Difference between revisions of "Anemia"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(+normocytic anemia) |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
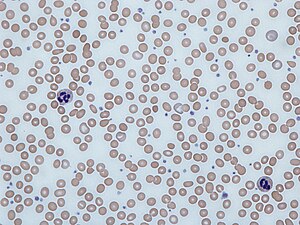
'''Anemia''' is low hemoglobin. | [[Image:Iron_deficiency_anemia_blood_film.jpg|thumb|Blood film in iron deficiency anemia. (WC)]] | ||
'''Anemia''' is an abnormally low hemoglobin. | |||
There is a long list of causes for anemia. Usually, anemia is grouped by RBC cell size, mean corpuscular volume (MCV). | There is a long list of causes for anemia. Usually, anemia is grouped by [[RBC]] cell size, mean corpuscular volume (MCV). | ||
==Classifications== | ==Classifications== | ||
| Line 14: | Line 15: | ||
*Thalassemia. | *Thalassemia. | ||
*Anemia of chronic diesease. | *Anemia of chronic diesease. | ||
*Iron deficiency anemia. | *[[Iron deficiency anemia]]. | ||
*[[Lead toxicity]]. | *[[Lead toxicity]]. | ||
*Sideroblastic anemia. | *Sideroblastic anemia. | ||
| Line 41: | Line 42: | ||
*Bone marrow failure. | *Bone marrow failure. | ||
*[[Renal failure]]. | *[[Renal failure]]. | ||
*Acute hemorrhage. | *Acute hemorrhage. | ||
=Specific types of anemia= | =Specific types of anemia= | ||
Latest revision as of 15:02, 2 May 2022
Anemia is an abnormally low hemoglobin.
There is a long list of causes for anemia. Usually, anemia is grouped by RBC cell size, mean corpuscular volume (MCV).
Classifications
| Anemia | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Macrocytic anemia (MCV>100 fl) | Normocytic anemia (MCV 80–100 fl) | Microcytic anemia (MCV<80 fl) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Microcytic anemia
Mnemonic TAILS:[1]
- Thalassemia.
- Anemia of chronic diesease.
- Iron deficiency anemia.
- Lead toxicity.
- Sideroblastic anemia.
Macrocytic anemia
Mnemonic Few Big RBCs May Lead To Palor:
- Folate deficiency.
- Vitamin B12 deficiency.
- Rx.
- Myelodysplastic syndromes.
- Liver disease (cirrhosis).
- Thyroid disease (hypothyroidism).
- Post-splenectomy.
Normocytic anemia
One DDx of normocytic anemia:[2]
- Acute blood loss.
- Hypersplenism.
- Hemolytic disorders.
- Congenital conditions.
- Hemoglobinopathies, e.g. sickle cell disease.
A cute mnemonic ABBRA:
- Anemia of chronic disease.
- Bone marrow infiltration.
- Bone marrow failure.
- Renal failure.
- Acute hemorrhage.
Specific types of anemia
Pernicious anemia
Main article: Pernicious anemia
Sickle cell anemia
Main article: Sickle cell anemia
References
- ↑ URL: http://www.step2review.com/content/sub_cat.php?cat_id=487__Microcytic_Anemia. Accessed on: 12 May 2011.
- ↑ Brill, JR.; Baumgardner, DJ. (Nov 2000). "Normocytic anemia.". Am Fam Physician 62 (10): 2255-64. PMID 11126852.