Sarcoidosis
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Sarcoidosis is non-necrotizing granulomatous disease of unknown etiology. It classically associated with (pulmonary) hilar lymphadenopathy. It may be found in almost any organ, e.g. heart, appendix.
| Sarcoidosis | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
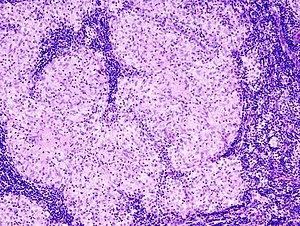 Sarcoidosis-like granulomas in a lymph node. H&E stain. | |
| LM DDx | fungal infection, tuberculosis, other infections, drug reactions |
| Stains | AFB -ve, GMS -ve, PASD -ve |
| Site | lung, hilar lymph nodes of the lung, other sites |
|
| |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Radiology | +/-bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy (very common), +/-interstitial pattern, +/- pulmonary infiltrates, +/-cystic/bullous changes |
| Other | flow cytometry to r/o lymphoma |
| Clin. DDx | lymphoma, metastatic carcinoma, Wegener's granulomatosis, others |
General
- Diagnosis of exclusion - infection must be excluded.
- Rare.
Gross
- Lungs - classic location.[1]
- Bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy.
DDx (radiologic):
Microscopic
Features:
- Granulomata, well-formed, non-necrotizing.
- Usu. minimal (lymphoid) inflammation; sarcoid granulomas are known as "naked granulomas".[4]
- In lung: interstitial location.
DDx:
- Reactive changes - may mimic sarcoidosis.
- Drug reaction.
- Infections.
- Common variable immunodeficiency.[8]
- Seminoma.[9]
Images
www:
Stains
- ZN -ve.
- PASD -ve.
- GMS -ve.
Note:
- Done to r/o infection.
Sign out
- Should be something like sarcoid-like granulomas and clinical correlation required.
See also
References
- ↑ Rao, DA.; Dellaripa, PF. (May 2013). "Extrapulmonary manifestations of sarcoidosis.". Rheum Dis Clin North Am 39 (2): 277-97. doi:10.1016/j.rdc.2013.02.007. PMID 23597964.
- ↑ URL: http://www.radiologyassistant.nl/en/46b480a6e4bdc. Accessed on: 23 May 2010.
- ↑ Boujaoude, Z.; Dahdel, M.; Pratter, M.; Kass, J. (Jan 2012). "Endobronchial ultrasound with transbronchial needle aspiration in the diagnosis of bilateral hilar and mediastinal lymphadenopathy.". J Bronchology Interv Pulmonol 19 (1): 19-23. doi:10.1097/LBR.0b013e3182442b89. PMID 23207258.
- ↑ Brinster, NK. (Nov 2008). "Dermatopathology for the surgical pathologist: a pattern-based approach to the diagnosis of inflammatory skin disorders (part II).". Adv Anat Pathol 15 (6): 350-69. doi:10.1097/PAP.0b013e31818b1ac6. PMID 18948765.
- ↑ Tong, D.; Manolios, N.; Howe, G.; Spencer, D. (Jan 2012). "New onset sarcoid-like granulomatosis developing during anti-TNF therapy: an under-recognised complication.". Intern Med J 42 (1): 89-94. PMID 22389903.
- ↑ Reule, RB.; North, JP. (Nov 2013). "Cutaneous and pulmonary sarcoidosis-like reaction associated with ipilimumab.". J Am Acad Dermatol 69 (5): e272-3. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2013.07.028. PMID 24124863.
- ↑ Hervier, B.; Wastiaux, H.; Freour, T.; Masseau, A.; Corvec, S.; Armingeat, T.; Hamidou, M. (Sep 2009). "[Sarcoidosis-like granulomatosis revealing a tertiary syphilis].". Rev Med Interne 30 (9): 806-8. doi:10.1016/j.revmed.2009.01.003. PMID 19249139.
- ↑ Vultaggio, A.; Matucci, A.; Parronchi, P.; Rossi, O.; Filì, L.; Giudizi, MG.; Palandri, F.; Agostini, C. et al. (Sep 2007). "Association between sarcoidosis-like disease and common variable immunodeficiency (CVI): a new CVI variant showing an activation of the immune system.". Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis 24 (2): 127-33. PMID 18496983.
- ↑ Jankilevich, G.; Mendizabal, J.; Massa, MA.; Pedernera, A.; Galmes, M.; Spizzamiglio, N. (2006). "[Mediastinal sarcoidal reaction in follow up for seminoma].". Medicina (B Aires) 66 (6): 552-4. PMID 17240627.