Difference between revisions of "Amebiasis"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→Image) |
|||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
===Image=== | ===Image=== | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
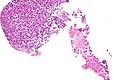
Image:Amebiasis - high mag.jpg | Amebiasis - high mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
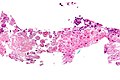
Image:Amebiasis_-_very_high_mag.jpg | Amebiasis - very high mag. (WC/Nephron) | Image:Amebiasis_-_very_high_mag.jpg | Amebiasis - very high mag. (WC/Nephron) | ||
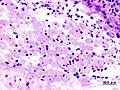
Image:Amoebic_dysentery_in_colon_biopsy_%281%29.jpg | Amebiasis (WC) | Image:Amoebic_dysentery_in_colon_biopsy_%281%29.jpg | Amebiasis (WC) | ||
Revision as of 03:09, 14 January 2014
Amebiasis, also be spelled amoebiasis, is an infectious disease, caused by the protozoan Entamoeba histolytica.
General
- Infection with Entamoeba histolytica.[1]
- May mimic colon cancer.[2]
May cause:[3]
- Dysentery (diarrhea containing mucus and/or blood in the feces).
- Colitis.
- Liver abscess.
Microscopic
Features:
- Entamoeba histolytica are round/ovoid eosinophilic bodies ~ 40-60 micrometers in maximal dimension.
- Found in bowel lumen.
- Ingest RBCs.
Image
See also
References
- ↑ URL: http://www.health.state.ny.us/diseases/communicable/amebiasis/fact_sheet.htm. Accessed on: 17 June 2010.
- ↑ Fernandes, H.; D'Souza, CR.; Swethadri, GK.; Naik, CN.. "Ameboma of the colon with amebic liver abscess mimicking metastatic colon cancer.". Indian J Pathol Microbiol 52 (2): 228-30. PMID 19332922. http://www.ijpmonline.org/article.asp?issn=0377-4929;year=2009;volume=52;issue=2;spage=228;epage=230;aulast=Fernandes.
- ↑ Mortimer, L.; Chadee, K. (Mar 2010). "The immunopathogenesis of Entamoeba histolytica.". Exp Parasitol. doi:10.1016/j.exppara.2010.03.005. PMID 20303955.