Difference between revisions of "Adrenocortical carcinoma"
(→DDX) |
|||
| (9 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
| LMDDx = | | LMDDx = | ||
| Stains = | | Stains = | ||
| IHC = vimentin +ve, melan A +ve, inhibin-alpha +ve, chromogranin A -ve, [[EMA]] -ve, S-100 -ve | | IHC = vimentin +ve, melan A +ve, inhibin-alpha +ve, chromogranin A -ve, [[EMA]] -ve, S-100 -ve, SF-1 +ve | ||
| EM = | | EM = | ||
| Molecular = | | Molecular = | ||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
In general: | In general: | ||
*Adrenocortical adenomas are small, circumscribed and have cells with largely bland nuclei and abundant foamy clear or pink cytoplasm. | |||
Adrenocortical adenomas are small, circumscribed and have cells with largely bland nuclei and abundant foamy clear or pink cytoplasm. | *Adrenocortical carcinomas are large, infiltrative, have fibrous bands and necrosis, and cells with less cytoplasm and more atypia including atypical mitotic figures. | ||
*Adrenocortical adenomas in children; however, can look really ugly. | |||
Adrenocortical carcinomas are large, infiltrative, have fibrous bands and necrosis, and cells with less cytoplasm and more atypia including atypical mitotic figures. | |||
Adrenocortical adenomas in children; however, can look really ugly. | |||
Notes: | Notes: | ||
*Tumour may contain fat.<ref name=pmid15688105>{{cite journal |author=Heye S, Woestenborghs H, Van Kerkhove F, Oyen R |title=Adrenocortical carcinoma with fat inclusion: case report |journal=Abdom Imaging |volume=30 |issue=5 |pages=641–3 |year=2005 |pmid=15688105 |doi=10.1007/s00261-004-0281-5 |url=}}</ref> | *Tumour may contain fat.<ref name=pmid15688105>{{cite journal |author=Heye S, Woestenborghs H, Van Kerkhove F, Oyen R |title=Adrenocortical carcinoma with fat inclusion: case report |journal=Abdom Imaging |volume=30 |issue=5 |pages=641–3 |year=2005 |pmid=15688105 |doi=10.1007/s00261-004-0281-5 |url=}}</ref> | ||
====DDx==== | |||
Diagnostic categories: | |||
*[[Large epithelioid tumours|Large pink polygonal cell neoplasms]]. | |||
*Retroperitonial large polygonal cell neoplasms. | |||
**[[Adrenocortical adenoma]]. | |||
**[[Pheochromocytoma]]. | |||
**[[Malignant melanoma|Metastatic melanoma]]. | |||
**[[Hepatocellular carcinoma|Metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma]]. | |||
**[[Renal cell carcinoma|Metastatic renal cell carcinoma]]. | |||
**[[Epithelioid angiomyolipoma]]. | |||
===Images=== | ===Images=== | ||
| Line 102: | Line 110: | ||
===Adult=== | ===Adult=== | ||
====Weiss criteria==== | ====Weiss criteria==== | ||
Three of the following:<ref name=pmid20551521>{{cite journal |author=Jain M, Kapoor S, Mishra A, Gupta S, Agarwal A |title=Weiss criteria in large adrenocortical tumors: a validation study |journal=Indian J Pathol Microbiol |volume=53 |issue=2 |pages=222–6 |year=2010 |pmid=20551521 |doi=10.4103/0377-4929.64325 |url=}}</ref> | Three of the following:<ref name=pmid20551521>{{cite journal |author=Jain M, Kapoor S, Mishra A, Gupta S, Agarwal A |title=Weiss criteria in large adrenocortical tumors: a validation study |journal=Indian J Pathol Microbiol |volume=53 |issue=2 |pages=222–6 |year=2010 |pmid=20551521 |doi=10.4103/0377-4929.64325 |url=}}</ref><ref name=pmid6703192>{{Cite journal | last1 = Weiss | first1 = LM. | title = Comparative histologic study of 43 metastasizing and nonmetastasizing adrenocortical tumors. | journal = Am J Surg Pathol | volume = 8 | issue = 3 | pages = 163-9 | month = Mar | year = 1984 | doi = | PMID = 6703192 }}</ref> | ||
#High nuclear grade. | #High nuclear grade. | ||
#High mitotic rate; >5/50 HPF (@ 40X obj.) - definition suffers from [[HPFitis]]. | #High mitotic rate; >5/50 HPF (@ 40X obj.) - definition suffers from [[HPFitis]]. | ||
