Ganglioglioma
Ganglioglioma is a epilepsy-associated glioneuronal tumour with benign course. Not to be confused with ganglioneuroma.
| Ganglioglioma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
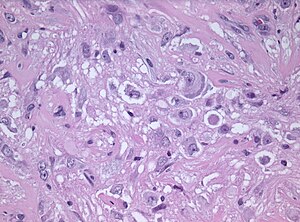 | |
| LM DDx | piloid gliosis, pilocytic astrocytoma, DNT |
| Stains | PAS-D +ve (eosinophilic granular bodies) |
| IHC | GFAP +ve, Synapto +ve |
| Gross | usually temporal +/-cystic |
| Site | brain - usu. supratentorial |
|
| |
| Syndromes | associated with epilepsy |
|
| |
| Prevalence | rare - esp. in children |
| Prognosis | good (WHO Grade I) |
General
- Gangliolioma: Grade I WHO mixed neuronal-glial tumour (ICD-O code: 9505/1).
- Anaplastic ganglioglioma: Grade III (ICD-O: 9505/3)
- Rare (approx. 0.5% of all CNS tumors).
- Usu. temporal lobe.
- Predominantly children (mean age: 9 years).
- Recognized as a cause of epilepsy.[1]
- Favourable prognosis (survival rates up to 97%)
- Insufficient data für anaplastic ganglioglioma.
Imaging
- Well-defined, T2-hyperintense.
- Strong CM enhancement.
- May contain cysts.
- Associated with temporal lobe.
Gross
- Circumscribed lesion.
- Usu. contrast enhancing.
- Solid, but intracortical cysts may be present.
- Little mass effect.
Microscopic
Microscopic
Features:
- Dysplastic neurons.
- Out of regular architecture / abnormal location.
- Cytomegaly
- Clustering
- Binucleated (very occassionally).
- Atypical glia (ie neoplastic).
- Eosinophilic granular bodies (more common than rosenthal fibers).
- Dystrophic calcification.
- Prominent capillary network.
- Lymphocytic cuffing.
- May contain some reticulin.
- Glial component may resemble:
- Fibrillary astrocytoma.
- Oligodendroglioma.
- Pilocytic astrocytoma.
Anaplastic ganglioglioma:
- Brisk mitotic activity
- Necrosis
IHC
- Neurons:
- MAP2 +ve
- Synaptophysin +ve
- Neurofilament +ve
- Chromogranin +ve
- Glia:
- CD34+/-ve
- BRAF V600E +ve (approx. 25%, mainly ganglion cells).
- MAP2: usu. absent.
- MIB-1 (low, but resembles proliferative tumor component).
Molecular
- BRAF V600E-mutated(approx. 25%).[2]
- BRAF V600E antibody stains especially neuronal cells.[3]
- IDH1/2 wt.
- No 1p/19q codeletion.
- Usu. Chr. 7 gain.
- CDKN2A deletions in anaplastic ganglioglioma.
Images
Prognosis
- Good (10-year OS: 90%), but epilepsy may continue.
- Primary treatment: surgery.
DDx:
- DNT.
- Oligodendroglioma.
- Trapped cortical neurons in diffuse astrocytoma.
- Papillary glioneuronal tumor.
- Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor.
See also
References
- ↑ Im, SH.; Chung, CK.; Cho, BK.; Lee, SK. (Mar 2002). "Supratentorial ganglioglioma and epilepsy: postoperative seizure outcome.". J Neurooncol 57 (1): 59-66. PMID 12125968.
- ↑ Schindler, G.; Capper, D.; Meyer, J.; Janzarik, W.; Omran, H.; Herold-Mende, C.; Schmieder, K.; Wesseling, P. et al. (Mar 2011). "Analysis of BRAF V600E mutation in 1,320 nervous system tumors reveals high mutation frequencies in pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma, ganglioglioma and extra-cerebellar pilocytic astrocytoma.". Acta Neuropathol 121 (3): 397-405. doi:10.1007/s00401-011-0802-6. PMID 21274720.
- ↑ Koelsche, C.; Wöhrer, A.; Jeibmann, A.; Schittenhelm, J.; Schindler, G.; Preusser, M.; Lasitschka, F.; von Deimling, A. et al. (Jun 2013). "Mutant BRAF V600E protein in ganglioglioma is predominantly expressed by neuronal tumor cells.". Acta Neuropathol 125 (6): 891-900. doi:10.1007/s00401-013-1100-2. PMID 23435618.