Difference between revisions of "Chromophobe renal cell carcinoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
*[[ISUP nucleolar grade|ISUP nucleolar grading]] (replaces ''Fuhrman grading'') not done for this entity, as it does not appear to have any predictive value.<ref name=pmid17527087>{{Cite journal | last1 = Delahunt | first1 = B. | last2 = Sika-Paotonu | first2 = D. | last3 = Bethwaite | first3 = PB. | last4 = McCredie | first4 = MR. | last5 = Martignoni | first5 = G. | last6 = Eble | first6 = JN. | last7 = Jordan | first7 = TW. | title = Fuhrman grading is not appropriate for chromophobe renal cell carcinoma. | journal = Am J Surg Pathol | volume = 31 | issue = 6 | pages = 957-60 | month = Jun | year = 2007 | doi = 10.1097/01.pas.0000249446.28713.53 | PMID = 17527087 }}</ref> | *[[ISUP nucleolar grade|ISUP nucleolar grading]] (replaces ''Fuhrman grading'') not done for this entity, as it does not appear to have any predictive value.<ref name=pmid17527087>{{Cite journal | last1 = Delahunt | first1 = B. | last2 = Sika-Paotonu | first2 = D. | last3 = Bethwaite | first3 = PB. | last4 = McCredie | first4 = MR. | last5 = Martignoni | first5 = G. | last6 = Eble | first6 = JN. | last7 = Jordan | first7 = TW. | title = Fuhrman grading is not appropriate for chromophobe renal cell carcinoma. | journal = Am J Surg Pathol | volume = 31 | issue = 6 | pages = 957-60 | month = Jun | year = 2007 | doi = 10.1097/01.pas.0000249446.28713.53 | PMID = 17527087 }}</ref> | ||
*May be associated with [[Birt–Hogg–Dubé syndrome]].<ref name=Ref_WMSP290>{{Ref WMSP|290}}</ref> | *May be associated with [[Birt–Hogg–Dubé syndrome]].<ref name=Ref_WMSP290>{{Ref WMSP|290}}</ref> | ||
*Can be seen in the context of [[renal oncocytosis]].<ref name=pmid23018240>{{Cite journal | last1 = Kuroda | first1 = N. | last2 = Tanaka | first2 = A. | last3 = Ohe | first3 = C. | last4 = Mikami | first4 = S. | last5 = Nagashima | first5 = Y. | last6 = Sasaki | first6 = T. | last7 = Inoue | first7 = K. | last8 = Hes | first8 = O. | last9 = Michal | first9 = M. | title = Review of renal oncocytosis (multiple oncocytic lesions) with focus on clinical and pathobiological aspects. | journal = Histol Histopathol | volume = 27 | issue = 11 | pages = 1407-12 | month = Nov | year = 2012 | doi = | PMID = 23018240 }}</ref> | |||
===Subtypes=== | ===Subtypes=== | ||
Revision as of 04:13, 4 December 2015
| Chromophobe renal cell carcinoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
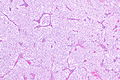
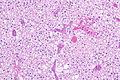
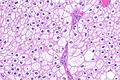
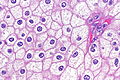
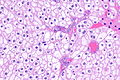
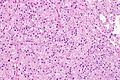
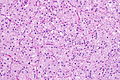
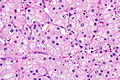
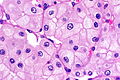
 Chromophobe renal cell carcinoma showing the characteristic perinuclear clearing and distinctive (plant-like) cellular borders. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | pale/clear (or eosinophilic) cytoplasm with wisps of eosinophilic material, perinuclear clearing (a pale halo surrounds the nucleus), periphery of cell distinct (cell membrane is easy to discern -- plant cell-like) |
| Subtypes | classic, eosinophilic variant |
| LM DDx | clear cell renal cell carcinoma (classic), renal oncocytoma, clear cell renal cell carcinoma eosinophilic variant |
| Stains | Hale's colloidal iron (Mueller-Mowry stain) +ve |
| IHC | CK7 +ve cell membrane, CD117 +ve, vimentin -ve |
| Gross | grey-beige, lacks central scar |
| Grossing notes | total nephrectomy for tumour grossing, partial nephrectomy grossing |
| Staging | kidney cancer staging |
| Site | kidney - see renal tumours |
|
| |
| Syndromes | Birt–Hogg–Dubé syndrome |
|
| |
| Prevalence | relatively common |
| Clin. DDx | other renal tumours |
| Treatment | surgical resection |
Chromophobe renal cell carcinoma, abbreviated ChRCC, is a relatively common form of renal cell carcinoma.
