Difference between revisions of "Vasculitides"
(→Wegener's granulomatosis: more) |
|||
| (102 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
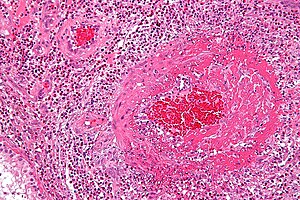
This article deals with the '''vasculitides''' (singular ''vasculitis''). | [[Image:Churg-Strauss syndrome - high mag.jpg|thumb|right|[[Micrograph]] showing a vasculitis. [[H&E stain]].]] | ||
This article deals with the '''vasculitides''' (singular ''vasculitis''). Vascular disease that is not vasculitides is covered in the article ''[[vascular disease]]''. | |||
The histology of normal vessels is dealt with in ''[[Vascular_disease#Normal_blood_vessels|normal blood vessels]]''. | |||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
===Most common<ref> | ===Most common<ref>{{Ref TN2005 |RH3}}</ref>=== | ||
*Polyarteritis nodosa (PAN). | *Polyarteritis nodosa (PAN). | ||
*Microscopic polyangiitis. | *Microscopic polyangiitis. | ||
*Wegener's granulomatosis. | *Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener's granulomatosis). | ||
*Predominantly cutaneous vasculitis. | *Predominantly cutaneous vasculitis. | ||
*Giant cell arteritis (GCA). | *Giant cell arteritis (GCA). | ||
| Line 11: | Line 14: | ||
===Grouping by size=== | ===Grouping by size=== | ||
====Small vessel vasculitides==== | ====Small vessel vasculitides==== | ||
=====Definition===== | |||
Small vessel vasculitis = vasculitis of vessels smaller than arteries; affects arterioles, venules, and capillaries.<ref name=pmid9366584>{{cite journal |author=Jennette JC, Falk RJ |title=Small-vessel vasculitis |journal=N. Engl. J. Med. |volume=337 |issue=21 |pages=1512–23 |year=1997 |month=November |pmid=9366584 |doi=10.1056/NEJM199711203372106 |url=http://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJM199711203372106}}</ref> | |||
*What is an arteriole? | |||
**There is no histologic definition according to ''Sternberg's Histology for Pathologists''; however, a diameter of <100 micrometers is suggested as a definition.<ref name=Ref_H4P2>{{Ref H4P2|769}}</ref> | |||
=====Types===== | |||
*Predominantly cutaneous vasculitis. | *Predominantly cutaneous vasculitis. | ||
*Henoch-Schoenlein purpura. | *[[Henoch-Schoenlein purpura]]. | ||
*Essential cryoglobulinemic vasculitis. | *Essential cryoglobulinemic vasculitis. | ||
*ANCA-associated: | *ANCA-associated: | ||
**Wegener's granulomatosis | **[[Granulomatosis with polyangiitis]] (Wegener's granulomatosis) - c-ANCA > p-ANCA. | ||
**Churg-Strauss syndrome | **[[Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis]] (Churg-Strauss syndrome) - 50% ANCA +ve. | ||
**Microscopic polyangiitis | **[[Microscopic polyangiitis]] - usually p-ANCA. | ||
Notes: | Notes: | ||
*ANCA = anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies. | *ANCA = anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies. | ||
**The terminology has changed as more knowledge has been gained: | |||
***MPO-ANCA = p-ANCA. | |||
***PR3-ANCA = c-ANCA. | |||
====Medium vessel vasculitides<ref name=Ref_PBoD8_512>{{Ref PBoD8|512}}</ref>==== | |||
*[[Polyarteritis nodosa]] (PAN). | |||
*[[Kawasaki disease]]. | |||
====Large vessel vasculitides<ref name=Ref_PBoD8_512>{{Ref PBoD8|512}}</ref>==== | |||
*[[Giant cell arteritis]] (AKA ''temporal arteritis''). | |||
*[[Takayasu's arteritis]]. | |||
===Grouping by hypersensitivity=== | |||
Cell-mediated [[hypersensitivity]]:<ref name=indian_guy>URL: [http://dermind.tripod.com/vasculitis.htm http://dermind.tripod.com/vasculitis.htm]. Accessed on: 30 April 2012.</ref> | |||
*Giant cell arteritis. | |||
