Difference between revisions of "Hemophagocytic syndrome"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (→Microscopic) |
|||
| (23 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ Infobox diagnosis | |||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | |||
| Image = Hemophagocytic_syndrome_-_cropped_-_very_high_mag.jpg | |||
| Width = | |||
| Caption = Micrograph showing phagocytosed RBCs in hemophagocytic syndrome. [[H&E stain]]. | |||
| Synonyms = | |||
| Micro = macrophages containing erythrocytes (red blood cells), leukocytes, platelets | |||
| Subtypes = primary, secondary | |||
| LMDDx = overlapping cells, [[emperipolesis]] | |||
| Stains = | |||
| IHC = | |||
| EM = | |||
| Molecular = FHL1 mutation or FHL2 mutation in primary form | |||
| IF = | |||
| Gross = | |||
| Grossing = | |||
| Site = [[lymph nodes]], [[liver]], [[spleen]], [[bone marrow]], others | |||
| Assdx = only in ''secondary'' form (EBV infection, malignancy, rheumatologic disease) | |||
| Syndromes = | |||
| Clinicalhx = +/-consanguinity for ''primary'' form (autosomal recessive) | |||
| Signs = fever, [[splenomegaly]], jaundice | |||
| Symptoms = | |||
| Prevalence = rare | |||
| Bloodwork = +/-EBV serology (secondary form), +/-HIV serology (secondary form) | |||
| Rads = | |||
| Endoscopy = | |||
| Prognosis = dependent on underlying cause | |||
| Other = | |||
| ClinDDx = malignancy | |||
| Tx = dependent on underlying cause | |||
}} | |||
'''Hemophagocytic syndrome''', also known as '''hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis''', is a rare condition often associated with viral infections. | '''Hemophagocytic syndrome''', also known as '''hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis''', is a rare condition often associated with viral infections. | ||
| Line 6: | Line 37: | ||
*[[Splenomegaly]]. | *[[Splenomegaly]]. | ||
*Jaundice. | *Jaundice. | ||
Involved organs: | |||
*[[Lymph nodes]]. | |||
*[[Liver]]. | |||
*[[Spleen]]. | |||
*[[Bone marrow]]. | |||
==Classification== | ==Classification== | ||
Classified by etiology:<ref name=pmid20383897>{{cite journal |author=Gupta S, Weitzman S |title=Primary and secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: clinical features, pathogenesis and therapy |journal=Expert Rev Clin Immunol |volume=6 |issue=1 |pages=137–54 |year=2010 |month=January |pmid=20383897 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | Classified by etiology:<ref name=pmid20383897>{{cite journal |author=Gupta S, Weitzman S |title=Primary and secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: clinical features, pathogenesis and therapy |journal=Expert Rev Clin Immunol |volume=6 |issue=1 |pages=137–54 |year=2010 |month=January |pmid=20383897 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
#Primary, i.e. inherited. | #Primary, i.e. inherited:<ref name=pmid21152410>{{cite journal |author=Nagai K, Yamamoto K, Fujiwara H, ''et al.'' |title=Subtypes of familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in Japan based on genetic and functional analyses of cytotoxic T lymphocytes |journal=PLoS ONE |volume=5 |issue=11 |pages=e14173 |year=2010 |pmid=21152410 |pmc=2994802 |doi=10.1371/journal.pone.0014173 |url=}}</ref> | ||
#*Etiology: dysfunction of cytotoxic T lymphocytes with macrophage activating cytokines. | |||
#*Autosomal recessive. | |||
#*Two genes identified: | |||
#**FHL1.<ref>{{OMIM|603552}}</ref> | |||
#**FHL2.<ref>{{OMIM|603553}}</ref> | |||
#Secondary: | #Secondary: | ||
#*Infection, e.g. EBV, HIV. | #*Infection, e.g. [[EBV]] (most common infectious etiology<ref>{{Ref WMSP|576}}</ref>),<ref name=pmid20819601>{{cite journal |author=Jin YK, Xie ZD, Yang S, Lu G, Shen KL |title=Epstein-Barr virus-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: a retrospective study of 78 pediatric cases in mainland of China |journal=Chin. Med. J. |volume=123 |issue=11 |pages=1426–30 |year=2010 |month=June |pmid=20819601 |doi= |url=}}</ref> [[HIV]]. | ||
#*Malignancy. | #*Malignancy. | ||
#*Rheumatologic condition. | #*Rheumatologic condition. | ||
| Line 18: | Line 60: | ||
Features:<ref name=pmid11076718/> | Features:<ref name=pmid11076718/> | ||