| Line 128: | Line 136: | ||
*"Intermediate risk" 200-400 g, no mets, +/-microscopic disease outside adrenal. | *"Intermediate risk" 200-400 g, no mets, +/-microscopic disease outside adrenal. | ||
*"High risk" >400 g, or mets, or gross invasion of adjacent structures. | *"High risk" >400 g, or mets, or gross invasion of adjacent structures. | ||
==IHC== | ==IHC== | ||
*SF-1 +ve.<ref>{{cite journal |authors=Wang R, Solomon B, Luen SJ, Prall OW, Khoo C, Gill AJ, Lewin J, Sachithanandan N |title=Pitfalls and progress in adrenocortical carcinoma diagnosis: the utility of a multidisciplinary approach, immunohistochemistry and genomics |journal=Endocrinol Diabetes Metab Case Rep |volume=2022 |issue= |pages= |date=January 2022 |pmid=35023475 |pmc=8789009 |doi=10.1530/EDM-21-0081 |url=}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |authors=Sbiera S, Schmull S, Assie G, Voelker HU, Kraus L, Beyer M, Ragazzon B, Beuschlein F, Willenberg HS, Hahner S, Saeger W, Bertherat J, Allolio B, Fassnacht M |title=High diagnostic and prognostic value of steroidogenic factor-1 expression in adrenal tumors |journal=J Clin Endocrinol Metab |volume=95 |issue=10 |pages=E161–71 |date=October 2010 |pmid=20660055 |doi=10.1210/jc.2010-0653 |url=}}</ref> | |||
*Vimentin +ve. | *Vimentin +ve. | ||
*Melan A +ve. | *Melan A +ve. | ||
*Inhibin-alpha +ve. | *Inhibin-alpha +ve. | ||
*Cytokeratins +ve/-ve. | *Cytokeratins +ve/-ve. | ||
*p53 +ve. | |||
**Rarely positive in [[adrenal cortical adenoma]]s.<ref name=pmid11196463>{{Cite journal | last1 = Arola | first1 = J. | last2 = Salmenkivi | first2 = K. | last3 = Liu | first3 = J. | last4 = Kahri | first4 = AI. | last5 = Heikkilä | first5 = P. | title = p53 and Ki67 in adrenocortical tumors. | journal = Endocr Res | volume = 26 | issue = 4 | pages = 861-5 | month = Nov | year = 2000 | doi = | PMID = 11196463 }}</ref> | |||
*Ki-67 >5%. | |||
**Typically 1-2 in adrenal cortical adenomas.<ref name=pmid11196463/> | |||
Others: | Others: | ||
| Line 156: | Line 156: | ||
*S100 -ve. | *S100 -ve. | ||
**[[Pheochromocytoma]] +ve (sustentacular cells).<ref>{{cite journal |author=Unger P, Hoffman K, Pertsemlidis D, Thung S, Wolfe D, Kaneko M |title=S100 protein-positive sustentacular cells in malignant and locally aggressive adrenal pheochromocytomas |journal=Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. |volume=115 |issue=5 |pages=484–7 |year=1991 |month=May |pmid=1673596 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | **[[Pheochromocytoma]] +ve (sustentacular cells).<ref>{{cite journal |author=Unger P, Hoffman K, Pertsemlidis D, Thung S, Wolfe D, Kaneko M |title=S100 protein-positive sustentacular cells in malignant and locally aggressive adrenal pheochromocytomas |journal=Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. |volume=115 |issue=5 |pages=484–7 |year=1991 |month=May |pmid=1673596 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
* | *[[PAX8]] -ve.<ref name=pmid21490444>{{Cite journal | last1 = Sangoi | first1 = AR. | last2 = Fujiwara | first2 = M. | last3 = West | first3 = RB. | last4 = Montgomery | first4 = KD. | last5 = Bonventre | first5 = JV. | last6 = Higgins | first6 = JP. | last7 = Rouse | first7 = RV. | last8 = Gokden | first8 = N. | last9 = McKenney | first9 = JK. | title = Immunohistochemical distinction of primary adrenal cortical lesions from metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma: a study of 248 cases. | journal = Am J Surg Pathol | volume = 35 | issue = 5 | pages = 678-86 | month = May | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1097/PAS.0b013e3182152629 | PMID = 21490444 }}</ref> | ||
