Difference between revisions of "Goblet cell adenocarcinoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(tweak) |
|||
| (10 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
| Image = Goblet_cell_carcinoid_-2-_very_high_mag.jpg | | Image = Goblet_cell_carcinoid_-2-_very_high_mag.jpg | ||
| Width = | | Width = | ||
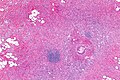
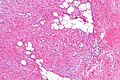
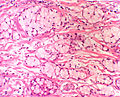
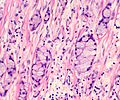
| Caption = | | Caption = Goblet cell adenocarcinoma. [[H&E stain]]. | ||
| Synonyms = goblet cell carcinoid (obsolete term), crypt cell carcinoma | |||
| Micro = small clusters of cells with stippled chromatin and a goblet cell-like appearance | | Micro = small clusters of cells with stippled chromatin and a goblet cell-like appearance | ||
| Subtypes = | | Subtypes = | ||
| Line 28: | Line 29: | ||
| ClinDDx = [[acute appendicitis]], other appendiceal tumours, other abdominal pathology | | ClinDDx = [[acute appendicitis]], other appendiceal tumours, other abdominal pathology | ||
}} | }} | ||
''' | '''Goblet cell adenocarcinoma''' is a rare malignant tumour that is typically seen in the [[vermiform appendix]].<ref>{{cite journal |authors=Kiyosawa N, Koyama M, Miyagawa Y, Kitazawa M, Tokumaru S, Soejima Y |title=Goblet cell adenocarcinoma of the appendix: A case report of three cases |journal=Int J Surg Case Rep |volume=106 |issue= |pages=108229 |date=April 2023 |pmid=37084554 |doi=10.1016/j.ijscr.2023.108229 |url=}}</ref> | ||
and '''[[neuroendocrine tumour]] with goblet cell differentiation''' | |||
It has gone by a number of different names in the past: '''crypt cell carcinoma''',<ref>{{cite journal |authors=Limaiem F, Omrani S, Hajri M |title=Goblet cell adenocarcinoma of the ascending colon: An underrecognized diagnostic pitfall |journal=Clin Case Rep |volume=11 |issue=1 |pages=e6822 |date=January 2023 |pmid=36654693 |pmc=9834544 |doi=10.1002/ccr3.6822 |url=}}</ref> '''goblet cell carcinoid'''<ref>{{cite journal |authors=Sigley K, Franklin M, Welch S |title=Appendiceal Goblet Cell Adenocarcinoma Case Report and Review of the Literature |journal=Cureus |volume=13 |issue=2 |pages=e13511 |date=February 2021 |pmid=33786220 |pmc=7992912 |doi=10.7759/cureus.13511 |url=}}</ref><ref name=pmid18042066>{{cite journal |author=van Eeden S, Offerhaus GJ, Hart AA, ''et al.'' |title=Goblet cell carcinoid of the appendix: a specific type of carcinoma |journal=Histopathology |volume=51 |issue=6 |pages=763–73 |year=2007 |month=December |pmid=18042066 |doi=10.1111/j.1365-2559.2007.02883.x |url=}}</ref><ref name=pmid15967038>{{Cite journal | last1 = Pahlavan | first1 = PS. | last2 = Kanthan | first2 = R. | title = Goblet cell carcinoid of the appendix. | journal = World J Surg Oncol | volume = 3 | issue = | pages = 36 | month = Jun | year = 2005 | doi = 10.1186/1477-7819-3-36 | PMID = 15967038 }}</ref> | |||
and '''[[neuroendocrine tumour]] with goblet cell differentiation'''. | |||
==General== | ==General== | ||
*Rare appendiceal tumour that typically has an aggressive course vis- | *Rare appendiceal tumour that typically has an aggressive course vis-à-vis [[appendiceal carcinoid]]s.<ref name=pmid18042066>{{cite journal |author=van Eeden S, Offerhaus GJ, Hart AA, ''et al.'' |title=Goblet cell carcinoid of the appendix: a specific type of carcinoma |journal=Histopathology |volume=51 |issue=6 |pages=763–73 |year=2007 |month=December |pmid=18042066 |doi=10.1111/j.1365-2559.2007.02883.x |url=}}</ref> | ||
*Mixed (biphasic) tumour with endocrine and exocrine features. | *Mixed (biphasic) tumour with endocrine and exocrine features. | ||
*Usually presents as [[acute appendicitis]].<ref name=pmid15967038/> | *Usually presents as [[acute appendicitis]].<ref name=pmid15967038/> | ||
| Line 40: | Line 43: | ||
==Gross== | ==Gross== | ||
*Typically no mass is apparent at gross.<ref name=pmid15967038/> | *Typically no mass is apparent at gross.<ref name=pmid15967038/> | ||
Note: | |||
*Should be [[submitted in total]]. | |||
==Microscopic== | ==Microscopic== | ||
Features:<ref name=pmid15967038 | Features:<ref name=pmid15967038/> | ||