*Takayasu arteritis. | |||
*Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Churg-Strauss disease). | |||
*Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener’s granulomatosis). | |||
Note: | |||
*All have granulomas. | |||
[[Immune complex mediated hypersensitivity]]:<ref name=indian_guy>URL: [http://dermind.tripod.com/vasculitis.htm http://dermind.tripod.com/vasculitis.htm]. Accessed on: 30 April 2012.</ref> | |||
*Polyarteritis nodosa. | |||
*Microscopic polyangiitis.{{fact}} | |||
*Leukocytoclastic vasculitis.{{fact}} | |||
**Henoch-Schonlein purpura. | |||
==Pathologist's role in the diagnosis of vasculitis== | |||
===General=== | |||
*Pathologists often cannot, based on morphology alone, arrive at the definitive diagnosis. | |||
*The presentation & distribution are more characteristic than the pathology.<ref>URL: [http://www.pathology.ubc.ca/path425/PrincipleofPathophysiology/CirculatoryDisorders/SystemicVasculitisDrBWalker.doc http://www.pathology.ubc.ca/path425/PrincipleofPathophysiology/CirculatoryDisorders/SystemicVasculitisDrBWalker.doc]. Accessed on: 26 November 2010.</ref><ref>URL: [http://www.icapture.ubc.ca/who/who_bios_david_walker.shtml http://www.icapture.ubc.ca/who/who_bios_david_walker.shtml]. Accessed on: 26 November 2010.</ref> | |||
===Microscopic=== | |||
Features - both #1 and #2 are required:<ref name=pmid19946711>{{Cite journal | last1 = Dillon | first1 = MJ. | last2 = Eleftheriou | first2 = D. | last3 = Brogan | first3 = PA. | title = Medium-size-vessel vasculitis. | journal = Pediatr Nephrol | volume = 25 | issue = 9 | pages = 1641-52 | month = Sep | year = 2010 | doi = 10.1007/s00467-009-1336-1 | PMID = 19946711 |PMC = 2908435 | URL = http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2908435/}}</ref> | |||
#Inflammatory cells within the blood vessel wall. | |||
#Vessel injury: | |||
#*Frank fibrinoid [[necrosis]] ''or'' nuclear dust: | |||
#**Fibrinoid necrosis = anucleate amorphous intensely eosinophilic material. | |||
#***Amorphous = no definite form.<ref>URL: [http://dictionary.weather.net/dictionary/amorphous http://dictionary.weather.net/dictionary/amorphous]. Accessed on: 26 November 2010.</ref> | |||
#**"Nuclear dust" = punctate hyperchromatic material ~ 1 micrometre. | |||
*+/-[[RBC extravasation]] - common. | |||
Notes: | |||
*Involvement is usually patchy. | |||
**If there is an inkling of vasculitis... it should prompt [[deeper cuts]]. | |||
====Features to consider==== | |||
#Presence of [[granuloma]]s. | |||
#Type inflammatory cells, i.e. eosinophils, mononuclear cells. | |||
#Size of vessels involved. | |||
#Extent of involvement. | |||
#Acuity (acute vs. subacute vs. chronic vs. acute on chronic). | |||
#*Chronic = thick fibrotic appearing vessels with a small lumen. | |||
====Vasculitis versus neuropathy==== | |||
{| class="wikitable sortable" | |||
! Domain | |||
! Vasculitis | |||
! Neuropathy | |||
|- | |||
|Clinical | |||
|pain, diffuse/<br>patchy distribution | |||
|focal/isolated | |||
|- | |||
|Pathological<br>(inflammatory cells) | |||
|epineurium | |||
|endoneurium | |||
|} | |||
=Small vessel vasculitides= | |||
The follow section has information specific to the individual types of small vessel vasculitis. | |||
==Small vessel leukocytoclastic vasculitis== | |||
*[[AKA]] ''leukocytoclastic vasculitis'', abbreviated ''LCV''. | |||
{{Main|Small vessel leukocytoclastic vasculitis}} | |||
==== | ==Microscopic polyangiitis== | ||
* | ===General=== | ||
*Classically MPO-ANCA (p-ANCA) +ve. | |||
== | ===Microscopic=== | ||