*CD10 +ve/-ve -- cannot be used to differentiate from [[RCC]].<ref name=pmid20390424>{{Cite journal | last1 = Mete | first1 = O. | last2 = Kapran | first2 = Y. | last3 = Güllüoğlu | first3 = MG. | last4 = Kiliçaslan | first4 = I. | last5 = Erbil | first5 = Y. | last6 = Senyürek | first6 = YG. | last7 = Dizdaroğlu | first7 = F. | title = Anti-CD10 (56C6) is expressed variably in adrenocortical tumors and cannot be used to discriminate clear cell renal cell carcinomas. | journal = Virchows Arch | volume = 456 | issue = 5 | pages = 515-21 | month = May | year = 2010 | doi = 10.1007/s00428-010-0901-0 | PMID = 20390424 }}</ref> | *CD10 +ve/-ve -- cannot be used to differentiate from [[RCC]].<ref name=pmid20390424>{{Cite journal | last1 = Mete | first1 = O. | last2 = Kapran | first2 = Y. | last3 = Güllüoğlu | first3 = MG. | last4 = Kiliçaslan | first4 = I. | last5 = Erbil | first5 = Y. | last6 = Senyürek | first6 = YG. | last7 = Dizdaroğlu | first7 = F. | title = Anti-CD10 (56C6) is expressed variably in adrenocortical tumors and cannot be used to discriminate clear cell renal cell carcinomas. | journal = Virchows Arch | volume = 456 | issue = 5 | pages = 515-21 | month = May | year = 2010 | doi = 10.1007/s00428-010-0901-0 | PMID = 20390424 }}</ref> | ||
A panel that may be useful for [[adrenal cortical adenoma|adenoma]] versus adrenal cortical carcinoma:<ref name=pmid11196463>{{Cite journal | last1 = Arola | first1 = J. | last2 = Salmenkivi | first2 = K. | last3 = Liu | first3 = J. | last4 = Kahri | first4 = AI. | last5 = Heikkilä | first5 = P. | title = p53 and Ki67 in adrenocortical tumors. | journal = Endocr Res | volume = 26 | issue = 4 | pages = 861-5 | month = Nov | year = 2000 | doi = | PMID = 11196463 }}</ref><ref name=pmid26317117>{{Cite journal | last1 = Kovach | first1 = AE. | last2 = Nucera | first2 = C. | last3 = Lam | first3 = QT. | last4 = Nguyen | first4 = A. | last5 = Dias-Santagata | first5 = D. | last6 = Sadow | first6 = PM. | title = Genomic and immunohistochemical analysis in human adrenal cortical neoplasia reveal beta-catenin mutations as potential prognostic biomarker. | journal = Discoveries (Craiova) | volume = 3 | issue = 2 | pages = | month = | year = | doi = 10.15190/d.2015.32 | PMID = 26317117 }} | |||
</ref> | |||
*Beta-catenin, p53, reticulin, inhibin, melan A, Ki-67. | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Latest revision as of 23:18, 18 January 2024
| Adrenocortical carcinoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
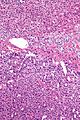
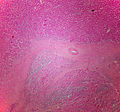
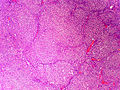
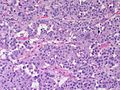
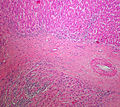
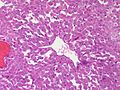
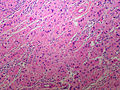
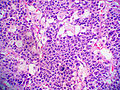
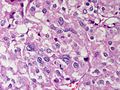
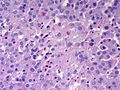
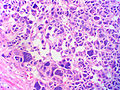
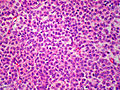
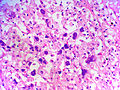
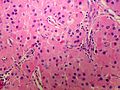
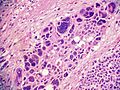
 Adrenocortical carcinoma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| Synonyms | adrenal cortical carcinoma |
|
| |
| LM | see below - various criteria, dependent on adult vs pediatric |
| IHC | vimentin +ve, melan A +ve, inhibin-alpha +ve, chromogranin A -ve, EMA -ve, S-100 -ve, SF-1 +ve |
| Site | adrenal gland - cortex |
|
| |
| Syndromes | Li-Fraumeni syndrome, Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome |
|
| |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Radiology | adrenal mass, typically large |
| Prognosis | poor |
| Clin. DDx | renal cell carcinoma, other abdominal masses |
| Treatment | surgical excision if feasible |
Adrenocortical carcinoma, abbreviated ACC, is a malignant tumour of the adrenal gland cortex.
