Difference between revisions of "Sarcina"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→Microscopic: +SO) |
|||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
*[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3193598/figure/F2/ Sarcina (nih.gov)]. | *[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3193598/figure/F2/ Sarcina (nih.gov)]. | ||
*[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3627895/figure/F2/ Sarcina (nih.gov)].<ref name=pmid23599657/> | *[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3627895/figure/F2/ Sarcina (nih.gov)].<ref name=pmid23599657/> | ||
==Sign out== | |||
===Urine cytology=== | |||
<pre> | |||
Abundant micro-organisms compatible with Sarcina, see comment. | |||
Acute inflammation. | |||
NEGATIVE for High-Grade Urothelial Carcinoma. | |||
Comment: | |||
The micro-organisms are arranged in distinctive tetrads, as is typical for Sarcina. | |||
This is an uncommon finding.[1] Treatment should be considered within the clinical context. | |||
1. Bommannan K, Gaspar BL, Sachdeva MUS. BMJ Case Rep. 2016 Oct 13;2016:bcr2016216991. doi:10.1136/bcr-2016-216991 | |||
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5073697/pdf/bcr-2016-216991.pdf | |||
</pre> | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Revision as of 20:21, 10 June 2022

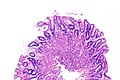
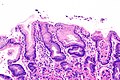
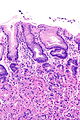
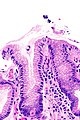
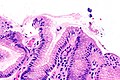
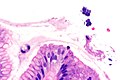
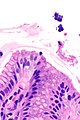
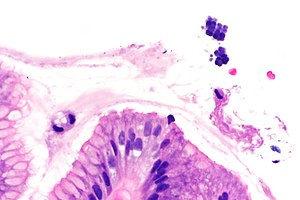
Micrograph showing Sarcina. H&E stain. (WC/Librepath)
Sarcina organisms are occasionally seen in the gastrointestinal tract. They are reported in urine.[1]
General
- Probably a commensal organism.[2]
- Gram positive coccus.[1]
- Uncommonly seen.
- Associated with gastroparesis,[2] as may be seen in diabetes mellitus.
Described complications:[2]
- Gastric perforation.
- Emphysematous gastritis.
Notes:
- Sarcina ventriculi = Gram-positive organism.[2]
Gross
Features:
- Erythema.
- +/-Gastric ulcer.
- +/-Retained food.
Microscopic
Features:[3]
- Small essentially spherical micro-organisms.
- Each micro-organism 1.8-3 micrometres - purple on H&E stain.
- Arranged in clusters of 4, 8 or more - classically in a tetrad - key feature.
DDx:
- Micrococcus - form larger clusters.[3]
Images
Case 1
www
Sign out
Urine cytology
Abundant micro-organisms compatible with Sarcina, see comment. Acute inflammation. NEGATIVE for High-Grade Urothelial Carcinoma. Comment: The micro-organisms are arranged in distinctive tetrads, as is typical for Sarcina. This is an uncommon finding.[1] Treatment should be considered within the clinical context. 1. Bommannan K, Gaspar BL, Sachdeva MUS. BMJ Case Rep. 2016 Oct 13;2016:bcr2016216991. doi:10.1136/bcr-2016-216991 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5073697/pdf/bcr-2016-216991.pdf
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Bommannan K, Gaspar BL, Sachdeva MU (October 2016). "Pathogenic Sarcina in urine". BMJ Case Rep 2016. doi:10.1136/bcr-2016-216991. PMC 5073697. PMID 27737866. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5073697/.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Ratuapli, SK.; Lam-Himlin, DM.; Heigh, RI. (2013). "Sarcina ventriculi of the stomach: a case report.". World J Gastroenterol 19 (14): 2282-5. doi:10.3748/wjg.v19.i14.2282. PMID 23599657.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Lam-Himlin, D.; Tsiatis, AC.; Montgomery, E.; Pai, RK.; Brown, JA.; Razavi, M.; Lamps, L.; Eshleman, JR. et al. (Nov 2011). "Sarcina organisms in the gastrointestinal tract: a clinicopathologic and molecular study.". Am J Surg Pathol 35 (11): 1700-5. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e31822911e6. PMID 21997690.