*[ | Features - small-sized vessels with: | ||
*Inflammatory cells (neutrophils, lymphocytes) within the tunica media. | |||
*Fibroid necrosis: dead vessel wall - pink anucleate stuff, nuclear debris (black specks of nuclear material). | |||
*No granulomas. | |||
Images: | |||
*[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case260/micro.html Microscopic polyangiitis - several images (upmc.edu)]. | |||
==Granulomatosis with polyangiitis== | |||
:Previously known as ''Wegener granulomatosis''. | |||
{{Main|Granulomatosis with polyangiitis}} | |||
=== | ==Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis== | ||
:Previously known as ''Churg-Strauss syndrome'' and ''Churg-Strauss disease''. | |||
{{Main|Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis}} | |||
=Medium vessel vasculitides= | |||
The follow section has information specific to the individual types of medium vessel vasculitis. | |||
==Kawasaki disease== | |||
* | ===General=== | ||
*Medium vessel disease. | |||
*Classically afflicts the coronary arteries of children - usu. less than 5 years old. | |||
**May lead to coronary artery aneurysms.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Taubert | first1 = KA. | last2 = Shulman | first2 = ST. | title = Kawasaki disease. | journal = Am Fam Physician | volume = 59 | issue = 11 | pages = 3093-102, 3107-8 | month = Jun | year = 1999 | doi = | PMID = 10392592 |URL = http://www.aafp.org/afp/1999/0601/p3093.html}}</ref> | |||
=== | Clinical features - mnemonic ''Warm CREAM'':<ref>URL: [http://www.medicalmnemonics.com/cgi-bin/return_browse.cfm?&system=Other%2FMiscellaneous&discipline=Pathology&browse=1 http://www.medicalmnemonics.com/cgi-bin/return_browse.cfm?&system=Other%2FMiscellaneous&discipline=Pathology&browse=1]. Accessed on: 14 January 2012.</ref> | ||
*'''Warm''' = fever. | |||
* | *'''C'''onjunctivitis, non-exudative. | ||
*'''R'''ash, polymorphous. | |||
*'''E'''rythema or edema of hands and feet. | |||
*'''A'''denopathy, usu. cervical and unilateral. | |||
*'''M'''ucosal manifestations - strawberry tongue, cracked lips. | |||
Treatment: | |||
*High dose IV aspirin. | |||
* | |||
===Microscopic=== | ===Microscopic=== | ||
Features: | Features: | ||
* | *Medium-sized vessels with intramural inflammatory cells. | ||
* | *Vessel destruction, e.g. [[fibrinoid necrosis]] (very pink anucleate arterial wall). | ||
==Polyarteritis nodosa== | ==Polyarteritis nodosa== | ||
*Abbreviated ''PAN'' | *Abbreviated ''PAN''. | ||
===General=== | |||
*Involves small and medium sized vessels. | *Involves small and medium sized vessels. | ||
*Often - renal vessels, mesenteric vessels.<ref>Klatt. | *Often - renal vessels, mesenteric vessels.<ref name=Ref_Klatt14>{{Ref Klatt|14}}</ref> | ||
*Strong association with ''hepatitis B'' (see [[medical liver diseases]]); ~1/3 of patients with PAN have HBV. | **Classically, [[lung]] involvement by PAN is considered to be rare, though this may not be entirely true.<ref name=pmid8100552>{{Cite journal | last1 = Matsumoto | first1 = T. | last2 = Homma | first2 = S. | last3 = Okada | first3 = M. | last4 = Kuwabara | first4 = N. | last5 = Kira | first5 = S. | last6 = Hoshi | first6 = T. | last7 = Uekusa | first7 = T. | last8 = Saiki | first8 = S. | title = The lung in polyarteritis nodosa: a pathologic study of 10 cases. | journal = Hum Pathol | volume = 24 | issue = 7 | pages = 717-24 | month = Jul | year = 1993 | doi = | PMID = 8100552 }}</ref> | ||
*Strong association with ''[[hepatitis B]]'' (see [[medical liver diseases]]); ~1/3 of patients with PAN have HBV. | |||
