Difference between revisions of "Mesenchymal chondrosarcoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
==General== | ==General== | ||
*Rare variant of chondrosarcoma. | *Rare variant of chondrosarcoma. | ||
*2–10% of primary chondrosarcomas | *2–10% of primary chondrosarcomas | ||
| Line 10: | Line 8: | ||
*Female predilection | *Female predilection | ||
*Most commonly intraosseous but can occur in extraskeletal sites especially the central nervous system (from the meminges) | *Most commonly intraosseous but can occur in extraskeletal sites especially the central nervous system (from the meminges) | ||
*The 'mesenchymal' in the name refers to the ability to arise in soft tissues.<ref name=pmid14161087>{{cite journal |author=Dowling EA |title=Mesenchymal chondrosarcoma |journal=J Bone Joint Surg Am |volume=46 |issue= |pages=747–54 |year=1964 |month=June |pmid=14161087 |doi= |url=http://www.ejbjs.org/cgi/reprint/46/4/747.pdf}}</ref> | |||
*Conceptualized as originating from a pleuripotential mesenchymal cell with foci recapitulating enchondral ossification. | *Conceptualized as originating from a pleuripotential mesenchymal cell with foci recapitulating enchondral ossification. | ||
*The small cells appear to be an undifferentiated cartilage stem cell which “differentiate” into benign cartilage <ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Fanburg-Smith | first1 = JC. | last2 = Auerbach | first2 = A. | last3 = Marwaha | first3 = JS. | last4 = Wang | first4 = Z. | last5 = Rushing | first5 = EJ. | title = Reappraisal of mesenchymal chondrosarcoma: novel morphologic observations of the hyaline cartilage and endochondral ossification and beta-catenin, Sox9, and osteocalcin immunostaining of 22 cases. | journal = Hum Pathol | volume = 41 | issue = 5 | pages = 653-62 | month = May | year = 2010 | doi = 10.1016/j.humpath.2009.11.006 | PMID = 20138330 }} | *The small cells appear to be an undifferentiated cartilage stem cell which “differentiate” into benign cartilage <ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Fanburg-Smith | first1 = JC. | last2 = Auerbach | first2 = A. | last3 = Marwaha | first3 = JS. | last4 = Wang | first4 = Z. | last5 = Rushing | first5 = EJ. | title = Reappraisal of mesenchymal chondrosarcoma: novel morphologic observations of the hyaline cartilage and endochondral ossification and beta-catenin, Sox9, and osteocalcin immunostaining of 22 cases. | journal = Hum Pathol | volume = 41 | issue = 5 | pages = 653-62 | month = May | year = 2010 | doi = 10.1016/j.humpath.2009.11.006 | PMID = 20138330 }} | ||
</ref>. | </ref>. | ||
==Gross== | ==Gross== | ||
Revision as of 10:55, 20 November 2014
Mesenchymal chondrosarcoma is a rare type of chondrosarcoma found in the soft tissue.
General
- Rare variant of chondrosarcoma.
- 2–10% of primary chondrosarcomas
- Adolescents and young adults
- Female predilection
- Most commonly intraosseous but can occur in extraskeletal sites especially the central nervous system (from the meminges)
- The 'mesenchymal' in the name refers to the ability to arise in soft tissues.[1]
- Conceptualized as originating from a pleuripotential mesenchymal cell with foci recapitulating enchondral ossification.
- The small cells appear to be an undifferentiated cartilage stem cell which “differentiate” into benign cartilage [2].
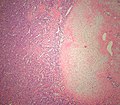
Gross
Pink and fleshy with foci of calcification.
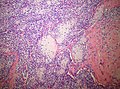
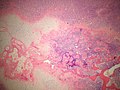
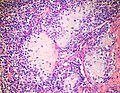
Microscopic
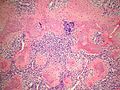
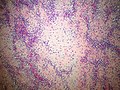
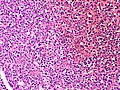
- "White clouds in a blue sky".
- Malignant tumor with a characteristic biphasic pattern
- Cellular poorly differentiated small round blue cells
- Islands of well-differentiated hyaline cartilage
- Progressive maturation of cartilage towards the center
- Central calcification or bone formation
Images
www:
IHC
- SOX9 (positive in small cells and chondrocytes).[3]
- S100 (positive in chondrocytes not in small cells).
- Osteocalcin (negative in small cells).
Molecular
t(8;8)(q21.1;q13.3) HEY1-NCOA2.[4]
See also
References
- ↑ Dowling EA (June 1964). "Mesenchymal chondrosarcoma". J Bone Joint Surg Am 46: 747–54. PMID 14161087. http://www.ejbjs.org/cgi/reprint/46/4/747.pdf.
- ↑ Fanburg-Smith, JC.; Auerbach, A.; Marwaha, JS.; Wang, Z.; Rushing, EJ. (May 2010). "Reappraisal of mesenchymal chondrosarcoma: novel morphologic observations of the hyaline cartilage and endochondral ossification and beta-catenin, Sox9, and osteocalcin immunostaining of 22 cases.". Hum Pathol 41 (5): 653-62. doi:10.1016/j.humpath.2009.11.006. PMID 20138330.
- ↑ Pang, ZG.; He, XZ.; Wu, LY.; Wei, W.; Liu, XY.; Liao, DY.; Li, FY.; Zhang, XL. (Jun 2011). "[Clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of 23 cases of mesenchymal chondrosarcoma].". Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi 40 (6): 368-72. PMID 21914343.
- ↑ Panagopoulos, I.; Gorunova, L.; Bjerkehagen, B.; Boye, K.; Heim, S. (Jul 2014). "Chromosome aberrations and HEY1-NCOA2 fusion gene in a mesenchymal chondrosarcoma.". Oncol Rep 32 (1): 40-4. doi:10.3892/or.2014.3180. PMID 24839999.