General
- Least common of the common types of RCC (clear cell RCC, papillary RCC, chromophobe RCC).
- ISUP nucleolar grading (replaces Fuhrman grading) not done for this entity, as it does not appear to have any predictive value.[1]
- May be associated with Birt–Hogg–Dubé syndrome.[2]
- Can be seen in the context of renal oncocytosis.[3]
Subtypes
There are two subtypes:[4]
- Classic.
- Eosinophilic variant.
Gross
- Grey-beige colour.[5]
- Solitary, usually.‡
- Well-circumscribed.
Note:
- ‡ Approximately 3% are multifocal.[6]
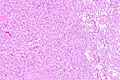
Image
Microscopic
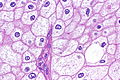
Classic
Features - classic type (3 P's memory device):[7][4]
- Pale cytoplasm, with wisps of eosinophilic material; the cells are not completely clear, they have "cobwebs".
- Perinuclear clearing, i.e. a pale halo surrounds the nucleus - key feature.
- Periphery of cell distinct, i.e. cell membrane is easy to discern.
Notes:
- May have psammoma bodies.
- May be described as "plant-like"; plant cells have (thick) cell walls.
- The perinuclear clearing is often somewhat patchy, i.e. it is usually not present in very tumour cell.
DDx:
- Clear cell RCC (classic).
- Perinuclear clearing is not seen in clear cell RCC.
- ChRCC has wisps in the cytoplasm.
Images
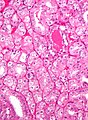
Eosinophilic variant
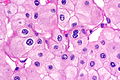
Features - eosinophilic variant:[4]
- Eosinophilic (finely granular) cytoplasm.
- Perinuclear clearing - key feature.
- Periphery of cell distinct.
- Smaller cells than classic subtype.
Notes:
- May have psammoma bodies.
DDx:
- Oncocytoma - particularly the eosinophilic variant.
- IHC may be useful to differentiate (CK7: oncocytoma = cytoplasm +ve, chromophobe = cell membrane +ve).
- A comparison based on histomorphology: Tabular comparison between ChRCC & oncocytoma.
- Oncocytoma typically has: no perinuclear clearing, no raisinoid nuclei, no binucleation.
- Clear cell RCC, eosinophilic variant.
- Perinuclear clearing is not seen in clear cell RCC.
- ChRCC has wisps in the cytoplasm.
- Other renal tumours with eosinophilic cytoplasm.
Images
Case 1
Case 2
www
Stains
- Hale's colloidal iron +ve (blue granular cytoplasmic).
- Oncocytoma -ve.
Note:
- This seems to be a difficult stain to get working.
Images
- ChRCC Hale's colloidal iron - several images (nature.com).
- ChRCC Hale's colloidal iron (ultrapath.org).[8]
- ChRCC Hale's colloidal iron (diagnosticpathology.org).
IHC
- CK7 +ve cell membrane.[4]
- Useful for differentiating from oncocytoma.
- CD117 +ve.
- Vimentin -ve.[9][10]
Uncommon stains for ChRCC versus oncocytoma:
ChRCC versus clear cell RCC
- CD117 +ve.
- -ve in CCRCC.
- CAIX (carbonic anhydrase CA IX) -ve.
- +ve (strong membranous) in CCRCC.[14]
- CK7 +ve.
- -ve in CCRCC.
Molecular
- Extensive aneusomy (monosomy?):[15]
- Loss of chromosomes: 1, 2, 6, 10, 13, 17, 21.
Sign out
KIDNEY, RIGHT UPPER POLE, PARTIAL NEPHRECTOMY: - CHROMOPHOBE RENAL CELL CARCINOMA. COMMENT: The sections show a mix of clear cells with wispy cytoplasm, and cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm and perinuclear halos. There are no true papillae. Stains and immunostains: Positive: CK7, CAM5.2, EMA, pankeratin, CD117, colloidal iron. Negative: AMACR, CD10, CD68, RCC, vimentin.
