Difference between revisions of "Chronic sialadenitis"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→Micro) |
|||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
infiltrate, fibrosis and a large benign calcification. No zonal necrosis is identified. | infiltrate, fibrosis and a large benign calcification. No zonal necrosis is identified. | ||
Significant nuclear atypia is not identified. | Significant nuclear atypia is not identified. | ||
=====Alternate===== | |||
The sections show a salivary gland with a patchy mixed mononuclear cell infiltrate and fibrosis. Significant nuclear atypia is not identified. Plasma cells are not prominent. Germinal centres are present. | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Revision as of 15:17, 24 December 2019
Chronic sialadenitis is a chronic inflammatory process involving a salivary gland.
Chronic sailolithiasis redirects here. Sialadenitis redirects here.
General
- Occasionally associated with malignancy, e.g. adenoid cystic carcinoma.[1]
Etiology:[2]
- Infection.
- Autoimmune (e.g. Sjögren syndrome, systemic lupus erythematosus).
- Other.
Associations:
Gross
Features:
- Typical location: submandibular salivary gland.
- Salivary gland swelling.[1]
Microscopic
Features:
- Non-neoplastic mononuclear inflammatory infiltrate (lymphocytes, plasma cells).
- Fibrosis.
- +/-Calcifications.
Note:
- If the infiltrate is predominantly lymphocytes Sjögren's is a possibility, and reporting a Focus score should be considered.
DDx:
- Lymphoma - especially MALT lymphoma.[4]
- IgG4-related sialadenitis.[5]
Image
Sign out
SUBMANDIBULAR GLAND, RIGHT, EXCISION: - CHRONIC SIALOADENITIS. - SIALOLITHIASIS. - TWO BENIGN LYMPH NODES. - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
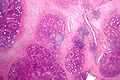
Micro
The sections show submandibular salivary gland with a mild patchy mixed mononuclear cell infiltrate, fibrosis and a large benign calcification. No zonal necrosis is identified. Significant nuclear atypia is not identified.
Alternate
The sections show a salivary gland with a patchy mixed mononuclear cell infiltrate and fibrosis. Significant nuclear atypia is not identified. Plasma cells are not prominent. Germinal centres are present.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Hasegawa M, Cheng J, Maruyama S, et al. (June 2011). "Complication of adenoid cystic carcinoma and sialolithiasis in the submandibular gland: report of a case and its etiological background". Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 40 (6): 647–50. doi:10.1016/j.ijom.2010.11.009. PMID 21159490.
- ↑ URL: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/882358-overviewhttp://emedicine.medscape.com/article/882358-overview. Accessed on: 10 January 2011.
- ↑ Eliasson L, Heyden G, Landahl S, Steen B (March 1991). "Effects of tobacco and diuretics on human palatal salivary glands". J. Oral Pathol. Med. 20 (3): 126–9. PMID 2037973.
- ↑ Beasley, MJ. (Apr 2012). "Lymphoma of the Thyroid and Head and Neck.". Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). doi:10.1016/j.clon.2012.02.010. PMID 22475637.
- ↑ "IgG4-Related Sialadenitis". Ear Nose Throat J: 145561319890153. November 2019. doi:10.1177/0145561319890153. PMID 31760789.