysmal bone cyst''', abbreviated '''ABC''', is a very common benign pathology of [[bone]]. | |||
'''[[Giant cell reparative granuloma]]''' (also known as ''solid aneurysmal bone cyst'') is dealt with separately. | |||
==General== | |||
Features:<ref name=emed_abc>URL: [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1254784-overview http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1254784-overview]. Accessed on: 4 February 2011.</ref> | |||
*Benign. | |||
**May grow rapidly. | |||
*Osteolysis -> cystic space -> filled with blood. | |||
*Relatively common; in children second only to [[osteosarcoma]].<ref name=pmid18157043>{{cite journal |author=van den Berg H, Kroon HM, Slaar A, Hogendoorn P |title=Incidence of biopsy-proven bone tumors in children: a report based on the Dutch pathology registration "PALGA" |journal=J Pediatr Orthop |volume=28 |issue=1 |pages=29–35 |year=2008 |pmid=18157043 |doi=10.1097/BPO.0b013e3181558cb5 |url=}}</ref> | |||
==Gross/radiologic== | |||
Features:<ref name=pmid22531523>{{Cite journal | last1 = Parashari | first1 = UC. | last2 = Khanduri | first2 = S. | last3 = Upadhyay | first3 = D. | last4 = Bhadury | first4 = S. | last5 = Singhal | first5 = S. | title = Radiologic and pathologic correlation of aneurysmal bone cysts at unusual sites. | journal = J Cancer Res Ther | volume = 8 | issue = 1 | pages = 103-5 | month = | year = | doi = 10.4103/0973-1482.95183 | PMID = 22531523 }}</ref> | |||
*Air-fluid levels (radiology). | |||
*Usually metaphysis of long bones, but uncommonly the femur. | |||
*May have an "aggressive" appearance, i.e. erode bone. | |||
==Microscopic== | |||
Features:<ref name=emed_abc/> | |||
*Bony trabeculae ''or'' osteoid tissue. | |||
*Osteoclast [[giant cell]]s. | |||
**Multi-nucleated giant-cells with round randomly arranged nuclei. | |||
*Benign spindle cells (fibroblasts) - surround bone/adjacent to the giant cells - '''important'''. | |||
*Blood +/- surrounded by giant cells. | |||
DDx: | |||
*[[Giant cell tumour of bone]] - the nuclei of the cells surrounding the giant cells are similar to those in the giant cells (round nuclei). | |||
*[[Telangiectatic osteosarcoma]]. | |||
*Other [[giant cell lesions]]. | |||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Aneurysmal_bone_cyst_-_intermed_mag.jpg | ABC - intermed. mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
Image:Aneurysmal_bone_cyst_-_high_mag.jpg | ABC - high mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
Image:Aneurysmal_bone_cyst_-_very_high_mag.jpg | ABC - very high mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
Image:[[File:Bone AneurysmalBoneCyst HP.JPG|thumb|High power view of giant cells in a less cellular version of aneurysmal bone cyst.]] | |||
</gallery> | |||
www: | |||
*[http://www.webpathology.com/image.asp?n=4&Case=344 ABC - low mag. (webpathology.com)]. | |||
*[http://www.webpathology.com/image.asp?n=5&Case=344 ABC - intermed. mag. (webpathology.com)]. | |||
*[http://www.webpathology.com/image.asp?case=344&n=6 ABC - high mag. (webpathology.com)]. | |||
==See also== | |||
*[[Bone]]. | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|2}} | |||
[[Category:Bone]] | |||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | [[Category:Diagnosis]] | ||
Latest revision as of 02:47, 3 December 2014
Aneurysmal bone cyst, abbreviated ABC, is a very common benign pathology of bone.
| Aneurysmal bone cyst | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
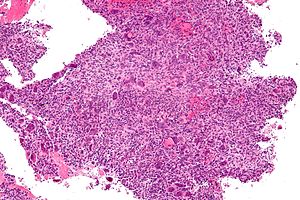 Aneurysmal bone cyst. H&E stain. | |
| LM DDx | giant cell tumour of bone, telangiectatic osteosarcoma, other giant cell lesions |
| Site | bone |
|
| |
| Prevalence | common |
| Prognosis | benign |
Giant cell reparative granuloma (also known as solid aneurysmal bone cyst) is dealt with separately.
General
Features:[1]
- Benign.
- May grow rapidly.
- Osteolysis -> cystic space -> filled with blood.
- Relatively common; in children second only to osteosarcoma.[2]
Gross/radiologic
Features:[3]
- Air-fluid levels (radiology).
- Usually metaphysis of long bones, but uncommonly the femur.
- May have an "aggressive" appearance, i.e. erode bone.
Microscopic
Features:[1]
- Bony trabeculae or osteoid tissue.
- Osteoclast giant cells.
- Multi-nucleated giant-cells with round randomly arranged nuclei.
- Benign spindle cells (fibroblasts) - surround bone/adjacent to the giant cells - important.
- Blood +/- surrounded by giant cells.
DDx:
- Giant cell tumour of bone - the nuclei of the cells surrounding the giant cells are similar to those in the giant cells (round nuclei).
- Telangiectatic osteosarcoma.
- Other giant cell lesions.
Images
www:
See also
- Bone.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 URL: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1254784-overview. Accessed on: 4 February 2011.
- ↑ van den Berg H, Kroon HM, Slaar A, Hogendoorn P (2008). "Incidence of biopsy-proven bone tumors in children: a report based on the Dutch pathology registration "PALGA"". J Pediatr Orthop 28 (1): 29–35. doi:10.1097/BPO.0b013e3181558cb5. PMID 18157043.
- ↑ Parashari, UC.; Khanduri, S.; Upadhyay, D.; Bhadury, S.; Singhal, S.. "Radiologic and pathologic correlation of aneurysmal bone cysts at unusual sites.". J Cancer Res Ther 8 (1): 103-5. doi:10.4103/0973-1482.95183. PMID 22531523.