Difference between revisions of "Amebiasis"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→Stains) |
|||
| (11 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ Infobox diagnosis | |||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | |||
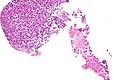
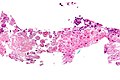
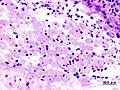
| Image = Amebiasis - very high mag.jpg | |||
| Width = | |||
| Caption = Amebiasis. [[H&E stain]]. | |||
| Synonyms = | |||
| Micro = entamoeba histolytica: round/ovoid eosinophilic bodies ~ 40-60 micrometers in maximal dimension; found in bowel lumen, usu. ingest (whole) [[red blood cell]]s | |||
| Subtypes = | |||
| LMDDx = [[fecal material]], necroinflammatory debris | |||
| Stains = | |||
| IHC = | |||
| EM = | |||
| Molecular = PCR testing | |||
| IF = | |||
| Gross = | |||
| Grossing = | |||
| Site = [[colon]] | |||
| Assdx = +/-[[liver abscess]] | |||
| Syndromes = | |||
| Clinicalhx = | |||
| Signs = diarrhea, blood per rectum | |||
| Symptoms = | |||
| Prevalence = uncommon | |||
| Bloodwork = | |||
| Rads = | |||
| Endoscopy = [[colitis]], mass lesion, [[granulation tissue]]-like | |||
| Prognosis = benign | |||
| Other = | |||
| ClinDDx = [[colorectal carcinoma]], [[colitis]], [[granulation tissue]] | |||
| Tx = | |||
}} | |||
'''Amebiasis''', also be spelled '''amoebiasis''', is an infectious disease, caused by the protozoan ''Entamoeba histolytica''. | '''Amebiasis''', also be spelled '''amoebiasis''', is an infectious disease, caused by the protozoan ''Entamoeba histolytica''. | ||
| Line 13: | Line 44: | ||
Features:<ref name=pmid8255341>{{Cite journal | last1 = Stuiver | first1 = PC. | last2 = Visser | first2 = LG. | title = [Ameboma of the large intestine and rectum]. | journal = Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd | volume = 137 | issue = 45 | pages = 2328-31 | month = Nov | year = 1993 | doi = | PMID = 8255341 }}</ref> | Features:<ref name=pmid8255341>{{Cite journal | last1 = Stuiver | first1 = PC. | last2 = Visser | first2 = LG. | title = [Ameboma of the large intestine and rectum]. | journal = Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd | volume = 137 | issue = 45 | pages = 2328-31 | month = Nov | year = 1993 | doi = | PMID = 8255341 }}</ref> | ||
*+/-Mass. | *+/-Mass. | ||
**May mimic carcinoma.<ref name=pmid12750955>{{Cite journal | last1 = Ooi | first1 = BS. | last2 = Seow-Choen | first2 = F. | title = Endoscopic view of rectal amebiasis mimicking a carcinoma. | journal = Tech Coloproctol | volume = 7 | issue = 1 | pages = 51-3 | month = Apr | year = 2003 | doi = 10.1007/s101510300008 | PMID = 12750955 }}</ref> | |||
*+/-[[Granulation tissue]]-like appearance. | *+/-[[Granulation tissue]]-like appearance. | ||
| Line 27: | Line 59: | ||
Image:Amoebic_dysentery_in_colon_biopsy_%281%29.jpg | Amebiasis (WC) | Image:Amoebic_dysentery_in_colon_biopsy_%281%29.jpg | Amebiasis (WC) | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==Stains== | |||
*Iron-hematoxylin stain - black.<ref name=pimd22523839>{{Cite journal | last1 = Chacín-Bonilla | first1 = L. | title = [Microscopic diagnosis of amebiasis: an obsolete method but necessary in the developing world]. | journal = Invest Clin | volume = 52 | issue = 4 | pages = 291-4 | month = Dec | year = 2011 | doi = | PMID = 22523839 }}</ref><ref>URL: [http://www.histopathology-india.net/amco.htm http://www.histopathology-india.net/amco.htm]. Accessed on: 29 June 2016.</ref> | |||
*Trichrome stain.<ref name=pmid2454958>{{Cite journal | last1 = Shetty | first1 = N. | last2 = Prabhu | first2 = T. | title = Evaluation of faecal preservation and staining methods in the diagnosis of acute amoebiasis and giardiasis. | journal = J Clin Pathol | volume = 41 | issue = 6 | pages = 694-9 | month = Jun | year = 1988 | doi = | PMID = 2454958 }}</ref><ref>URL: [http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/212029-workup http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/212029-workup]. Accessed on: 29 June 2016.</ref> | |||
==IHC== | |||
*Entamoeba histolytica +ve.<ref name=pmid1283004>{{Cite journal | last1 = Prasad | first1 = R. | last2 = Tola | first2 = M. | last3 = Bhattacharya | first3 = S. | last4 = Sharma | first4 = MP. | last5 = Bhattacharya | first5 = A. | title = Recognition of Entamoeba histolytica lipophosphoglycan by a strain-specific monoclonal antibody and human immune sera. | journal = Mol Biochem Parasitol | volume = 56 | issue = 2 | pages = 279-87 | month = Dec | year = 1992 | doi = | PMID = 1283004 }}</ref> | |||
