Micropapillary urothelial carcinoma
| Micropapillary urothelial carcinoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
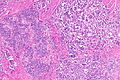
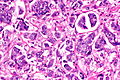
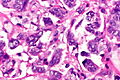
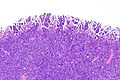
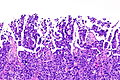
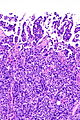
 Urothelial carcinoma with invasive micropapillary features. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | nests of tumour cells with clefting to the surrounding stroma (invasive pattern) |
| Subtypes | (subtype of urothelial carcinoma) |
| LM DDx | conventional urothelial carcinoma, other micropapillary carcinomas (metastases) |
| IHC | CK7 +ve, CK20 +ve/-ve, GATA3 +ve, p63 -ve/+ve |
| Grossing notes | radical cystectomy grossing, cystoprostatectomy grossing, nephroureterectomy grossing |
| Staging | bladder cancer staging |
| Site | urothelium - urinary bladder, ureter, renal pelvis, urethra (males) |
|
| |
| Signs | hematuria (typical presentation) |
| Prevalence | rare |
| Prognosis | poor (aggressive course) |
| Treatment | cystectomy/cytoprostatectomy - advocated for cT1 disease by some |
Micropapillary urothelial carcinoma (abbreviated MPUC), also micropapillary urothelial cell carcinoma (abbreviated MPUCC), is an aggressive variant of urothelial carcinoma.[1]
General
Treatment:
- cT1 disease treated by radical cystectomy in some centres.[3]
Microscopic
Features:[1]
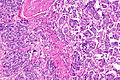
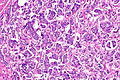
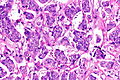
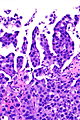
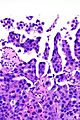
- Micropapillae - definitional.
- Nipple-like structures without fibrovascular cores.
- Quantity of micropapillary pattern (percentage) is variable.[2]
- +/-Conventional urothelial carcinoma (typical).
Notes:
- The invasive pattern of micropapillary urothelial carcinoma is nests of tumour cells with clefting to the surrounding stroma.
- In other organs, adenocarcinoma would be in the differential diagnosis. It should be noted that adenocarcinoma of the urinary bladder looks quite different than micropapillary urothelial carcinoma.
DDx:
- Metastasis (breast, ovary, lung, pancreas, salivary gland).
Images
Case 1
Case 2
www
IHC
Features:
Others:[4]
- p63 -ve/+ve.
- p40 -ve/+ve.
Sign out
- Report percentage of micropapillary pattern - suggested.[citation needed]
- In 2012, Amin and Epstein suggested that one distinguish between the invasive and non-invasive micropapillary pattern.[5] The WHO GU Book of 2016 suggests not using the term micropapillary carcinoma if only the non-invasive pattern is present.[6]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Compérat, E.; Roupret, M.; Yaxley, J.; Reynolds, J.; Varinot, J.; Ouzaïd, I.; Cussenot, O.; Samaratunga, H. (Dec 2010). "Micropapillary urothelial carcinoma of the urinary bladder: a clinicopathological analysis of 72 cases.". Pathology 42 (7): 650-4. doi:10.3109/00313025.2010.522173. PMID 21080874.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 Chatterjee, D.; Das, A.; Radotra, BD.. "Invasive micropapillary carcinoma of urinary bladder: a clinicopathological study.". Indian J Pathol Microbiol 58 (1): 2-6. doi:10.4103/0377-4929.151153. PMID 25673582.
- ↑ Willis, DL.; Fernandez, MI.; Dickstein, RJ.; Parikh, S.; Shah, JB.; Pisters, LL.; Guo, CC.; Henderson, S. et al. (Apr 2015). "Clinical outcomes of cT1 micropapillary bladder cancer.". J Urol 193 (4): 1129-34. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2014.09.092. PMID 25254936.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Lin, X.; Zhu, B.; Villa, C.; Zhong, M.; Kundu, S.; Rohan, SM.; Yang, XJ. (Sep 2014). "The utility of p63, p40, and GATA-binding protein 3 immunohistochemistry in diagnosing micropapillary urothelial carcinoma.". Hum Pathol 45 (9): 1824-9. doi:10.1016/j.humpath.2014.04.015. PMID 24993315.
- ↑ Amin, A.; Epstein, JI. (Dec 2012). "Noninvasive micropapillary urothelial carcinoma: a clinicopathologic study of 18 cases.". Hum Pathol 43 (12): 2124-8. doi:10.1016/j.humpath.2012.04.013. PMID 22939957.
- ↑ The International Agency for Research on Cancer (Author), H. Moch (Editor), P.A. Humphrey (Editor), T.M. Ulbright (Editor), V.E. Reuter (Editor) (2016). WHO Classification of Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs (4th ed.). Lyon: World Health Organization. pp. 90. ISBN 978-9283224372.