Serology: | Serology: | ||
| Line 68: | Line 165: | ||
===Microscopic=== | ===Microscopic=== | ||
Features: | Features - medium-sized vessels with: | ||
*Inflammatory cells (neutrophils, lymphocytes) within the tunica media. | *Inflammatory cells (neutrophils, lymphocytes) within the tunica media. | ||
* | *Fibroid necrosis: dead vessel wall - pink anucleate stuff, nuclear debris (black specks of nuclear material). | ||
**Usu. focal (wall) involvement; classically leads to berry microaneurysms - ergo the name ''polyarteritis nodosa''. | |||
Image: | |||
*[http://www.immunologyclinic.com/figure.asp?chap=10&fig=14-05d PAN (immunologyclinic.com)]. | |||
=Large vessel vasculitides= | |||
The follow section has information specific to the individual types of large vessel vasculitis. | |||
==Giant cell arteritis== | |||
:''Temporal artery'' redirects here. | |||
*Abbreviated ''GCA''. | |||
*[[AKA]] ''temporal arteritis''. | |||
{{Main|Giant cell arteritis}} | |||
==Takayasu arteritis== | |||
===General=== | |||
Features:<ref name=Ref_PBoD538>{{Ref PBoD|538}}</ref> | |||
*Disease of medium/large arteries. | |||
**Classically involves the aortic arch - leading to decreased pulses in the upper limbs. | |||
*Typically in patients <40 yrs old. | |||
*Usually Asian. | |||
Pathogenesis: | |||
*Cell-mediated hypersensitivity.<ref name=pmid21855656>{{Cite journal | last1 = Arnaud | first1 = L. | last2 = Haroche | first2 = J. | last3 = Mathian | first3 = A. | last4 = Gorochov | first4 = G. | last5 = Amoura | first5 = Z. | title = Pathogenesis of Takayasu's arteritis: a 2011 update. | journal = Autoimmun Rev | volume = 11 | issue = 1 | pages = 61-7 | month = Nov | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1016/j.autrev.2011.08.001 | PMID = 21855656 }}</ref><ref>URL: [http://dermind.tripod.com/vasculitis.htm http://dermind.tripod.com/vasculitis.htm]. Accessed on: 30 April 2012.</ref>{{fact}} | |||
== | ===Gross=== | ||
Features:<ref name=Ref_PBoD538>{{Ref PBoD|538}}</ref> | |||
*Classically involves the aortic arch. | |||
* | |||
===Microscopic=== | |||
Features:<ref name=Ref_PBoD538>{{Ref PBoD|538}}</ref> | |||
*Adventitial mononuclear infiltrate with perivascular cuffing of the vasa vasorum. | |||
*Mononuclear inflammation in media. | |||
*Granulomas, [[giant cells]]. | |||
*+/-Patchy necrosis of media. | |||
=Other= | |||
==Aortitis== | |||
===General=== | |||
*Uncommon. | |||
===Gross=== | |||
Features: | |||
*Tree bark-like appearance. | |||
Notes: | Notes: | ||
* | *Several blocks should be submitted. | ||
Image: | |||
*[http://www.ijpmonline.org/viewimage.asp?img=IndianJPatholMicrobiol_2010_53_4_624_72002_f4.jpg Tree barking (ijpmonline.org)].<ref name=pmid21045381>{{Cite journal | last1 = Vaideeswar | first1 = P. | title = Syphilitic aortitis: rearing of the ugly head. | journal = Indian J Pathol Microbiol | volume = 53 | issue = 4 | pages = 624-7 | month = | year = | doi = 10.4103/0377-4929.72002 | PMID = 21045381 }}</ref> | |||
===Microscopic=== | ===Microscopic=== | ||
Features: | Features: | ||
* | *Inflammatory cells. | ||
Subclassification: | |||
*Granulomatous. | |||
*Lymphoplasmacytic pattern. | |||
*Mixed inflammatory. | |||
*Suppurative. | |||
==LAMP-2 vasculitis== | |||
*Associated with pauci-immune necrotizing and crescentic glomerulonephritis.<ref name=pmid19384321>{{cite journal |author=Bosch X, Mirapeix E |title=Vasculitis syndromes: LAMP-2 illuminates pathogenesis of ANCA glomerulonephritis |journal=Nat Rev Nephrol |volume=5 |issue=5 |pages=247–9 |year=2009 |month=May |pmid=19384321 |doi=10.1038/nrneph.2009.51 |url=http://www.nature.com/ki/journal/v76/n1/abs/ki2009123a.html}}</ref> | |||