==Molecular== | |||
*May be identified by [[PCR]] with an appropriate primer.<ref name=pmid24192618>{{Cite journal | last1 = Zeyrek | first1 = FY. | last2 = Turgay | first2 = N. | last3 = Unver | first3 = A. | last4 = Ustün | first4 = S. | last5 = Akarca | first5 = U. | last6 = Töz | first6 = S. | title = Differentiation of Entamoeba histolytica/Entamoeba dispar by the polymerase chain reaction in stool samples of patients with gastrointestinal symptoms in the Sanliurfa Province. | journal = Turkiye Parazitol Derg | volume = 37 | issue = 3 | pages = 174-8 | month = | year = 2013 | doi = 10.5152/tpd.2013.39 | PMID = 24192618 }}</ref> | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
*[[Colon]]. | *[[Colon]]. | ||
*[[Red blood cells]]. | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 12:50, 29 June 2016
| Amebiasis | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
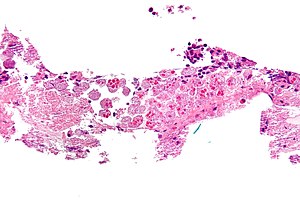 Amebiasis. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | entamoeba histolytica: round/ovoid eosinophilic bodies ~ 40-60 micrometers in maximal dimension; found in bowel lumen, usu. ingest (whole) red blood cells |
| LM DDx | fecal material, necroinflammatory debris |
| Molecular | PCR testing |
| Site | colon |
|
| |
| Associated Dx | +/-liver abscess |
| Signs | diarrhea, blood per rectum |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Endoscopy | colitis, mass lesion, granulation tissue-like |
| Prognosis | benign |
| Clin. DDx | colorectal carcinoma, colitis, granulation tissue |
Amebiasis, also be spelled amoebiasis, is an infectious disease, caused by the protozoan Entamoeba histolytica.
General
- Infection with Entamoeba histolytica.[1]
- May mimic colon cancer.[2]
May cause:[3]
- Dysentery (diarrhea containing mucus and/or blood in the feces).
- Colitis.
- Liver abscess.
Gross
Features:[4]
- +/-Mass.
- May mimic carcinoma.[5]
- +/-Granulation tissue-like appearance.
Microscopic
Features:
- Entamoeba histolytica are round/ovoid eosinophilic bodies ~ 40-60 micrometers in maximal dimension.
- Found in bowel lumen.
- Ingest RBCs.
Image
Stains
IHC
- Entamoeba histolytica +ve.[10]
Molecular
See also
References
- ↑ URL: http://www.health.state.ny.us/diseases/communicable/amebiasis/fact_sheet.htm. Accessed on: 17 June 2010.
- ↑ Fernandes, H.; D'Souza, CR.; Swethadri, GK.; Naik, CN.. "Ameboma of the colon with amebic liver abscess mimicking metastatic colon cancer.". Indian J Pathol Microbiol 52 (2): 228-30. PMID 19332922. http://www.ijpmonline.org/article.asp?issn=0377-4929;year=2009;volume=52;issue=2;spage=228;epage=230;aulast=Fernandes.
- ↑ Mortimer, L.; Chadee, K. (Mar 2010). "The immunopathogenesis of Entamoeba histolytica.". Exp Parasitol. doi:10.1016/j.exppara.2010.03.005. PMID 20303955.
- ↑ Stuiver, PC.; Visser, LG. (Nov 1993). "[Ameboma of the large intestine and rectum].". Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd 137 (45): 2328-31. PMID 8255341.
- ↑ Ooi, BS.; Seow-Choen, F. (Apr 2003). "Endoscopic view of rectal amebiasis mimicking a carcinoma.". Tech Coloproctol 7 (1): 51-3. doi:10.1007/s101510300008. PMID 12750955.
- ↑ Chacín-Bonilla, L. (Dec 2011). "[Microscopic diagnosis of amebiasis: an obsolete method but necessary in the developing world].". Invest Clin 52 (4): 291-4. PMID 22523839.
- ↑ URL: http://www.histopathology-india.net/amco.htm. Accessed on: 29 June 2016.
- ↑ Shetty, N.; Prabhu, T. (Jun 1988). "Evaluation of faecal preservation and staining methods in the diagnosis of acute amoebiasis and giardiasis.". J Clin Pathol 41 (6): 694-9. PMID 2454958.
- ↑ URL: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/212029-workup. Accessed on: 29 June 2016.
- ↑ Prasad, R.; Tola, M.; Bhattacharya, S.; Sharma, MP.; Bhattacharya, A. (Dec 1992). "Recognition of Entamoeba histolytica lipophosphoglycan by a strain-specific monoclonal antibody and human immune sera.". Mol Biochem Parasitol 56 (2): 279-87. PMID 1283004.
- ↑ Zeyrek, FY.; Turgay, N.; Unver, A.; Ustün, S.; Akarca, U.; Töz, S. (2013). "Differentiation of Entamoeba histolytica/Entamoeba dispar by the polymerase chain reaction in stool samples of patients with gastrointestinal symptoms in the Sanliurfa Province.". Turkiye Parazitol Derg 37 (3): 174-8. doi:10.5152/tpd.2013.39. PMID 24192618.