Difference between revisions of "Mastocytosis"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→Stains) |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
DDx: | DDx: | ||
*[[Intradermal nevus]]. | *[[Intradermal nevus]]. | ||
*[[Pleomorphic undifferentiated sarcoma]], [[Langerhans cell histiocytosis]] and other [[pleomorphic tumours]] - for ''aggressive systemic mastocytosis''. | |||
===Images=== | ===Images=== | ||
Latest revision as of 03:19, 20 March 2018
| Mastocytosis | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
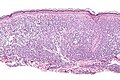
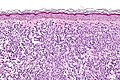
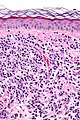
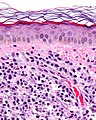
 Mastocytosis. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | mast cells (cells in the superficial/mid dermis that are: lymphocyte-like with more cytoplasm that is granular; cells may have spindled or stellate morphology); +/-eosinophils (common) |
| LM DDx | intradermal nevus |
| Stains | Giemsa stain +ve |
| IHC | CD117 +ve, tryptase +ve |
| Site | skin |
|
| |
| Prevalence | not very common |
| Prognosis | dependent on underlying cause |
| Treatment | dependent on underlying cause |
Mastocytosis is the abundance of mast cells. It can be due to a number of causes.
General
- Abundance of mast cells.
Classification:[1]
- Cutaneous (only) - usually children.
- Urticaria pigmentosa.
- Others.
- Systemic - usually adults.
- Indolent subvariant.
- Aggressive subvariant.
- Leukemic subvariant.
Microscopic
Features:[2]
- Cells in the superficial/mid dermis that are:
- Lymphocyte-like with more cytoplasm that is granular.
- Cells may have spindled or stellate morphology.
- Tend to be more abundant around vessels.
- Lymphocyte-like with more cytoplasm that is granular.
- +/-Eosinophils (common).
- +/-Edema - often prominent; gives cells a white halo.
Notes:
- Lymphocyte versus mast cell:
- Lymphocytes = round; mast cells = ovoid.
DDx:
- Intradermal nevus.
- Pleomorphic undifferentiated sarcoma, Langerhans cell histiocytosis and other pleomorphic tumours - for aggressive systemic mastocytosis.
Images
www:
- Mastocytosis - low res. (jameswpattersonmd.com).
- Mastocytosis - bone marrow - several images (upmc.edu).
- Systemic mastocytosis - several images (upmc.edu).
Stains
- Toluidine blue -- highlights the granules.
- Giemsa stain +ve
IHC
- CD117 +ve.
- Tryptase +ve.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ Arock, M.; Valent, P. (Aug 2010). "Pathogenesis, classification and treatment of mastocytosis: state of the art in 2010 and future perspectives.". Expert Rev Hematol 3 (4): 497-516. doi:10.1586/ehm.10.42. PMID 21083038.
- ↑ Kumar, Vinay; Abbas, Abul K.; Fausto, Nelson; Aster, Jon (2009). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 1185. ISBN 978-1416031215.
- ↑ Rudzki, Z.; Sotlar, K.; Kudela, A.; Starzak-Gwóźdź, J.; Horny, HP. (2011). "Systemic mastocytosis (SM) and associated malignant bone marrow histiocytosis - a hitherto undescribed form of SM-AHNMD.". Pol J Pathol 62 (2): 101-4. PMID 21866466.