Difference between revisions of "Acinic cell carcinoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→IHC) |
|||
| Line 120: | Line 120: | ||
==Molecular== | ==Molecular== | ||
*t(4;9)(q13;q31)<ref name=pmid33959239>{{cite journal |vauthors=Owosho A, Tyler D, Adesina O, Odujoko O, Summersgill K |title=NR4A3 (NOR-1) Immunostaining Shows Better Performance than DOG1 Immunostaining in Acinic Cell Carcinoma of Salivary Gland: a Preliminary Study |journal=J Oral Maxillofac Res |volume=12 |issue=1 |pages=e4 |date=2021 |pmid=33959239 |pmc=8085676 |doi=10.5037/jomr.2021.12104 |url=}}</ref> | *t(4;9)(q13;q31).<ref name=pmid33959239>{{cite journal |vauthors=Owosho A, Tyler D, Adesina O, Odujoko O, Summersgill K |title=NR4A3 (NOR-1) Immunostaining Shows Better Performance than DOG1 Immunostaining in Acinic Cell Carcinoma of Salivary Gland: a Preliminary Study |journal=J Oral Maxillofac Res |volume=12 |issue=1 |pages=e4 |date=2021 |pmid=33959239 |pmc=8085676 |doi=10.5037/jomr.2021.12104 |url=}}</ref> | ||
**''Secretory Ca-binding phosphoprotein'' (SCPP) at 4q13.<ref name=pmid30664630>{{cite journal |vauthors=Haller F, Bieg M, Will R, Körner C, Weichenhan D, Bott A, Ishaque N, Lutsik P, Moskalev EA, Mueller SK, Bähr M, Woerner A, Kaiser B, Scherl C, Haderlein M, Kleinheinz K, Fietkau R, Iro H, Eils R, Hartmann A, Plass C, Wiemann S, Agaimy A |title=Enhancer hijacking activates oncogenic transcription factor NR4A3 in acinic cell carcinomas of the salivary glands |journal=Nat Commun |volume=10 |issue=1 |pages=368 |date=January 2019 |pmid=30664630 |pmc=6341107 |doi=10.1038/s41467-018-08069-x |url=}}</ref> | |||
**''Nuclear Receptor Subfamily 4 Group A Member 3'' (NR4A3) at 9q31.<ref name=pmid30664630/> | |||
==EM== | ==EM== | ||
Revision as of 16:05, 27 October 2021
| Acinic cell carcinoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
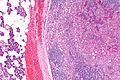
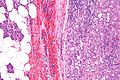
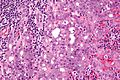
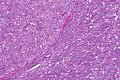
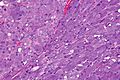
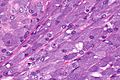
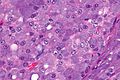
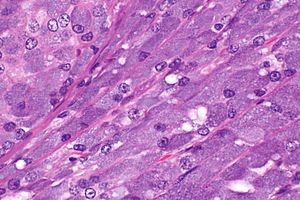 Acinic cell carcinoma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | "acinic cells" (abundant finely vacuolated cytoplasm with basophilic granules, small nuclei with stippled chromatin), scattered "intercalcated duct type cells" (eosinophilic cytoplasm with moderate amount of cytoplasm and bland nuclei), +/-peri-tumoural lymphocytes, +/-glassy extracellular bluish/purple blobs |
| Subtypes | oncocytic variant, clear cell variant, papillary cystic variant |
| LM DDx | oncocytoma of the salivary gland, mucoepidermoid carcinoma, adenocarcinoma NOS, secretory carcinoma of the salivary gland |
| Stains | PAS +ve, PASD +ve |
| IHC | p63 -ve, S-100 -ve |
| EM | zymogen granules |
| Gross | tan or reddish |
| Site | salivary gland - usu. parotid gland |
|
| |
| Signs | salivary gland mass |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Prognosis | good |
Acinic cell carcinoma, abbreviated AcCC, is a rare type of salivary gland cancer. It is also known as acinic cell adenocarcinoma.
It should not to be confused with pancreatic acinar cell carcinoma.
General
- Malignant neoplasm of salivary gland arising from acinic cells.
- The relative prevalence of the neoplasm in the various salivary gland reflects the abundance of acinic cells: parotid gland (~80%) > minor salivary glands (~17%) > submandibular glands (~3%).
- Affects wide age range -- including children.
- Site affect prognosis (most aggressive to least aggressive): submandibular > parotid > minor salivary.
- Good prognosis - in one large cohort:[1]
- ~97% five year survival.
- ~93% 10 year survival.
Gross
- Tan or reddish.
Microscopic
Features:
- Sheets of acinic cells with:
- Abundant finely vacuolated cytoplasm with basophilic granules - key feature.
