Atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumour
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumour, abbreviated AT/RT, is malignant tumour usually found supratentorially.
It may be written atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumour, i.e. without the forward slash (abbreviated ATRT, or atypical teratoid-rhabdoid tumour (abbreviated AT-RT).
It should not be confused with the extrarenal malignant rhabdoid tumour.
General
- Usually supratentorial, occasionally in posterior fossa, case reports of spinal cord.
- Individuals usually <3 years old, uncommon in adults.[1]
- Prognosis very poor.[1]
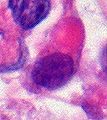
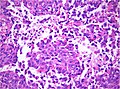
Microscopic
Features:
- Cellular.
- Small round cells usu. with a prominent nucleolus.
- Rhabdoid cells.
- Cells with eosinophilic granular cytoplasm + eccentric nucleus.
- Mitoses.
- +/-Necrosis (common).
DDx:
- Primitive neuroectodermal tumour (PNET).
- Medulloblastoma.
- Diffuse astrocytoma.
- Choroid plexus carcinoma.
- Embryonal carcinoma.
Images
www:
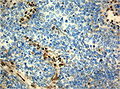
IHC
- BAF-47 -ve (AKA INI1, AKA SMARCB1 - the HGNC symbol[2]) - virtually diagnostic.
- Endothelial cells +ve control.
- S-100 +ve.
- Few other brain tumours express it.
- Vimentin +ve (perinuclear condensation).
Others:
- GFAP +ve (focal - in tumour cells).
- EMA +ve (patchy cytoplasmic).
- Smooth muscle actin +ve.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Kanoto, M.; Toyoguchi, Y.; Hosoya, T.; Kuchiki, M.; Sugai, Y. (Jan 2014). "Radiological Image Features of the Atypical Teratoid/Rhabdoid Tumor in Adults: A Systematic Review.". Clin Neuroradiol. doi:10.1007/s00062-013-0282-2. PMID 24477665.
- ↑ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 601607