It is also known as adrenal cortical carcinoma.
General
- A tumour of both children and adults.
- Prognosis poor, especially in adults.
Epidemiology:
- May be associated with a syndrome:[1]
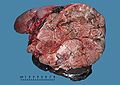
Gross
- +/-Encapsulated.
- Necrotic-appearing.
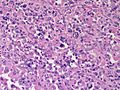
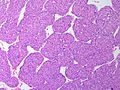
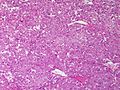
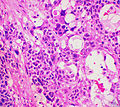
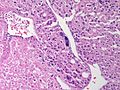
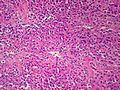
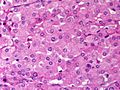
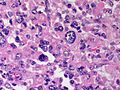
Image:
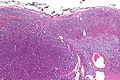
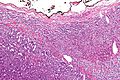
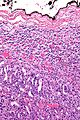
Microscopic
Various criteria exist for this diagnosis. The most widely used is the Weiss criteria, which is a big long clunker. This area is prone to regular re-jiggering of criteria and a literature update or expert opinion is recommended prior to signing out one of these rare lesions.
In general:
- Adrenocortical adenomas are small, circumscribed and have cells with largely bland nuclei and abundant foamy clear or pink cytoplasm.
- Adrenocortical carcinomas are large, infiltrative, have fibrous bands and necrosis, and cells with less cytoplasm and more atypia including atypical mitotic figures.
- Adrenocortical adenomas in children; however, can look really ugly.
Notes:
- Tumour may contain fat.[2]
DDx
Diagnostic categories:
- Large pink polygonal cell neoplasms.
- Retroperitonial large polygonal cell neoplasms.
Images
www:
Adult
Weiss criteria
- High nuclear grade.
- High mitotic rate; >5/50 HPF (@ 40X obj.) - definition suffers from HPFitis.
- Atypical mitoses.
- Cleared cytoplasm in >= 25% of tumour cells.
- Sheeting (diffuse architecture) in >= 1/3 of tumour cells.
- Necrosis in nests.
- Venous invasion.
- Adrenal sinusoid invasion; lymphovascular space invasion within the adrenal gland.
- Capsular invasion.
Volante criteria
There is a simplified set of criteria by Volante et al. - that is not widely used:[5]
- Reticular network disruption (with reticulin staining).
- One of the three following:
- Abundant mitoses >5/50 high-power fields - definition suffers from HPFitis.
- Necrosis.
- Vascular invasion.
Pediatric
The criteria in the pediatric setting are somewhat different. This is discussed by Wieneke et al.[6] and Dehner and Hill.[7]
Dehner and Hill propose a very simple system:[7]
- "Low risk" < 200 g & confined to the adrenal.
- "Intermediate risk" 200-400 g, no mets, +/-microscopic disease outside adrenal.
- "High risk" >400 g, or mets, or gross invasion of adjacent structures.
IHC
- SF-1 +ve.[8][9]
- Vimentin +ve.
- Melan A +ve.
- Inhibin-alpha +ve.
- Cytokeratins +ve/-ve.
- p53 +ve.
- Rarely positive in adrenal cortical adenomas.[10]
- Ki-67 >5%.
- Typically 1-2 in adrenal cortical adenomas.[10]
Others:
- Synaptophysin +ve/-ve.
- Chromogranin A -ve.
- Pheochromocytoma +ve.
- EMA -ve.
- Renal cell carcinoma +ve.
- S100 -ve.
- Pheochromocytoma +ve (sustentacular cells).[11]
- PAX8 -ve.[12]
- CD10 +ve/-ve -- cannot be used to differentiate from RCC.[13]
A panel that may be useful for adenoma versus adrenal cortical carcinoma:[10][14]
- Beta-catenin, p53, reticulin, inhibin, melan A, Ki-67.
See also
References
- ↑ Kumar, Vinay; Abbas, Abul K.; Fausto, Nelson; Aster, Jon (2009). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 1157. ISBN 978-1416031215.
