Difference between revisions of "Solitary fibrous tumour"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (→Images) |
Jensflorian (talk | contribs) (reformatted. @Mitchell: Do you have the permission to re-use the images here? Am J Surg Pathol is not OpenAccess by default.) |
||
| Line 70: | Line 70: | ||
*[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case272.html SFT of the brain - several images (upmc.edu)]. | *[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case272.html SFT of the brain - several images (upmc.edu)]. | ||
<gallery> | |||
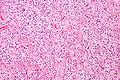
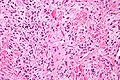
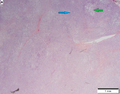
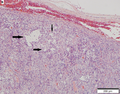
Malignant solitary fibrous tumor (low to intermediate grade tumor). 15 cm mass in upper arm of 50 year old man.<ref>Am J Surg Pathol 2014;38:552-559</ref> | |||
File:3 18039322534203 sl 1.png|malignant solitary fibrous tumor | Hypocellular (green arrow) and hypercellular (cyan arrow) areas alternate. | |||
[[File:3 18039322534203 sl 4.png|malignant solitary fibrous tumor | File:3 18039322534203 sl 2.png|malignant solitary fibrous tumor | Vascular spaces suggest antlers (staghorn). Note subcapsular hemorrhage. | ||
File:3 18039322534203 sl 3.png|malignant solitary fibrous tumor | Stromal hyalinization | |||
[[File:3 18039322534203 sl 4.png|malignant solitary fibrous tumor | Nuclei, lacking organization, show varied size and shape, with some cells being round to ovoid. The arrow points to myxoid focus in stroma. When a majority of the following are present, a low to intermediate grade malignant solitary fibrous tumor is present: 1) size > 5 cm (this case), 2) pleomorphism with round cells/epithelioid cells (this case), 3) subcapsular hemorrhage (this case), 4) ≥4 mitoses per 10 high power fields, 5) necrosis with perivascular tumor sparing. STAT 6 positivity is very helpful in separating this tumor from its mimics | |||
</gallery> | |||
==IHC== | ==IHC== | ||
Revision as of 07:14, 15 December 2016
| Solitary fibrous tumour | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
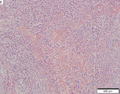
 Solitary fibrous tumour. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | spindle cells in a patternless pattern, hemangiopericytoma-like areas (staghorn vessels), keloid-like collagen bundles, +/-well-circumscribed (common) |
| Subtypes | benign (common), malignant (uncommon) |
| IHC | CD34 ~90% +ve, CD99 ~70% +ve, BCL2 ~50% +ve |
| Site | soft tissue - fibroblastic/myofibroblastic tumours, pleura |
|
| |
| Syndromes | Doege-Potter syndrome |
|
| |
| Prognosis | usu. good |
Solitary fibrous tumour, abbreviated SFT, is a type of soft tissue tumour that fits in the fibroblastic/myofibroblastic tumours. It is usually benign.
SFT of the pleura is dealt with in a separate article solitary fibrous tumour of the pleura.
General
- Grouped with hemangiopericytoma in the WHO classification - as it is thought to be the same tumour because both share the same molecular alteration.[1][2]
- May be benign or malignant; more commonly benign.[3][4]
- May be associated with hypoglycemia.
- Known as Doege-Potter syndrome.[5]
- Leptomeningeal SFTs/hemangiopericytomas are classified as follows:
- WHO grade I: classical SFT
- WHO grade II: classical hemangiopericytoma
- WHO grade III: anaplastic hemangiopericytoma / malignant SFT
Gross
- Soft tissue mass.
Microscopic
Features - benign:
- Spindle cells in a patternless pattern.
- Occasionally epithelioid cells - rare.[6]
- Hemangiopericytoma-like area (staghorn vessels).
- Keloid-like collagen bundles - key feature.
- +/-Well-circumscribed (common).
Criteria for malignancy:[1]
- Necrosis.
- Mitoses >4/10 HPF -- definition suffers from HPFitis.
- Increased cellularity.
- Marked nuclear atypia.
- Infiltrative margin.
Images
www:
IHC
- CD34 ~90% +ve.
- CD99 ~70% +ve.
- BCL2 ~50% +ve.
- Stat6 nuclear +ve.[7]
Molecular
DDx
- Meningioma
- Cellular angiofibroma
- Myofibroblastoma
- Benign fibrous histiocytoma
- Dermatofibrosarcoma protruberans
- Fibromyxoid sarcoma
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 609. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ Schweizer, L.; Koelsche, C.; Sahm, F.; Piro, RM.; Capper, D.; Reuss, DE.; Pusch, S.; Habel, A. et al. (May 2013). "Meningeal hemangiopericytoma and solitary fibrous tumors carry the NAB2-STAT6 fusion and can be diagnosed by nuclear expression of STAT6 protein.". Acta Neuropathol 125 (5): 651-8. doi:10.1007/s00401-013-1117-6. PMID 23575898.
- ↑ URL: http://www.pathconsultddx.com/pathCon/diagnosis?pii=S1559-8675%2806%2970528-9. Accessed on: 25 June 2010.
- ↑ URL: http://wjso.com/content/6/1/86. Accessed on: 25 June 2010.
- ↑ Roy, TM.; Burns, MV.; Overly, DJ.; Curd, BT. (Nov 1992). "Solitary fibrous tumor of the pleura with hypoglycemia: the Doege-Potter syndrome.". J Ky Med Assoc 90 (11): 557-60. PMID 1474302.
- ↑ Martorell, M.; Pérez-Vallés, A.; Gozalbo, F.; Garcia-Garcia, JA.; Gutierrez, J.; Gaona, J. (2007). "Solitary fibrous tumor of the thigh with epithelioid features: a case report.". Diagn Pathol 2: 19. doi:10.1186/1746-1596-2-19. PMID 17577399.
- ↑ Cheah, AL.; Billings, SD.; Goldblum, JR.; Carver, P.; Tanas, MZ.; Rubin, BP. (Aug 2014). "STAT6 rabbit monoclonal antibody is a robust diagnostic tool for the distinction of solitary fibrous tumour from its mimics.". Pathology 46 (5): 389-95. doi:10.1097/PAT.0000000000000122. PMID 24977739.
- ↑ Mohajeri, A.; Tayebwa, J.; Collin, A.; Nilsson, J.; Magnusson, L.; von Steyern, FV.; Brosjö, O.; Domanski, HA. et al. (Oct 2013). "Comprehensive genetic analysis identifies a pathognomonic NAB2/STAT6 fusion gene, nonrandom secondary genomic imbalances, and a characteristic gene expression profile in solitary fibrous tumor.". Genes Chromosomes Cancer 52 (10): 873-86. doi:10.1002/gcc.22083. PMID 23761323.
- ↑ Robinson, DR.; Wu, YM.; Kalyana-Sundaram, S.; Cao, X.; Lonigro, RJ.; Sung, YS.; Chen, CL.; Zhang, L. et al. (Feb 2013). "Identification of recurrent NAB2-STAT6 gene fusions in solitary fibrous tumor by integrative sequencing.". Nat Genet 45 (2): 180-5. doi:10.1038/ng.2509. PMID 23313952.