- Granules may be focal.
- Small nuclei stippled chromatin.
- Abundant finely vacuolated cytoplasm with basophilic granules - key feature.
- Scattered intercalcated duct type cells with:
- Eosinophilic cytoplasm with moderate amount of cytoplasm.
- Bland nuclei with slightly larger than seen in acinic cells.
- +/-Peri-tumoural lymphocytes.
- +/-Glassy extracellular bluish/purple blobs.
Notes:
- Adipose tissue -- present in the salivary glands -- is absent in AcCC.
- May focally resemble thyroid tissue.
- Smaller (characteristic) microvacuoles (unreported in the literature) may be present that have a bubbly appearance and glassy basophilic inclusions.[2]
Memory device:
- AcCC - lots of "C"s - chromatin stipled, cytoplasm generous.
DDx:
- Oncocytoma of the salivary gland.
- Adenocarcinoma not otherwise specified.[3]
- Secretory carcinoma of the salivary gland (previously mammary analogue secretory carcinoma).[4]
Images
Case
Case
www
Grading
General:
- Not prognostic.
- Done to avoid phone calls from clinician.
Factors Weinreb uses:[2]
- Necrosis.
- Nuclear atypia.
- Perineural invasion.
- Mitoses.
- Infiltrative margin.
- Tumour sclerosis.
Subtypes
- Oncocytic variant - rare.
- Clear cell variant - rare.
- Papillary cystic variant.
Stains
- PAS +ve.
- PAS-D +ve.
IHC
- S-100 -ve.
- p63 -ve (30 -ve of 30 cases[5]).
- p63 +ve in mucoepidermoid carcinoma (24 +ve of 24 cases).[5]
- NR4A3 +ve (nuclear) (5 of 6 cases[6]).
There are a bunch of other stains that are touted to be useful (amylase, anti-chymotrypsin, lactoferrin). Weinreb thinks these are not helpful.[2]
Molecular
- t(4;9)(q13;q31).[6]
EM
Sign out
A. Tumour, Left Parotid Gland, Excision: - ACINIC CELL CARCINOMA, see comment. -- Margins clear. -- Please see synoptic report. B. Lymph Nodes, Left - Level 2 & 3, Lymphadenectomy: - Five lymph nodes NEGATIVE for malignancy (0/5). Comment: Immunostains are in keeping with acinic cell carcinoma (mammaglobin, S-100 and p63 are all NEGATIVE). A PAS stain is positive in the tumour.
See also
References
- ↑ Patel, NR.; Sanghvi, S.; Khan, MN.; Husain, Q.; Baredes, S.; Eloy, JA. (Jan 2014). "Demographic trends and disease-specific survival in salivary acinic cell carcinoma: an analysis of 1129 cases.". Laryngoscope 124 (1): 172-8. doi:10.1002/lary.24231. PMID 23754708.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 IW. 11 January 2011.
- ↑ Ihrler, S.; Blasenbreu-Vogt, S.; Sendelhofert, A.; Lang, S.; Zietz, C.; Löhrs, U. (2002). "Differential diagnosis of salivary acinic cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma (NOS). A comparison of (immuno-)histochemical markers.". Pathol Res Pract 198 (12): 777-83. PMID 12608654.
- ↑ Lei, Y.; Chiosea, SI. (Jun 2012). "Re-evaluating historic cohort of salivary acinic cell carcinoma with new diagnostic tools.". Head Neck Pathol 6 (2): 166-70. doi:10.1007/s12105-011-0312-9. PMID 22127547.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Sams, RN.; Gnepp, DR. (Mar 2013). "P63 expression can be used in differential diagnosis of salivary gland acinic cell and mucoepidermoid carcinomas.". Head Neck Pathol 7 (1): 64-8. doi:10.1007/s12105-012-0403-2. PMID 23054955.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "NR4A3 (NOR-1) Immunostaining Shows Better Performance than DOG1 Immunostaining in Acinic Cell Carcinoma of Salivary Gland: a Preliminary Study". J Oral Maxillofac Res 12 (1): e4. 2021. doi:10.5037/jomr.2021.12104. PMC 8085676. PMID 33959239. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8085676/.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "Enhancer hijacking activates oncogenic transcription factor NR4A3 in acinic cell carcinomas of the salivary glands". Nat Commun 10 (1): 368. January 2019. doi:10.1038/s41467-018-08069-x. PMC 6341107. PMID 30664630. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6341107/.
- ↑ Sun, Y.; Wasserman, PG. (Feb 2004). "Acinar cell carcinoma arising in the stomach: a case report with literature review.". Hum Pathol 35 (2): 263-5. PMID 14991547.