*Grouped with the ANCA-associated vasculitides.<ref name=pmid19646356>{{cite journal |author=Chen M, Kallenberg CG |title=New advances in the pathogenesis of ANCA-associated vasculitides |journal=Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. |volume=27 |issue=1 Suppl 52 |pages=S108–14 |year=2009 |pmid=19646356 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | |||
=See also= | |||
*[[Cardiovascular pathology]]. | |||
*[[Vascular disease]] - covers atherosclerosis, medial cystic degeneration. | |||
*[[Inflammatory skin disorders]]. | |||
*[[Umbilical cord vasculitis]]. | |||
=References= | |||
{{reflist|2}} | {{reflist|2}} | ||
[[Category:Cardiovascular pathology]] | [[Category:Cardiovascular pathology]] | ||
[[Category:Vasculitides]] | |||
Latest revision as of 11:42, 25 November 2016
This article deals with the vasculitides (singular vasculitis). Vascular disease that is not vasculitides is covered in the article vascular disease.
The histology of normal vessels is dealt with in normal blood vessels.
Overview
Most common[1]
- Polyarteritis nodosa (PAN).
- Microscopic polyangiitis.
- Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener's granulomatosis).
- Predominantly cutaneous vasculitis.
- Giant cell arteritis (GCA).
Grouping by size
Small vessel vasculitides
Definition
Small vessel vasculitis = vasculitis of vessels smaller than arteries; affects arterioles, venules, and capillaries.[2]
- What is an arteriole?
- There is no histologic definition according to Sternberg's Histology for Pathologists; however, a diameter of <100 micrometers is suggested as a definition.[3]
Types
- Predominantly cutaneous vasculitis.
- Henoch-Schoenlein purpura.
- Essential cryoglobulinemic vasculitis.
- ANCA-associated:
- Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener's granulomatosis) - c-ANCA > p-ANCA.
- Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Churg-Strauss syndrome) - 50% ANCA +ve.
- Microscopic polyangiitis - usually p-ANCA.
Notes:
- ANCA = anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies.
- The terminology has changed as more knowledge has been gained:
- MPO-ANCA = p-ANCA.
- PR3-ANCA = c-ANCA.
- The terminology has changed as more knowledge has been gained:
Medium vessel vasculitides[4]
- Polyarteritis nodosa (PAN).
- Kawasaki disease.
Large vessel vasculitides[4]
- Giant cell arteritis (AKA temporal arteritis).
- Takayasu's arteritis.
Grouping by hypersensitivity
Cell-mediated hypersensitivity:[5]
- Giant cell arteritis.
- Takayasu arteritis.
- Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Churg-Strauss disease).
- Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener’s granulomatosis).
Note:
- All have granulomas.
Immune complex mediated hypersensitivity:[5]
- Polyarteritis nodosa.
- Microscopic polyangiitis.[citation needed]
- Leukocytoclastic vasculitis.[citation needed]
- Henoch-Schonlein purpura.
Pathologist's role in the diagnosis of vasculitis
General
- Pathologists often cannot, based on morphology alone, arrive at the definitive diagnosis.
- The presentation & distribution are more characteristic than the pathology.[6][7]
Microscopic
Features - both #1 and #2 are required:[8]
- Inflammatory cells within the blood vessel wall.
- Vessel injury:
- +/-RBC extravasation - common.
Notes:
- Involvement is usually patchy.
- If there is an inkling of vasculitis... it should prompt deeper cuts.
Features to consider
- Presence of granulomas.
