Difference between revisions of "Sickle cell disease"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (→Liver: w) |
|||
| (9 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
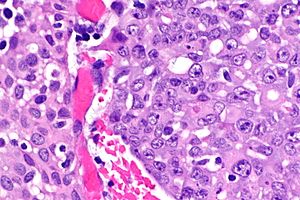
[[Image:Renal_medullary_carcinoma_-_2_--_very_high_mag.jpg|thumb|Extravascular drepanocytes (sickled [[red blood cell]]s) in [[renal medullary carcinoma]]. [[H&E stain]].]] | |||
'''Sickle cell disease''', also '''sickle cell [[anemia]]''', is a heritable [[haematopathology|haematologic]] disorder associated with serious pathologies. | '''Sickle cell disease''', also '''sickle cell [[anemia]]''', is a heritable [[haematopathology|haematologic]] disorder associated with serious pathologies. | ||
==Red blood cells== | |||
*Sickled red blood cells (drepanocytes). | |||
==Liver== | ==Liver== | ||
{{Main|Liver}} | {{Main|Liver}} | ||
*[[Cirrhosis]] and liver failure.<ref name=pmid21445921>{{Cite journal | last1 = Hurtova | first1 = M. | last2 = Bachir | first2 = D. | last3 = Lee | first3 = K. | last4 = Calderaro | first4 = J. | last5 = Decaens | first5 = T. | last6 = Kluger | first6 = MD. | last7 = Zafrani | first7 = ES. | last8 = Cherqui | first8 = D. | last9 = Mallat | first9 = A. | title = Transplantation for liver failure in patients with sickle cell disease: challenging but feasible. | journal = Liver Transpl | volume = 17 | issue = 4 | pages = 381-92 | month = Apr | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1002/lt.22257 | PMID = 21445921 }}</ref> | *[[Cirrhosis]] and liver failure.<ref name=pmid21445921>{{Cite journal | last1 = Hurtova | first1 = M. | last2 = Bachir | first2 = D. | last3 = Lee | first3 = K. | last4 = Calderaro | first4 = J. | last5 = Decaens | first5 = T. | last6 = Kluger | first6 = MD. | last7 = Zafrani | first7 = ES. | last8 = Cherqui | first8 = D. | last9 = Mallat | first9 = A. | title = Transplantation for liver failure in patients with sickle cell disease: challenging but feasible. | journal = Liver Transpl | volume = 17 | issue = 4 | pages = 381-92 | month = Apr | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1002/lt.22257 | PMID = 21445921 }}</ref> | ||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
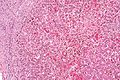
Image:Sickle_cell_disease_and_cirrhosis_-_intermed_mag.jpg | Sickle cell disease and cirrhosis - intermed. mag. (WC) | |||
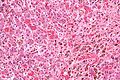
Image:Sickle_cell_disease_and_cirrhosis_-_high_mag.jpg | Sickle cell disease and cirrhosis - high mag. (WC) | |||
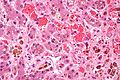
Image:Sickle_cell_disease_and_cirrhosis_-_very_high_mag.jpg | Sickle cell disease and cirrhosis - very high mag. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==Spleen== | ==Spleen== | ||
{{Main|Spleen}} | {{Main|Spleen}} | ||
*It may lead to auto infarction - result in hypofunction. | *It may lead to auto [[splenic infarction|infarction]] - result in hypofunction. | ||
**Splenectomy have increased risk from ''polysaccharide encapsulated bacteria'', i.e. Neisseria meningitis, Haemophilus influenzae, and Streptococcus pneumoniae. | **Splenectomy have increased risk from ''polysaccharide encapsulated bacteria'', i.e. Neisseria meningitis, Haemophilus influenzae, and Streptococcus pneumoniae. | ||
==Gallbladder== | ==Gallbladder== | ||
{{Main|Gallbladder}} | {{Main|Gallbladder}} | ||
*Pigment stones. | *Pigment stones. | ||
==Kidney== | ==Kidney== | ||
*[[Renal medullary carcinoma]] associated with sickle cell trait (heterozygotes for the sickle cell allele | *[[Renal medullary carcinoma]] associated with sickle cell trait (heterozygotes for the sickle cell allele<ref name=pmid7528470>{{cite journal |author=Davis CJ, Mostofi FK, Sesterhenn IA |title=Renal medullary carcinoma. The seventh sickle cell nephropathy |journal=Am. J. Surg. Pathol. |volume=19 |issue=1 |pages=1–11 |year=1995 |month=January |pmid=7528470 |doi= |url=}}</ref>) or sickle cell disease. | ||
*Papillary necrosis.<ref name=pmid7528470/> | |||
*[[Nephrotic syndrome]].<ref name=pmid7528470/> | |||
*Renal [[infarction]].<ref name=pmid7528470/> | |||
*[[Pyelonephritis]].<ref name=pmid7528470/> | |||
==Femoral head== | |||
*[[Avascular necrosis of the femoral head]]. | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Latest revision as of 13:42, 29 October 2021
Sickle cell disease, also sickle cell anemia, is a heritable haematologic disorder associated with serious pathologies.
Red blood cells
- Sickled red blood cells (drepanocytes).
Liver
Main article: Liver
Images
Spleen
Main article: Spleen
- It may lead to auto infarction - result in hypofunction.
- Splenectomy have increased risk from polysaccharide encapsulated bacteria, i.e. Neisseria meningitis, Haemophilus influenzae, and Streptococcus pneumoniae.
Gallbladder
Main article: Gallbladder
- Pigment stones.
Kidney
- Renal medullary carcinoma associated with sickle cell trait (heterozygotes for the sickle cell allele[2]) or sickle cell disease.
- Papillary necrosis.[2]
- Nephrotic syndrome.[2]
- Renal infarction.[2]
- Pyelonephritis.[2]
Femoral head
See also
References
- ↑ Hurtova, M.; Bachir, D.; Lee, K.; Calderaro, J.; Decaens, T.; Kluger, MD.; Zafrani, ES.; Cherqui, D. et al. (Apr 2011). "Transplantation for liver failure in patients with sickle cell disease: challenging but feasible.". Liver Transpl 17 (4): 381-92. doi:10.1002/lt.22257. PMID 21445921.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Davis CJ, Mostofi FK, Sesterhenn IA (January 1995). "Renal medullary carcinoma. The seventh sickle cell nephropathy". Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 19 (1): 1–11. PMID 7528470.