*Mixed neuroendocrine-nonneuroendocrine tumour;<ref name=pmid17684764>{{cite journal |author=Volante M, Righi L, Asioli S, Bussolati G, Papotti M |title=Goblet cell carcinoids and other mixed neuroendocrine/nonneuroendocrine neoplasms |journal=Virchows Arch. |volume=451 Suppl 1 |issue= |pages=S61–9 |year=2007 |month=August |pmid=17684764 |doi=10.1007/s00428-007-0447-y |url=}}</ref> features of both ''carcinoid'' and ''adenocarcinoma.<ref name=pmid15967038/> | *Mixed neuroendocrine-nonneuroendocrine tumour;<ref name=pmid17684764>{{cite journal |author=Volante M, Righi L, Asioli S, Bussolati G, Papotti M |title=Goblet cell carcinoids and other mixed neuroendocrine/nonneuroendocrine neoplasms |journal=Virchows Arch. |volume=451 Suppl 1 |issue= |pages=S61–9 |year=2007 |month=August |pmid=17684764 |doi=10.1007/s00428-007-0447-y |url=}}</ref> features of both ''carcinoid'' and ''adenocarcinoma.<ref name=pmid15967038/> | ||
**Archictecture: cells arranged in nests or clusters without a lumen. | **Archictecture: cells arranged in nests or clusters without a lumen. | ||
| Line 58: | Line 64: | ||
===Images=== | ===Images=== | ||
====Case 1==== | |||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
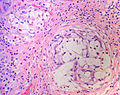
Image:Goblet cell carcinoid - low mag.jpg| CCC - low mag. (WC/Nephron) | Image:Goblet cell carcinoid - low mag.jpg| CCC - low mag. (WC/Nephron) | ||
| Line 68: | Line 75: | ||
Image:Goblet cell carcinoid -2- high mag.jpg| CCC - high mag. (WC/Nephron) | Image:Goblet cell carcinoid -2- high mag.jpg| CCC - high mag. (WC/Nephron) | ||
Image:Goblet cell carcinoid -2- very high mag.jpg| CCC - very high mag. (WC/Nephron) | Image:Goblet cell carcinoid -2- very high mag.jpg| CCC - very high mag. (WC/Nephron) | ||
</gallery> | |||
====Case 2==== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Appendix Carcinoid GobletCell HP PA.JPG|Goblet cell carcinoid - high power (SKB) | |||
Image:Appendix Carcinoid GobletCell HP (5) PA.JPG|Appendix - Goblet cell carcinoid - high power (SKB) | |||
Image:Appendix Carcinoid GobletCell MP PA.JPG|Appendix - Goblet cell carcinoid - medium power (SKB) | |||
Image:Appendix Carcinoid GobletCell HP (4) - Copy PA.JPG|Appendix - Goblet cell carcinoid - high power (SKB) | |||
Image:Appendix Carcinoid GobletCell HP (3) - Copy PA.JPG|Appendix - Goblet cell carcinoid - high power (SKB) | |||
Image:Appendix Carcinoid GobletCell HP-2 PA.JPG|Appendix - Goblet cell carcinoid - high power (SKB) | |||
Image:Appendix Carcinoid GobletCell HP-2 (2) PA.JPG|Appendix - Goblet cell carcinoid - high power (SKB) | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| Line 78: | Line 95: | ||
**Synaptophysin +ve. | **Synaptophysin +ve. | ||
**Chromogranin +ve. | **Chromogranin +ve. | ||
*S-100 +ve. | *[[S-100]] +ve. | ||
*NSE +ve. | *NSE +ve. | ||
*Serotonin +ve. | *Serotonin +ve. | ||
Keratins: | Keratins: | ||
*Usually CK20 +ve > CK7 +ve. | *Usually [[CK20]] +ve > [[CK7]] +ve. | ||
*CEA +ve (membrane). | *CEA +ve (membrane). | ||
Notes: | Notes: | ||
* | *Review of stains in Pahlavan and Kanthan.<ref name=pmid15967038/> | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Latest revision as of 17:53, 27 April 2023
| Goblet cell adenocarcinoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
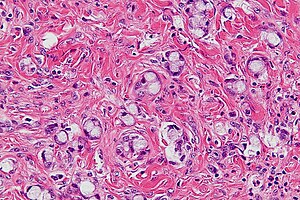 Goblet cell adenocarcinoma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| Synonyms | goblet cell carcinoid (obsolete term), crypt cell carcinoma |
|
| |
| LM | small clusters of cells with stippled chromatin and a goblet cell-like appearance |
| LM DDx | signet ring cell carcinoma, appendiceal neuroendocrine tumour, poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma |
| Stains | alcian blue +ve, PASD +ve, mucicarmine +ve |
| IHC | synaptophysin +ve, chromogranin +ve, S-100 +ve, CK20 +ve |
| Gross | usu. no mass apparent |
| Site | vermiform appendix, elsewhere in the GI tract |
|
| |
| Clinical history | "acute appendicitis" |
| Prevalence | rare |
| Prognosis | moderate |
| Clin. DDx | acute appendicitis, other appendiceal tumours, other abdominal pathology |
Goblet cell adenocarcinoma is a rare malignant tumour that is typically seen in the vermiform appendix.[1]
It has gone by a number of different names in the past: crypt cell carcinoma,[2] goblet cell carcinoid[3][4][5] and neuroendocrine tumour with goblet cell differentiation.