See also
References
- ↑ Delahunt, B.; Sika-Paotonu, D.; Bethwaite, PB.; McCredie, MR.; Martignoni, G.; Eble, JN.; Jordan, TW. (Jun 2007). "Fuhrman grading is not appropriate for chromophobe renal cell carcinoma.". Am J Surg Pathol 31 (6): 957-60. doi:10.1097/01.pas.0000249446.28713.53. PMID 17527087.
- ↑ Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 290. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ Kuroda, N.; Tanaka, A.; Ohe, C.; Mikami, S.; Nagashima, Y.; Sasaki, T.; Inoue, K.; Hes, O. et al. (Nov 2012). "Review of renal oncocytosis (multiple oncocytic lesions) with focus on clinical and pathobiological aspects.". Histol Histopathol 27 (11): 1407-12. PMID 23018240.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 Zhou, Ming; Magi-Galluzzi, Cristina (2006). Genitourinary Pathology: A Volume in Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 293. ISBN 978-0443066771.
- ↑ Kuroda, N.; Toi, M.; Hiroi, M.; Enzan, H. (Jan 2003). "Review of chromophobe renal cell carcinoma with focus on clinical and pathobiological aspects.". Histol Histopathol 18 (1): 165-71. PMID 12507296.
- ↑ Siracusano, S.; Novara, G.; Antonelli, A.; Artibani, W.; Bertini, R.; Carini, M.; Carmignani, G.; Ciciliato, S. et al. (Dec 2012). "Prognostic role of tumour multifocality in renal cell carcinoma.". BJU Int 110 (11 Pt B): E443-8. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.2012.11121.x. PMID 22502873.
- ↑ Cotran, Ramzi S.; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Nelso Fausto; Robbins, Stanley L.; Abbas, Abul K. (2005). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (7th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. pp. 1016-7. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.
- ↑ URL: http://www.ultrapath.org/oldsite/cases99/sep99/cotm9-2.html. Accessed on: 9 October 2011.
- ↑ Zhang, W.; Yu, WJ.; Jiang, YX.; Li, YJ.; Han, F.; Liu, Y.; Han, ZL. (Feb 2012). "[Chromophobe renal cell carcinoma: a clinicopathologic study and immunophenotypes of 42 cases].". Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi 41 (2): 76-80. PMID 22455881.
- ↑ Din, NU.; Fatima, S.; Ahmad, Z. (Dec 2013). "Chromophobe renal cell carcinoma: a morphologic and immunohistochemical study of 45 cases.". Ann Diagn Pathol 17 (6): 508-13. doi:10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2013.06.005. PMID 24095630.
- ↑ Memeo L, Jhang J, Assaad AM, et al. (February 2007). "Immunohistochemical analysis for cytokeratin 7, KIT, and PAX2: value in the differential diagnosis of chromophobe cell carcinoma". Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 127 (2): 225–9. doi:10.1309/9KWEA4W9Y94D1AEE. PMID 17210525. http://ajcp.ascpjournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=17210525.
- ↑ Jain, S.; Roy, S.; Amin, M.; Acquafondata, M.; Yin, M.; Laframboise, W.; Bastacky, S.; Pantanowitz, L. et al. (Dec 2013). "Amylase α-1A (AMY1A): A Novel Immunohistochemical Marker to Differentiate Chromophobe Renal Cell Carcinoma From Benign Oncocytoma.". Am J Surg Pathol 37 (12): 1824-30. doi:10.1097/PAS.0000000000000108. PMID 24225843.
- ↑ Amin MB, Epstein JI, Ulbright TM, et al. (August 2014). "Best practices recommendations in the application of immunohistochemistry in urologic pathology: report from the international society of urological pathology consensus conference". Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 38 (8): 1017–22. doi:10.1097/PAS.0000000000000254. PMID 25025364.
- ↑ Al-Ahmadie HA, Alden D, Fine SW, et al. (July 2011). "Role of immunohistochemistry in the evaluation of needle core biopsies in adult renal cortical tumors: an ex vivo study". Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 35 (7): 949–61. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e31821e25cd. PMID 21677535.
- ↑ Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 292. ISBN 978-0781765275.