Gynecomastoid hyperplasia
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Gynecomastoid hyperplasia, also gynecomastia, is a benign pathology of the breast classically seen in young men.
| Gynecomastoid hyperplasia | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
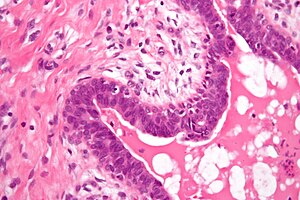 Gynecomastoid hyperplasia. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| Synonyms | gynecomastia |
|
| |
| LM | moderate hyperplasia - glands have more than 2 cell layers, "budding" (cells jut into the lumen, buds may be multicellular -- but narrower toward the centre of the lumen), stromal palor |
| LM DDx | Micropapillary DCIS |
| Site | breast |
|
| |
| Associated Dx | Liver failure, Klinefelter syndrome, testicular estrogen-producing germ cell tumour |
| Signs | excessive breast tissue |
| Prognosis | benign |
| Treatment | surgery |
General
- Benign enlargement of breasts in males.
- Histologic changes may be seen in females.[1]
May be seen in the context of:
- Liver failure.
- Klinefelter syndrome.
- Testicular estrogen-producing germ cell tumour.
Gross
- Excessive breast tissue in males.
Images
Microscopic
Features:[1]
- Moderate hyperplasia.
- Glands have more than 2 cell layers.
- "Budding" - individual cells jut into the lumen - key feature.
- Buds may be multicellular; however, narrower toward the centre of the lumen.
- Stromal palor.[2]
DDx:
- Micropapillary DCIS - buds not narrower toward the centre of the lumen.
Images
www:
Sign out
A. Breast Tissue (60 g), Right, Excision: - Benign breast tissue. B. Breast Tissue (70 g), Left, Excision: - Benign breast tissue.
Alternate
Left Chest Mass, Excision: - Breast tissue with gynecomastoid hyperplasia. - NEGATIVE for malignancy.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 URL: http://www.hsc.stonybrook.edu/breast-atlas/XIII-03.htm. Accessed on: 16 November 2011.
- ↑ URL: http://radiology.uchc.edu/eAtlas/Breast/1693.htm. Accessed on: 16 November 2011.