- Type inflammatory cells, i.e. eosinophils, mononuclear cells.
- Size of vessels involved.
- Extent of involvement.
- Acuity (acute vs. subacute vs. chronic vs. acute on chronic).
- Chronic = thick fibrotic appearing vessels with a small lumen.
Vasculitis versus neuropathy
| Domain | Vasculitis | Neuropathy |
|---|---|---|
| Clinical | pain, diffuse/ patchy distribution |
focal/isolated |
| Pathological (inflammatory cells) |
epineurium | endoneurium |
Small vessel vasculitides
The follow section has information specific to the individual types of small vessel vasculitis.
Small vessel leukocytoclastic vasculitis
- AKA leukocytoclastic vasculitis, abbreviated LCV.
Microscopic polyangiitis
General
- Classically MPO-ANCA (p-ANCA) +ve.
Microscopic
Features - small-sized vessels with:
- Inflammatory cells (neutrophils, lymphocytes) within the tunica media.
- Fibroid necrosis: dead vessel wall - pink anucleate stuff, nuclear debris (black specks of nuclear material).
- No granulomas.
Images:
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis
- Previously known as Wegener granulomatosis.
Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis
- Previously known as Churg-Strauss syndrome and Churg-Strauss disease.
Medium vessel vasculitides
The follow section has information specific to the individual types of medium vessel vasculitis.
Kawasaki disease
General
- Medium vessel disease.
- Classically afflicts the coronary arteries of children - usu. less than 5 years old.
- May lead to coronary artery aneurysms.[10]
Clinical features - mnemonic Warm CREAM:[11]
- Warm = fever.
- Conjunctivitis, non-exudative.
- Rash, polymorphous.
- Erythema or edema of hands and feet.
- Adenopathy, usu. cervical and unilateral.
- Mucosal manifestations - strawberry tongue, cracked lips.
Treatment:
- High dose IV aspirin.
Microscopic
Features:
- Medium-sized vessels with intramural inflammatory cells.
- Vessel destruction, e.g. fibrinoid necrosis (very pink anucleate arterial wall).
Polyarteritis nodosa
- Abbreviated PAN.
General
- Involves small and medium sized vessels.
- Often - renal vessels, mesenteric vessels.[12]
- Strong association with hepatitis B (see medical liver diseases); ~1/3 of patients with PAN have HBV.
Serology:
- ANCA is usually negative.
Microscopic
Features - medium-sized vessels with:
- Inflammatory cells (neutrophils, lymphocytes) within the tunica media.
- Fibroid necrosis: dead vessel wall - pink anucleate stuff, nuclear debris (black specks of nuclear material).
- Usu. focal (wall) involvement; classically leads to berry microaneurysms - ergo the name polyarteritis nodosa.
Image:
Large vessel vasculitides
The follow section has information specific to the individual types of large vessel vasculitis.
Giant cell arteritis
- Temporal artery redirects here.
- Abbreviated GCA.
- AKA temporal arteritis.
Takayasu arteritis
General
Features:[14]
- Disease of medium/large arteries.
- Classically involves the aortic arch - leading to decreased pulses in the upper limbs.
- Typically in patients <40 yrs old.
- Usually Asian.
Pathogenesis:
- Cell-mediated hypersensitivity.[15][16][citation needed]
Gross
Features:[14]
- Classically involves the aortic arch.
Microscopic
Features:[14]
- Adventitial mononuclear infiltrate with perivascular cuffing of the vasa vasorum.
- Mononuclear inflammation in media.
- Granulomas, giant cells.
- +/-Patchy necrosis of media.
Other
Aortitis
General
- Uncommon.
Gross
Features:
- Tree bark-like appearance.
Notes:
- Several blocks should be submitted.
Image:
Microscopic
Features:
- Inflammatory cells.
Subclassification:
- Granulomatous.
- Lymphoplasmacytic pattern.
- Mixed inflammatory.
- Suppurative.
LAMP-2 vasculitis
- Associated with pauci-immune necrotizing and crescentic glomerulonephritis.[18]
- Grouped with the ANCA-associated vasculitides.[19]
See also
- Cardiovascular pathology.
