Thymus
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Thymus is an annoying little organ that is in the mediastinum. It is often removed in pediatric cardiac surgery 'cause it is in the way. In adults, it is commonly removed 'cause the patient has myasthenia gravis.
Overview
General
- Important for development of the immune system.
- One of two primary lymphoid organs - the other one is the bone marrow.[1]
- Thymus involutes after childhood.
- May be absent due to genetic abnormalities, e.g. DiGeorge syndrome.
Anatomy
Location:
- Anterior mediastinum.
Anatomically in contact with:
- Pericardium.
- Medistinal pleural.
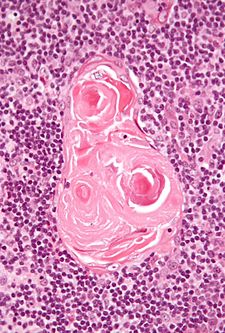
Normal histology
General
Features:[2]
- No germinal centres.
- Hassall's corpusle (thymic corpusle).
- Round eosinophilic thingy.
- Thought to arise from medullary epithelial cells (see cell types).[3]
Note:
- The thymus may contain within it parathyroid.[3]
Cell types
Cells of the thymus (short version):
- Cortical epithelial cells.[3]
- Epithelioid.
- Abundant cytoplasm.
- Pale nuclei with small nucleoli.
- Medullary epithelial cells.[3]
- Spindle morphology.
- Scant cytoplasm.
- Oval dark nuclei.
- T lymphocytes.
Other cells:
- Macrophages.
- Dendritic cells.
- Other WBCs: B lymphocytes, neutrophils, eosinophils.
- Myoid cells.
Note:
- Thymic tumours are derived from the epithelial component of the thymus, i.e. the cortical epithelial cells and medullary epithelial cells.
Images
IHC and thymus
Types A, AB, B:[4]
Type C:
All types:[4]
- CD1a +ve (immature T cells, Langerhans cells, dendritic cells[6]), CEA +ve (focal), vimentin -ve.
Others (immature T cells):
- TdT +ve.
- CD99 +ve.
Anterior mediastinum mass DDx
Main article: Mediastinum
4 Ts (mnemonic):
Thymus and stress
- Stress -> increased endogenous steroid -> lymphocyte death -> increased tingible body macrophages.[7]
Specific conditions
Thymic follicular hyperplasia
- AKA thymic follicular hyperplasia.
Features:[8]
- Follicular centres in the thymus.
Associations:[8]
- Myasthenia gravis.
- Graves' disease.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
- Rheumatoid arthritis.
- Other autoimmune diseases.
Thymoma
Main article: Thymoma
Metaplastic thymoma
General
- Extremely rare - only 17 case reports as of 2011.[10]
- Two reports of transformation into thymic carcinoma.[10]
Microscopic
Features:[9]
- Epithelioid cells.
- Spindle cells.
- Few lymphocytes.
DDx:
- Thymic carcinoma with sarcomatoid differentiation.
Images
www:
IHC
CD5 -ve.[9]
Thymic carcinoma
- Previously Thymic tumour type C.
General
- Rare.
- Usually arise de novo, i.e. thymoma is not generally a precursor.
- Risk factors - possibly: smoking, radiation.[12]
Microscopic
Features:[13]
- Cytologically malignant - variable morphology.
- Squamous cell carcinoma is the most common (65-73% of cases[12][14]).
- +/-Squamous differentiation.
Notes:
- Staging depends on capsular invasion.
DDx:
Images
- Thymic carcinoma - low mag. (webpathology.com).
- Thymic carcinoma - high mag. (webpathology.com).
- Thymic carcinoma - lymphoepithelioma-like - high mag. (webpathology.com).
IHC
Features:[13]
Note:
- Should stain with keratins.
See also
References
- ↑ URL: http://www.life.umd.edu/classroom/bsci423/song/Lab1.html. Accessed on: 28 March 2012.
- ↑ URL: http://www.kumc.edu/instruction/medicine/anatomy/histoweb/lymphoid/lymph03.htm. Accessed on: 17 June 2010.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Cotran, Ramzi S.; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Nelso Fausto; Robbins, Stanley L.; Abbas, Abul K. (2005). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (7th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. pp. 706. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 CJS. January 2010.
- ↑ Yokota, K.; Tateyama, H.; Yano, M.; Moriyama, S.; Hikosaka, Y.; Okuda, K.; Shitara, M.; Okumura, M. et al. (Jan 2013). "Clinicopathological analysis of small-sized thymoma with podoplanin and Ki 67 expression analysis.". Mol Clin Oncol 1 (1): 88-92. doi:10.3892/mco.2012.2. PMID 24649128.
- ↑ URL: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1886385/pdf/amjpathol00102-0156.pdf. Accessed on: 26 August 2010.
- ↑ Toti P, De Felice C, Stumpo M, et al. (September 2000). "Acute thymic involution in fetuses and neonates with chorioamnionitis". Hum. Pathol. 31 (9): 1121–8. PMID 11014581.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Cotran, Ramzi S.; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Nelso Fausto; Robbins, Stanley L.; Abbas, Abul K. (2005). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (7th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. pp. 707-8. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 URL: http://surgpathcriteria.stanford.edu/thymus/thymoma/metaplastic_thymoma.html. Accessed on: 22 December 2011.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Lu, HS.; Gan, MF.; Zhou, T.; Wang, SZ. (Oct 2011). "Sarcomatoid thymic carcinoma arising in metaplastic thymoma: a case report.". Int J Surg Pathol 19 (5): 677-80. doi:10.1177/1066896909355458. PMID 20034984.
- ↑ Kang, G.; Yoon, N.; Han, J.; Kim, YE.; Kim, TS.; Kim, K. (Feb 2012). "Metaplastic thymoma: report of 4 cases.". Korean J Pathol 46 (1): 92-5. doi:10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.1.92. PMID 23109986.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 12.3 Thomas de Montpréville, V.; Ghigna, MR.; Lacroix, L.; Besse, B.; Broet, P.; Dartevelle, P.; Fadel, E.; Dorfmuller, P. (Mar 2013). "Thymic carcinomas: clinicopathologic study of 37 cases from a single institution.". Virchows Arch 462 (3): 307-13. doi:10.1007/s00428-013-1371-y. PMID 23319214.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 147. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ Zhao, Y.; Zhao, H.; Hu, D.; Fan, L.; Shi, J.; Fang, W. (Sep 2013). "Surgical treatment and prognosis of thymic squamous cell carcinoma: a retrospective analysis of 105 cases.". Ann Thorac Surg 96 (3): 1019-24. doi:10.1016/j.athoracsur.2013.04.078. PMID 23866799.
- ↑ Rossi, V.; Donini, M.; Sergio, P.; Passalacqua, R.; Rossi, G.; Buti, S. (Apr 2013). "When a thymic carcinoma becomes a GIST.". Lung Cancer 80 (1): 106-8. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2013.01.003. PMID 23375402.
- ↑ Cotran, Ramzi S.; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Nelso Fausto; Robbins, Stanley L.; Abbas, Abul K. (2005). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (7th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. pp. 708. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.