Difference between revisions of "Hyperplastic polyp with perineuromatous stroma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→See also: more) |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
'''Hyperplastic polyp with perineuromatous stroma''', also known as '''benign serrated colorectal fibroblastic polyps/intramucosal perineurioma''' and '''hybrid hyperplastic polyp/mucosal perineurioma''', is a benign [[colorectal polyp]]. | '''Hyperplastic polyp with perineuromatous stroma''', also known as '''benign serrated colorectal fibroblastic polyps/intramucosal perineurioma''' and '''hybrid hyperplastic polyp/mucosal perineurioma''', is a benign [[colorectal polyp]]. | ||
It may be referred to as '''[[perineurioma]]''' and '''fibroblastic polyp'''.<ref name=pmid18520438>{{cite journal | | It may be referred to as '''[[perineurioma]]''' and '''fibroblastic polyp'''.<ref name=pmid18520438>{{cite journal |authors=Groisman GM, Polak-Charcon S |title=Fibroblastic polyp of the colon and colonic perineurioma: 2 names for a single entity? |journal=Am J Surg Pathol |volume=32 |issue=7 |pages=1088–94 |date=July 2008 |pmid=18520438 |doi=10.1097/PAS.0b013e318160df3f |url=}}</ref> | ||
==General== | ==General== | ||
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
==IHC== | ==IHC== | ||
Features:<ref name=pmid15104300>{{cite journal | | Features:<ref name=pmid15104300>{{cite journal |authors=Eslami-Varzaneh F, Washington K, Robert ME, Kashgarian M, Goldblum JR, Jain D |title=Benign fibroblastic polyps of the colon: a histologic, immunohistochemical, and ultrastructural study |journal=Am J Surg Pathol |volume=28 |issue=3 |pages=374–8 |date=March 2004 |pmid=15104300 |doi=10.1097/00000478-200403000-00010 |url=}}</ref> | ||
*Vimentin +ve. | *Vimentin +ve. | ||
*SMA -ve. | *SMA -ve. | ||
| Line 67: | Line 67: | ||
*S-100 -ve | *S-100 -ve | ||
*EMA -ve. | *EMA -ve. | ||
==Sign out== | |||
<pre> | |||
Polyp, Colon at 35 cm, Polypectomy or Biopsy: | |||
- Hyperplastic polyp with perineuromatous stroma. | |||
</pre> | |||
===Micro=== | |||
The sections show a polypoid fragment of colonic-type serrated epithelium with small round glands at the deep aspect. Fibroblastic/perineuromatous type stroma is present and NSE NEGATIVE, S100 NEGATIVE and desmin NEGATIVE. The tissue is NEGATIVE for atypia and NEGATIVE for apparent proliferative activity. | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Latest revision as of 21:15, 20 April 2021
| Hyperplastic polyp with perineuromatous stroma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
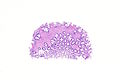
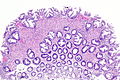
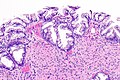
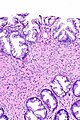
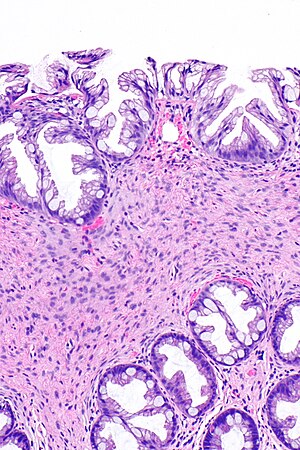 Hyperplastic polyp with perineuromatous stroma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| Synonyms | benign serrated colorectal fibroblastic polyps/intramucosal perineurioma, hybrid hyperplastic polyp/mucosal perineurioma |
|
| |
| LM | serrated epithelial cells (at the surface), perineuromatous stroma |
| LM DDx | colonic ganglioneuroma, hyperplastic polyp |
| Site | colon and rectum |
|
| |
| Prevalence | rare |
| Endoscopy | polyp |
| Prognosis | benign |
| Clin. DDx | other types of colorectal polyps |
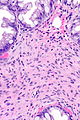
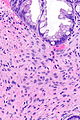
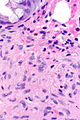
Hyperplastic polyp with perineuromatous stroma, also known as benign serrated colorectal fibroblastic polyps/intramucosal perineurioma and hybrid hyperplastic polyp/mucosal perineurioma, is a benign colorectal polyp.
It may be referred to as perineurioma and fibroblastic polyp.[1]
General
- Rare.
- Benign.[2]
Microscopic
Features:
- Serrated epithelial cells (at the surface of the gland) - key feature.
- Serrated appearance = saw-tooth appearance, epithelium has jagged edge.
- Perineuromatous stroma.
DDx:
Images
IHC
Features:[3]
- Vimentin +ve.
- SMA -ve.
- Desmin -ve.
- CD117 -ve.
- S-100 -ve
- EMA -ve.
Sign out
Polyp, Colon at 35 cm, Polypectomy or Biopsy:
- Hyperplastic polyp with perineuromatous stroma.
Micro
The sections show a polypoid fragment of colonic-type serrated epithelium with small round glands at the deep aspect. Fibroblastic/perineuromatous type stroma is present and NSE NEGATIVE, S100 NEGATIVE and desmin NEGATIVE. The tissue is NEGATIVE for atypia and NEGATIVE for apparent proliferative activity.
See also
References
- ↑ Groisman GM, Polak-Charcon S (July 2008). "Fibroblastic polyp of the colon and colonic perineurioma: 2 names for a single entity?". Am J Surg Pathol 32 (7): 1088–94. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e318160df3f. PMID 18520438.
- ↑ Agaimy, A.; Stoehr, R.; Vieth, M.; Hartmann, A. (Nov 2010). "Benign serrated colorectal fibroblastic polyps/intramucosal perineuriomas are true mixed epithelial-stromal polyps (hybrid hyperplastic polyp/mucosal perineurioma) with frequent BRAF mutations.". Am J Surg Pathol 34 (11): 1663-71. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181f4a458. PMID 20962618.
- ↑ Eslami-Varzaneh F, Washington K, Robert ME, Kashgarian M, Goldblum JR, Jain D (March 2004). "Benign fibroblastic polyps of the colon: a histologic, immunohistochemical, and ultrastructural study". Am J Surg Pathol 28 (3): 374–8. doi:10.1097/00000478-200403000-00010. PMID 15104300.