Difference between revisions of "Renal failure"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(create) |
(+image) |
||
| (11 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
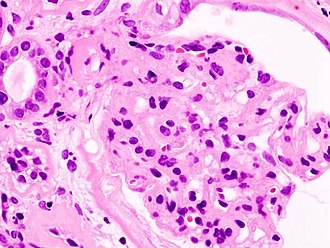
[[Image:Diabetic glomerulosclerosis (1) HE.jpg|thumb|right|[[Nodular glomerulosclerosis]] in diabetes, a common cause of chronic renal failure. [[H&E stain]]. (WC/KGH)]] | |||
'''Renal failure''', also '''kidney failure''', is dysfunction of the kidneys. | '''Renal failure''', also '''kidney failure''', is dysfunction of the kidneys. | ||
It can be subdivided in a number of different ways | It can be subdivided in a number of different ways. | ||
==Acutity== | ==Acutity== | ||
*Chronic renal failure. | *Acute kidney injury (abbreviated ''AKI'') - previously ''acute renal failure'' (abbreviated ''ARF''). | ||
*Acute renal failure. | *Chronic renal failure (CRF). | ||
===Acute kidney injury=== | |||
*[[Acute tubular necrosis]]. | |||
*Acute cardiac failure, e.g. [[myocardial infarction]]. | |||
*[[Cholesterol embolism]].<ref>{{cite journal |author=Saric M, Kronzon I |title=Cholesterol embolization syndrome |journal=Curr. Opin. Cardiol. |volume=26 |issue=6 |pages=472–9 |year=2011 |month=November |pmid=21993354 |doi=10.1097/HCO.0b013e32834b7fdd |url=}}</ref> | |||
*[[Hepatorenal syndrome]]. | |||
===Chronic renal failure=== | |||
*[[Diabetic nephropathy]] ([[diabetes mellitus]]). | |||
*[[IgA nephropathy]]. | |||
*[[Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease]]. | |||
*[[Lupus nephritis]] ([[systemic lupus erythematosus]]). | |||
*[[Wegener's granulomatosis]]. | |||
*Chronic cardiac insufficiency ([[congestive heart failure]]). | |||
Note: | |||
*The cause of [[end-stage renal disease]] (like end-stage liver disease) may be difficult to determine. | |||
==Anatomical cause== | ==Anatomical cause== | ||
''Renal failure 101'': | |||
*Pre-renal. | *Pre-renal. | ||
*Renal. | *Renal. | ||
*Post-renal. | *Post-renal. | ||
===Pre-renal=== | |||
*Hypotension due to blood loss (e.g. [[blunt force trauma]], [[sharp force trauma]], [[gunshot wound]]). | |||
*Reduced cardiac output, e.g. [[myocardial infarction]]. | |||
*Renal artery stenosis. | |||
===Renal=== | |||
*[[Diabetic nephropathy]]. | |||
*[[Lupus nephritis]]. | |||
===Post-renal=== | |||
*[[Nodular hyperplasia of the prostate]]. | |||
*Obstruction due to abdominal malignancy. | |||
*Posterior urethral valves. | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
*[[Medical renal disease]]. | *[[Medical renal disease]]. | ||
*[[End-stage kidney]]. | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|1}} | |||
[[Category: | [[Category:Genitourinary pathology]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:07, 31 December 2018

Nodular glomerulosclerosis in diabetes, a common cause of chronic renal failure. H&E stain. (WC/KGH)
Renal failure, also kidney failure, is dysfunction of the kidneys.
It can be subdivided in a number of different ways.
Acutity
- Acute kidney injury (abbreviated AKI) - previously acute renal failure (abbreviated ARF).
- Chronic renal failure (CRF).
Acute kidney injury
- Acute tubular necrosis.
- Acute cardiac failure, e.g. myocardial infarction.
- Cholesterol embolism.[1]
- Hepatorenal syndrome.
Chronic renal failure
- Diabetic nephropathy (diabetes mellitus).
- IgA nephropathy.
- Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.
- Lupus nephritis (systemic lupus erythematosus).
- Wegener's granulomatosis.
- Chronic cardiac insufficiency (congestive heart failure).
Note:
- The cause of end-stage renal disease (like end-stage liver disease) may be difficult to determine.
Anatomical cause
Renal failure 101:
- Pre-renal.
- Renal.
- Post-renal.
Pre-renal
- Hypotension due to blood loss (e.g. blunt force trauma, sharp force trauma, gunshot wound).
- Reduced cardiac output, e.g. myocardial infarction.
- Renal artery stenosis.
Renal
Post-renal
- Nodular hyperplasia of the prostate.
- Obstruction due to abdominal malignancy.
- Posterior urethral valves.
See also
References
- ↑ Saric M, Kronzon I (November 2011). "Cholesterol embolization syndrome". Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 26 (6): 472–9. doi:10.1097/HCO.0b013e32834b7fdd. PMID 21993354.