General
- Rare appendiceal tumour that typically has an aggressive course vis-à-vis appendiceal carcinoids.[4]
- Mixed (biphasic) tumour with endocrine and exocrine features.
- Usually presents as acute appendicitis.[5]
- Less common presentations: appendiceal mass, pain.
- Five year survival in one series: 60-85%.[5]
Gross
- Typically no mass is apparent at gross.[5]
Note:
- Should be submitted in total.
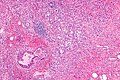
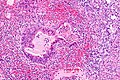
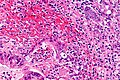
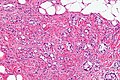
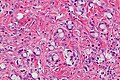
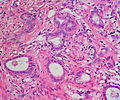
Microscopic
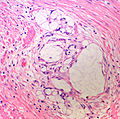
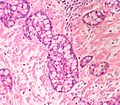
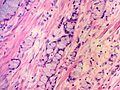
Features:[5]
- Mixed neuroendocrine-nonneuroendocrine tumour;[6] features of both carcinoid and adenocarcinoma.[5]
- Archictecture: cells arranged in nests or clusters without a lumen.
- Location: deep to the intestinal crypts (crypts of Lieberkühn); usually do not involve the mucosa.
- Cytoplasm distended with mucin.
- DNA: crescentic nucleus (similar to in signet ring cells).
- +/-Multi-nucleation.
- +/-High mitotic rate.
- Usually minimal nuclear atypia.
DDx:
- Appendiceal neuroendocrine tumour.
- Signet ring cell carcinoma[7] - cells more detached, no neuroendocrine differentiation.
- Poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma - see colorectal carcinoma.
Images
Case 1
Case 2
Stains
- Mucin stains +ve:
IHC
- Classic neuroendocrine markers:
- Synaptophysin +ve.
- Chromogranin +ve.
- S-100 +ve.
- NSE +ve.
- Serotonin +ve.
Keratins:
- CEA +ve (membrane).
Notes:
- Review of stains in Pahlavan and Kanthan.[5]
See also
References
- ↑ Kiyosawa N, Koyama M, Miyagawa Y, Kitazawa M, Tokumaru S, Soejima Y (April 2023). "Goblet cell adenocarcinoma of the appendix: A case report of three cases". Int J Surg Case Rep 106: 108229. doi:10.1016/j.ijscr.2023.108229. PMID 37084554.
- ↑ Limaiem F, Omrani S, Hajri M (January 2023). "Goblet cell adenocarcinoma of the ascending colon: An underrecognized diagnostic pitfall". Clin Case Rep 11 (1): e6822. doi:10.1002/ccr3.6822. PMC 9834544. PMID 36654693. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9834544/.
- ↑ Sigley K, Franklin M, Welch S (February 2021). "Appendiceal Goblet Cell Adenocarcinoma Case Report and Review of the Literature". Cureus 13 (2): e13511. doi:10.7759/cureus.13511. PMC 7992912. PMID 33786220. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7992912/.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 van Eeden S, Offerhaus GJ, Hart AA, et al. (December 2007). "Goblet cell carcinoid of the appendix: a specific type of carcinoma". Histopathology 51 (6): 763–73. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2559.2007.02883.x. PMID 18042066.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 Pahlavan, PS.; Kanthan, R. (Jun 2005). "Goblet cell carcinoid of the appendix.". World J Surg Oncol 3: 36. doi:10.1186/1477-7819-3-36. PMID 15967038.
- ↑ Volante M, Righi L, Asioli S, Bussolati G, Papotti M (August 2007). "Goblet cell carcinoids and other mixed neuroendocrine/nonneuroendocrine neoplasms". Virchows Arch. 451 Suppl 1: S61–9. doi:10.1007/s00428-007-0447-y. PMID 17684764.
- ↑ Pericleous, M.; Lumgair, H.; Baneke, A.; Morgan-Rowe, L.; E Caplin, M.; Luong, TV.; Thirlwell, C.; Gillmore, R. et al. (May 2012). "Appendiceal goblet cell carcinoid tumour: a case of unexpected lung metastasis.". Case Rep Oncol 5 (2): 332-8. doi:000339607. PMID 22933998.