- Vascular disease - covers atherosclerosis, medial cystic degeneration.
- Inflammatory skin disorders.
- Umbilical cord vasculitis.
References
- ↑ Yeung, J.C.; Leonard, Blair J. N. (2005). The Toronto Notes 2005 - Review for the MCCQE and Comprehensive Medical Reference (2005 ed.). The Toronto Notes Inc. for Medical Students Inc.. pp. RH3. ISBN 978-0968592854.
- ↑ Jennette JC, Falk RJ (November 1997). "Small-vessel vasculitis". N. Engl. J. Med. 337 (21): 1512–23. doi:10.1056/NEJM199711203372106. PMID 9366584. http://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJM199711203372106.
- ↑ Sternberg, Stephen S. (1997). Histology for Pathologists (2nd ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 769. ISBN 978-0397517183.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Kumar, Vinay; Abbas, Abul K.; Fausto, Nelson; Aster, Jon (2009). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 512. ISBN 978-1416031215.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 URL: http://dermind.tripod.com/vasculitis.htm. Accessed on: 30 April 2012.
- ↑ URL: http://www.pathology.ubc.ca/path425/PrincipleofPathophysiology/CirculatoryDisorders/SystemicVasculitisDrBWalker.doc. Accessed on: 26 November 2010.
- ↑ URL: http://www.icapture.ubc.ca/who/who_bios_david_walker.shtml. Accessed on: 26 November 2010.
- ↑ Dillon, MJ.; Eleftheriou, D.; Brogan, PA. (Sep 2010). "Medium-size-vessel vasculitis.". Pediatr Nephrol 25 (9): 1641-52. doi:10.1007/s00467-009-1336-1. PMC 2908435. PMID 19946711. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2908435/.
- ↑ URL: http://dictionary.weather.net/dictionary/amorphous. Accessed on: 26 November 2010.
- ↑ Taubert, KA.; Shulman, ST. (Jun 1999). "Kawasaki disease.". Am Fam Physician 59 (11): 3093-102, 3107-8. PMID 10392592.
- ↑ URL: http://www.medicalmnemonics.com/cgi-bin/return_browse.cfm?&system=Other%2FMiscellaneous&discipline=Pathology&browse=1. Accessed on: 14 January 2012.
- ↑ Klatt, Edward C. (2006). Robbins and Cotran Atlas of Pathology (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 14. ISBN 978-1416002741.
- ↑ Matsumoto, T.; Homma, S.; Okada, M.; Kuwabara, N.; Kira, S.; Hoshi, T.; Uekusa, T.; Saiki, S. (Jul 1993). "The lung in polyarteritis nodosa: a pathologic study of 10 cases.". Hum Pathol 24 (7): 717-24. PMID 8100552.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 14.2 Cotran, Ramzi S.; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Nelso Fausto; Robbins, Stanley L.; Abbas, Abul K. (2005). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (7th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. pp. 538. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.
- ↑ Arnaud, L.; Haroche, J.; Mathian, A.; Gorochov, G.; Amoura, Z. (Nov 2011). "Pathogenesis of Takayasu's arteritis: a 2011 update.". Autoimmun Rev 11 (1): 61-7. doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2011.08.001. PMID 21855656.
- ↑ URL: http://dermind.tripod.com/vasculitis.htm. Accessed on: 30 April 2012.
- ↑ Vaideeswar, P.. "Syphilitic aortitis: rearing of the ugly head.". Indian J Pathol Microbiol 53 (4): 624-7. doi:10.4103/0377-4929.72002. PMID 21045381.
- ↑ Bosch X, Mirapeix E (May 2009). "Vasculitis syndromes: LAMP-2 illuminates pathogenesis of ANCA glomerulonephritis". Nat Rev Nephrol 5 (5): 247–9. doi:10.1038/nrneph.2009.51. PMID 19384321. http://www.nature.com/ki/journal/v76/n1/abs/ki2009123a.html.
- ↑ Chen M, Kallenberg CG (2009). "New advances in the pathogenesis of ANCA-associated vasculitides". Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 27 (1 Suppl 52): S108–14. PMID 19646356.