Difference between revisions of "Human papillomavirus"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
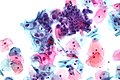
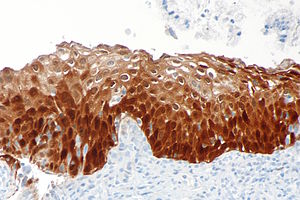
[[Image:High grade squamous intraepithelial lesion - 2 - p16 -- high mag.jpg|thumb|Micrograph showing block positive [[p16]] immunostaining in [[high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion]] of the cervix. (WC)]] | [[Image:High grade squamous intraepithelial lesion - 2 - p16 -- high mag.jpg|thumb|Micrograph showing block positive [[p16]] immunostaining in [[high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion]] of the cervix. ''p16'' is commonly used as a surrogate marker for human papillomavirus (HPV). (WC)]] | ||
'''Human papillomavirus''', abbreviated '''HPV''', is virus implicated in a large number of [[cancer]]s. | '''Human papillomavirus''', abbreviated '''HPV''', is virus implicated in a large number of [[cancer]]s. | ||
| Line 68: | Line 68: | ||
===Images=== | ===Images=== | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
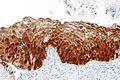
Image: High grade squamous intraepithelial lesion - 2 - p16 -- high mag.jpg | Block positive p16 staining in HSIL. (WC) | Image: High grade squamous intraepithelial lesion - 2 - p16 -- high mag.jpg | Block positive p16 staining in [[HSIL]]. (WC) | ||
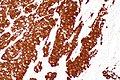
Image:Consistent with HPV-associated SCC - p16 -- intermed mag.jpg | c/w [[Human papillomavirus-associated head and neck squamous cell carcinoma|HPV-assoc. SCC]] - p16 - intermed. mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
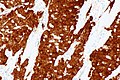
Image:Consistent with HPV-associated SCC - p16 -- high mag.jpg | c/w HPV-assoc. SCC - p16 - high mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Latest revision as of 15:35, 9 December 2021

Micrograph showing block positive p16 immunostaining in high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion of the cervix. p16 is commonly used as a surrogate marker for human papillomavirus (HPV). (WC)
Human papillomavirus, abbreviated HPV, is virus implicated in a large number of cancers.
General
- Sexually transmitted.
Note:
- Some tests can be done on formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue.[1]
Associated pathology
- Benign:
- Malignant:
- Cervical cancer and precursors (LSIL, HSIL).
- Anal cancer and precursors (AIN).[2]
- Vulvar cancer.[2]
- Vaginal cancer.[2]
- Penile cancer.[2]
- HPV-associated head and neck squamous cell carcinoma - oropharynx (specifically - tonsils, base of tongue).
- Human papillomavirus-related multiphenotypic sinonasal carcinoma (previously known as HPV-related carcinoma with adenoid cystic-like features).
Oncocytic types
Known as "high risk" types; this grouping includes:[5]
- HPV 18 - predominantly adenocarcinoma.[6]
- Eighteen = adenocarcinoma.
- HPV 16 - predominantly squamous cell carcinoma.[6]
- Sixteen = squamous.
- HPV 31.
- HPV 33.
- HPV 45.
Oncogenesis
Quick & dirty explanation of pathogenesis:[7][8]
- Virus integrates into host genome.
- This is accompanied by loss of viral gene E2 (which suppresses function of E6 & E7).
- Viral gene E6 dysregulates p53.
- Viral gene E7 dysregulates RB.
Vaccine
Recombinant vaccine (Gardasil, Silgard) - covers:[9]
- HPV 6.
- HPV 11.
- HPV 16.
- HPV 18.
Microscopic
Features:
- Koilocytes:
- Perinuclear clearing.
- Nuclear changes.
- Size similar (or larger) to those in the basal layer of the epithelium.
- Nuclear enlargement should be evident on low power, i.e. 25x.
- Central location - nucleus should be smack in the middle of the cell.
Images
IHC
- p16 +ve -- stains most cells infected by HPV.
Images
Block positive p16 staining in HSIL. (WC)
c/w HPV-assoc. SCC - p16 - intermed. mag. (WC/Nephron)
See also
References
- ↑ Black, CC.; Bentley, HA.; Davis, TH.; Tsongalis, GJ. (Dec 2010). "Use of a linear array for the detection of human papillomavirus genotypes in head and neck cancer.". Arch Pathol Lab Med 134 (12): 1813-7. doi:10.1043/2009-0592-OAR.1. PMID 21128780.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Borget, I.; Abramowitz, L.; Mathevet, P. (Jul 2011). "Economic burden of HPV-related cancers in France.". Vaccine 29 (32): 5245-9. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.05.018. PMID 21616117.
- ↑ Zhang, QY.; Zhang, DH.; Shen, ZY.; Xu, LY.; Li, EM.; Au, WW. (Mar 2011). "Infection and integration of human papillomavirus in esophageal carcinoma.". Int J Hyg Environ Health 214 (2): 156-61. doi:10.1016/j.ijheh.2010.11.001. PMID 21130683.
- ↑ Iyer, A.; Rajendran, V.; Adamson, CS.; Peng, Z.; Cooper, K.; Evans, MF. (Mar 2011). "Human papillomavirus is detectable in Barrett's esophagus and esophageal carcinoma but is unlikely to be of any etiologic significance.". J Clin Virol 50 (3): 205-8. doi:10.1016/j.jcv.2010.11.015. PMID 21169053.
- ↑ Ntova, CK.; Kottaridi, C.; Chranioti, A.; Spathis, A.; Kassanos, D.; Paraskevaidis, E.; Karakitsos, P. (2012). "Genetic Variability and Phylogeny of High Risk HPV Type 16, 18, 31, 33 and 45 L1 Gene in Greek Women.". Int J Mol Sci 13 (1): 1-17. doi:10.3390/ijms13010001. PMID 22312235.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 De Boer, MA.; Peters, LA.; Aziz, MF.; Siregar, B.; Cornain, S.; Vrede, MA.; Jordanova, ES.; Fleuren, GJ. (Apr 2005). "Human papillomavirus type 18 variants: histopathology and E6/E7 polymorphisms in three countries.". Int J Cancer 114 (3): 422-5. doi:10.1002/ijc.20727. PMID 15551313.
- ↑ Münger, K.; Howley, PM. (Nov 2002). "Human papillomavirus immortalization and transformation functions.". Virus Res 89 (2): 213-28. PMID 12445661.
- ↑ Mitchell, Richard; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Abbas, Abul K.; Aster, Jon (2011). Pocket Companion to Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 169. ISBN 978-1416054542.
- ↑ McCormack, PL.; Joura, EA. (Oct 2011). "Spotlight on Quadrivalent Human Papillomavirus(Types 6, 11, 16, 18) Recombinant Vaccine(Gardasil®) in the Prevention of PremalignantGenital Lesions, Genital Cancer, and Genital Warts in Women†.". BioDrugs 25 (5): 339-43. doi:10.2165/11205060-000000000-00000. PMID 21942919.