Difference between revisions of "Follicular thyroid adenoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
| Width = | | Width = | ||
| Caption = Follicular adenoma. [[H&E stain]]. | | Caption = Follicular adenoma. [[H&E stain]]. | ||
| Synonyms = | | Synonyms = follicular adenoma | ||
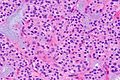
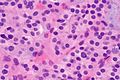
| Micro = cellular appearance (low magnification), microfollicles, thick fibrous capsule without invasion, negative for nuclear features of papillary thyroid carcinoma | | Micro = cellular appearance (low magnification), microfollicles, thick fibrous capsule without invasion, negative for nuclear features of papillary thyroid carcinoma | ||
| Subtypes = | | Subtypes = | ||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
*Most common neoplasm of thyroid.<ref name=Ref_EP51>{{Ref EP|51}}</ref> | *Most common neoplasm of thyroid.<ref name=Ref_EP51>{{Ref EP|51}}</ref> | ||
*Encapusled lesion (surrounded by fibrous capsule). | *Encapusled lesion (surrounded by fibrous capsule). | ||
*Cannot be diagnosed on [[thyroid cytopathology|thyroid FNA]], as one cannot exclude invasion through the capsule without examining all of it. | |||
==Gross== | ==Gross== | ||
| Line 55: | Line 56: | ||
Negatives. | Negatives. | ||
*No invasion of the capsule - see | *No invasion of the capsule - see [[follicular thyroid carcinoma]]. | ||
*No nuclear features suggestive of [[papillary thyroid carcinoma]]. | *No nuclear features suggestive of [[papillary thyroid carcinoma]]. | ||
| Line 73: | Line 74: | ||
Image: Follicular adenoma -- very high mag.jpg | FA - very high mag. (WC) | Image: Follicular adenoma -- very high mag.jpg | FA - very high mag. (WC) | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==Sign out== | ==Sign out== | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
Latest revision as of 03:41, 10 June 2016
| Follicular thyroid adenoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
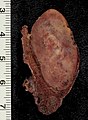
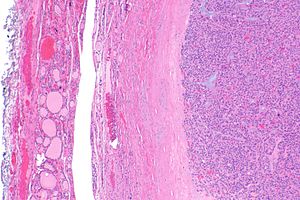 Follicular adenoma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| Synonyms | follicular adenoma |
|
| |
| LM | cellular appearance (low magnification), microfollicles, thick fibrous capsule without invasion, negative for nuclear features of papillary thyroid carcinoma |
| LM DDx | thyroid gland nodular hyperplasia, follicular thyroid carcinoma, noninvasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features (NIFTP), Papillary thyroid carcinoma follicular variant |
| Gross | lesion with thick capsule |
| Site | thyroid gland |
|
| |
| Signs | thyroid mass |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Prognosis | benign |
| Clin. DDx | follicular carcinoma, other thyroid tumours |
| Treatment | excision to exclude carcinoma |
Follicular thyroid adenoma, abbreviated FTA, is a benign lesion of the thyroid gland.
General
- Most common neoplasm of thyroid.[1]
- Encapusled lesion (surrounded by fibrous capsule).
- Cannot be diagnosed on thyroid FNA, as one cannot exclude invasion through the capsule without examining all of it.
Gross
- Thick capsule.
Notes:
- The entire capsule should be submitted.[2]
- A good start for most thyroid specimens with a thick capsule is 10 blocks.
Images
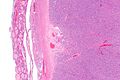
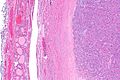
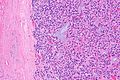
Microsopic
Features:
- Cellular.
- Thick capsule - key feature.
Negatives.
- No invasion of the capsule - see follicular thyroid carcinoma.
- No nuclear features suggestive of papillary thyroid carcinoma.
DDx:
- Thyroid gland nodular hyperplasia with an encapsulated nodule - not as cellular.
- Follicular thyroid carcinoma.
- Noninvasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features (NIFTP).
- Papillary thyroid carcinoma follicular variant.
Images
Sign out
Left Hemithyroid, Hemithyroidectomy: - Follicular adenoma. - Parathyroid gland. - Five benign lymph nodes (0/5). - NEGATIVE for evidence of malignancy.
Block letters
LEFT THYROID, SUPERIOR POLE, EXCISION: - FOLLICULAR ADENOMA, MAXIMAL DIMENSION 5 MM. - LYMPHOCYTIC THYROIDITIS. - NODULAR HYPERPLASIA. - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
Micro
The section shows a well-circumscribed lesion encapsulated by a thick fibrous capsule (~0.4 mm thick).
The lesions consists of microfollicles with a dense appearing colloid. The nuclei have round regular nuclear membranes. Small indistinct nucleoli are seen at high power.
Focally, the lesional cells overlap. However, the chromatin is not cleared. Nuclear grooves are not readily apparent and nuclear pseudoinclusions are not readily identified.
See also
References
- ↑ Thompson, Lester D. R. (2006). Endocrine Pathology: A Volume in Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 51. ISBN 978-0443066856.
- ↑ SR. 17 January 2011.