- ↑ Heye S, Woestenborghs H, Van Kerkhove F, Oyen R (2005). "Adrenocortical carcinoma with fat inclusion: case report". Abdom Imaging 30 (5): 641–3. doi:10.1007/s00261-004-0281-5. PMID 15688105.
- ↑ Jain M, Kapoor S, Mishra A, Gupta S, Agarwal A (2010). "Weiss criteria in large adrenocortical tumors: a validation study". Indian J Pathol Microbiol 53 (2): 222–6. doi:10.4103/0377-4929.64325. PMID 20551521.
- ↑ Weiss, LM. (Mar 1984). "Comparative histologic study of 43 metastasizing and nonmetastasizing adrenocortical tumors.". Am J Surg Pathol 8 (3): 163-9. PMID 6703192.
- ↑ Volante M, Bollito E, Sperone P, et al. (November 2009). "Clinicopathological study of a series of 92 adrenocortical carcinomas: from a proposal of simplified diagnostic algorithm to prognostic stratification". Histopathology 55 (5): 535–43. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2559.2009.03423.x. PMID 19912359.
- ↑ Wieneke JA, Thompson LD, Heffess CS (July 2003). "Adrenal cortical neoplasms in the pediatric population: a clinicopathologic and immunophenotypic analysis of 83 patients". Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 27 (7): 867–81. PMID 12826878.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Dehner LP, Hill DA (2009). "Adrenal cortical neoplasms in children: why so many carcinomas and yet so many survivors?". Pediatr. Dev. Pathol. 12 (4): 284–91. doi:10.2350/08-06-0489.1. PMID 19326954.
- ↑ Wang R, Solomon B, Luen SJ, Prall OW, Khoo C, Gill AJ, Lewin J, Sachithanandan N (January 2022). "Pitfalls and progress in adrenocortical carcinoma diagnosis: the utility of a multidisciplinary approach, immunohistochemistry and genomics". Endocrinol Diabetes Metab Case Rep 2022. doi:10.1530/EDM-21-0081. PMC 8789009. PMID 35023475. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8789009/.
- ↑ Sbiera S, Schmull S, Assie G, Voelker HU, Kraus L, Beyer M, Ragazzon B, Beuschlein F, Willenberg HS, Hahner S, Saeger W, Bertherat J, Allolio B, Fassnacht M (October 2010). "High diagnostic and prognostic value of steroidogenic factor-1 expression in adrenal tumors". J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95 (10): E161–71. doi:10.1210/jc.2010-0653. PMID 20660055.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 Arola, J.; Salmenkivi, K.; Liu, J.; Kahri, AI.; Heikkilä, P. (Nov 2000). "p53 and Ki67 in adrenocortical tumors.". Endocr Res 26 (4): 861-5. PMID 11196463.
- ↑ Unger P, Hoffman K, Pertsemlidis D, Thung S, Wolfe D, Kaneko M (May 1991). "S100 protein-positive sustentacular cells in malignant and locally aggressive adrenal pheochromocytomas". Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 115 (5): 484–7. PMID 1673596.
- ↑ Sangoi, AR.; Fujiwara, M.; West, RB.; Montgomery, KD.; Bonventre, JV.; Higgins, JP.; Rouse, RV.; Gokden, N. et al. (May 2011). "Immunohistochemical distinction of primary adrenal cortical lesions from metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma: a study of 248 cases.". Am J Surg Pathol 35 (5): 678-86. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e3182152629. PMID 21490444.
- ↑ Mete, O.; Kapran, Y.; Güllüoğlu, MG.; Kiliçaslan, I.; Erbil, Y.; Senyürek, YG.; Dizdaroğlu, F. (May 2010). "Anti-CD10 (56C6) is expressed variably in adrenocortical tumors and cannot be used to discriminate clear cell renal cell carcinomas.". Virchows Arch 456 (5): 515-21. doi:10.1007/s00428-010-0901-0. PMID 20390424.
- ↑ Kovach, AE.; Nucera, C.; Lam, QT.; Nguyen, A.; Dias-Santagata, D.; Sadow, PM.. "Genomic and immunohistochemical analysis in human adrenal cortical neoplasia reveal beta-catenin mutations as potential prognostic biomarker.". Discoveries (Craiova) 3 (2). doi:10.15190/d.2015.32. PMID 26317117.
.