Difference between revisions of "Sickle cell disease"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→Kidney) |
m (touch) |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
==Gallbladder== | ==Gallbladder== | ||
{{Main|Gallbladder}} | {{Main|Gallbladder}} | ||
*Pigment stones. | *Pigment stones. | ||
==Kidney== | ==Kidney== | ||
Revision as of 21:57, 27 October 2014
Sickle cell disease, also sickle cell anemia, is a heritable haematologic disorder associated with serious pathologies.
Liver
Main article: Liver
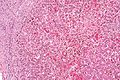
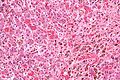
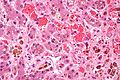
Images
Spleen
Main article: Spleen
- It may lead to auto infarction - result in hypofunction.
- Splenectomy have increased risk from polysaccharide encapsulated bacteria, i.e. Neisseria meningitis, Haemophilus influenzae, and Streptococcus pneumoniae.
Gallbladder
Main article: Gallbladder
- Pigment stones.
Kidney
- Renal medullary carcinoma associated with sickle cell trait (heterozygotes for the sickle cell allele[2]) or sickle cell disease.
- Papillary necrosis.[2]
- Nephrotic syndrome.[2]
- Renal infarction.[2]
- Pyelonephritis.[2]
Femoral head
See also
References
- ↑ Hurtova, M.; Bachir, D.; Lee, K.; Calderaro, J.; Decaens, T.; Kluger, MD.; Zafrani, ES.; Cherqui, D. et al. (Apr 2011). "Transplantation for liver failure in patients with sickle cell disease: challenging but feasible.". Liver Transpl 17 (4): 381-92. doi:10.1002/lt.22257. PMID 21445921.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Davis CJ, Mostofi FK, Sesterhenn IA (January 1995). "Renal medullary carcinoma. The seventh sickle cell nephropathy". Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 19 (1): 1–11. PMID 7528470.