Difference between revisions of "An introduction to gastrointestinal pathology"
(→Cell types: more) |
(→Layers) |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
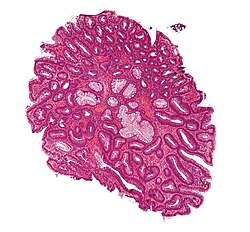
[[Image:Tubular adenoma 4 low mag.jpg|thumb|right|250px|[[Micrograph]] of a [[Traditional adenoma|tubular adenoma]], a very common diagnosis in gastrointestinal pathology. [[H&E stain]].]] | |||
'''Gastrointestinal pathology''', also '''gastrointestinal tract pathology''', is a large part of pathology as [[radiologist]]s can often describe the extent of disease... but don't get the [[diagnosis]] right all the time. | '''Gastrointestinal pathology''', also '''gastrointestinal tract pathology''', is a large part of pathology as [[radiologist]]s can often describe the extent of disease... but don't get the [[diagnosis]] right all the time. | ||
| Line 5: | Line 6: | ||
=Normal= | =Normal= | ||
===Layers=== | ===Layers=== | ||
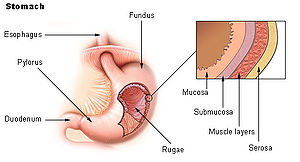
[[Image:Illu stomach2.jpg|thumb|right|Layers of the stomach. (WC)]] | |||
Layers of the alimentary canal:<ref>URL: [http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/CorePages/Oral/Oral.htm http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/CorePages/Oral/Oral.htm].</ref><ref>URL: [http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/CorePages/Oral/Images/gitplan.gif http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/CorePages/Oral/Images/gitplan.gif].</ref> | Layers of the alimentary canal:<ref>URL: [http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/CorePages/Oral/Oral.htm http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/CorePages/Oral/Oral.htm].</ref><ref>URL: [http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/CorePages/Oral/Images/gitplan.gif http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/CorePages/Oral/Images/gitplan.gif].</ref> | ||
*Mucosa (epithelium, lamina propria, muscularis mucosa). | *Mucosa (epithelium, lamina propria, muscularis mucosa). | ||
| Line 17: | Line 19: | ||
**Subnuclear eosinophilic granules. | **Subnuclear eosinophilic granules. | ||
***Serotonin. | ***Serotonin. | ||
*Paneth | *[[Paneth cell]]s. | ||
**Supranuclear eosinophilic granules. | **Supranuclear eosinophilic granules. | ||
| Line 149: | Line 151: | ||
==Eosinophilic enterocolitis== | ==Eosinophilic enterocolitis== | ||
{{Main|Eosinophilic enterocolitis}} | |||
==Pneumatosis intestinalis== | ==Pneumatosis intestinalis== | ||
{{Main|Pneumatosis intestinalis}} | |||
==Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis== | ==Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis== | ||
{{Main|Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis}} | |||
=See also= | =See also= | ||
Latest revision as of 05:55, 3 February 2016
Gastrointestinal pathology, also gastrointestinal tract pathology, is a large part of pathology as radiologists can often describe the extent of disease... but don't get the diagnosis right all the time.
Cytopathology of the gastrointestinal tract is dealt with in the gastrointestinal cytopathology article.
Normal
Layers
Layers of the alimentary canal:[1][2]
- Mucosa (epithelium, lamina propria, muscularis mucosa).
- Submuscosa and submucosal plexus (or Meissner's plexus).
- Muscularis externa (inner longitudinal, myenteric plexus (or Auerbach's plexus) outer circumferential).
- Adventitia (if retroperitoneal), serosa (if intraperitoneal).
Cell types
- Goblet cells.
- Secrete mucin.
- Enterochromaffin cells, AKA Kulchitsky cells.
- Subnuclear eosinophilic granules.
- Serotonin.
- Subnuclear eosinophilic granules.
- Paneth cells.
- Supranuclear eosinophilic granules.
Memory device:
- Supranuclear granules = paneth cell.
Images
www:
- Paneth cell versus neuroendocrine cell (amazonaws.com).
- Goblet cells versus pseudogoblet cells (washington.edu).
Bowel
Small bowel
- Villi - should see three good ones in a normal biopsy.
- Crypts.
- Paneth cells.
- Goblet cells.
- Few in proximal small bowel (duodenum).
- Abundant in distal small bowel (ileum).
Duodenum
- Small bowel (as above).
- Submucosal glands (Brunner's glands).
Large bowel versus small bowel
- Small intestine.
- Villi (key feature).
- Brunner's glands - duodenum only (key feature).
- Paneth cells more common.
- Paneth cells are in the base of the crypts and have eosinophilic granules. They are found (normally) in the small bowel and right colon. They may appear on the left side (i.e. descending colon) in pathologic states, e.g. IBD.
- Large intestine
- More goblet cells.
- More lymphocytes usually.
Cecum versus rectum
- Cecum.
- Less goblet cells - more absorptive cells.[3]
- More inflammation (plasma cells, eosinophils, lymphoid aggregates).[3]
- Paneth cells.
- Rectum.
- More goblet cells.
- No Paneth cells normally.
DDx by location
A short DDx for location of abnormality:
- Lumen:
- Surface of epithelium:
- Infiltration of epithelium:
- Intraepithelial lymphocytes - lymphocytic colitis & collagenous colitis.
- Intraepithelial neutrophils - infection, IBD, ischemia.
- Epithelial architeture:
- Serration - SSA, hyperplastic polyp.
- Increased lamina propria/loss of crypts - IBD, juvenile polyp).
- Distortion - IBD, infection, ischemia.
- Crypt branching - IBD, ischemia, chronic infection, SSA.
- Back-to-back glands - malignancy, dysplasia.
- Single cell infiltrates - lamina propria:
- Epithelial - signet ring cell carcinoma.
- Macrophages - MAI, TB, Whipple disease, Yersinia.
- Nuclear abnormalities:
- Pseudostratification - repair, dysplasia, malignancy.
- Nuclear enlargement - malignancy, viral cytopathic effect.
- Submucosal:
- Brunner's gland - duodenum.
- Fibrosis - IBD, prolapse.
- Nests - neuroendocrine tumours.
Luminal gastroenterology
Non-regional
Intestinal polyps
The bread and butter of gastrointestinal pathology.
Regional
Esophagus
Largely forgotten organ at SB... but no shortage of these at SMH.
Stomach
H. pylori, cancer and more...
Small bowel
The part of the GI tract that pathology has mostly forgot. Crohn's disease is dealt with in a separate article.
Duodenum
Commonly biopsied. Celiac... cancer... giardia?
Cecum
The first part of the large intestine. Technically, it is not part of the colon.
Appendix
It hangs off the cecum. Commonly, it comes to the pathologist because of acute appendicitis.
Colon
Colorectal tumours are dealt with in colorectal tumours. Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis are dealt with in the inflammatory bowel disease article. Includes discussion of the rectum. The anus is a separate article.
Accessory organs of the gastrointestinal tract
Gallbladder
A growth industry... with the expanding waist lines in the (Western) world.
Liver
An organ that pathologists now sometimes forget. There are separate articles for the medical liver diseases, liver neoplasms and liver transplantation pathology.
Pancreas
An organ that is occasionally afflicted by cancer. It is primarily seen in large centers where they do ERCPs and Whipples.
Pathology (detail articles)
Inflammatory bowel disease
The bread and butter of gastroenterology and GI pathology.
Gastrointestinal stromal tumour
The most common GI stromal tumour.
Graft-versus-host disease
An uncommon thing that complicates bone marrow transplants.
Eosinophilic enterocolitis
Pneumatosis intestinalis
Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis
See also
References
- ↑ URL: http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/CorePages/Oral/Oral.htm.
- ↑ URL: http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/CorePages/Oral/Images/gitplan.gif.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Mills, Stacey E. (2006). Histology for Pathologists (3rd ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 633. ISBN 9780781762410.