*Macrophages with phagocytosed: | *Macrophages with phagocytosed: | ||
** | **[[Erythrocyte]]s. | ||
**Leukocytes. | **Leukocytes. | ||
**Platelets. | **Platelets. | ||
Image( | DDx: | ||
*Overlapping cells (red blood cells overlapping macrophages). | |||
*[[Emperipolesis]] in the context of other pathology. | |||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
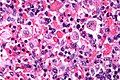
Image:Hemophagocytic_syndrome_-_cropped_-_very_high_mag.jpg | Hemophagocytic syndrome - cropped - very high mag. (WC) | |||
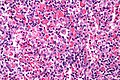
Image:Hemophagocytic_syndrome_-_very_high_mag.jpg | Hemophagocytic syndrome - very high mag. (WC) | |||
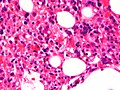
Image:Haemophagocytic_lymphohistiocytosis_Bone_marrow.JPG | HLH (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
www: | |||
*[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case601.html Hemophagocytic syndrome - several images (upmc.edu)]. | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
*[[Hematopathology]]. | *[[Hematopathology]]. | ||
*[[Myospherulosis]]. | |||
*[[Emperipolesis]]. | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| Line 31: | Line 86: | ||
[[Category:Haematopathology]] | [[Category:Haematopathology]] | ||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | |||
Latest revision as of 00:50, 16 July 2015
| Hemophagocytic syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
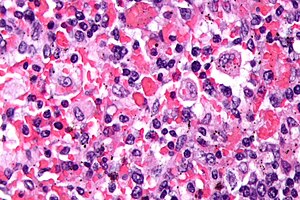 Micrograph showing phagocytosed RBCs in hemophagocytic syndrome. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | macrophages containing erythrocytes (red blood cells), leukocytes, platelets |
| Subtypes | primary, secondary |
| LM DDx | overlapping cells, emperipolesis |
| Molecular | FHL1 mutation or FHL2 mutation in primary form |
| Site | lymph nodes, liver, spleen, bone marrow, others |
|
| |
| Associated Dx | only in secondary form (EBV infection, malignancy, rheumatologic disease) |
| Clinical history | +/-consanguinity for primary form (autosomal recessive) |
| Signs | fever, splenomegaly, jaundice |
| Prevalence | rare |
| Blood work | +/-EBV serology (secondary form), +/-HIV serology (secondary form) |
| Prognosis | dependent on underlying cause |
| Clin. DDx | malignancy |
| Treatment | dependent on underlying cause |
Hemophagocytic syndrome, also known as hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, is a rare condition often associated with viral infections.
Clinical
Features:[1]
- Fever.
- Splenomegaly.
- Jaundice.
Involved organs:
Classification
Classified by etiology:[2]
- Primary, i.e. inherited:[3]
- Secondary:
Microscopic
Features:[1]
- Macrophages with phagocytosed:
- Erythrocytes.
- Leukocytes.
- Platelets.
DDx:
- Overlapping cells (red blood cells overlapping macrophages).
- Emperipolesis in the context of other pathology.
Images
www:
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Fisman DN (2000). "Hemophagocytic syndromes and infection". Emerging Infect. Dis. 6 (6): 601–8. PMC 2640913. PMID 11076718. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2640913/?tool=pubmed.
- ↑ Gupta S, Weitzman S (January 2010). "Primary and secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: clinical features, pathogenesis and therapy". Expert Rev Clin Immunol 6 (1): 137–54. PMID 20383897.
- ↑ Nagai K, Yamamoto K, Fujiwara H, et al. (2010). "Subtypes of familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in Japan based on genetic and functional analyses of cytotoxic T lymphocytes". PLoS ONE 5 (11): e14173. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0014173. PMC 2994802. PMID 21152410. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2994802/.
- ↑ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 603552
- ↑ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 603553
- ↑ Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 576. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ Jin YK, Xie ZD, Yang S, Lu G, Shen KL (June 2010). "Epstein-Barr virus-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: a retrospective study of 78 pediatric cases in mainland of China". Chin. Med. J. 123 (11): 1426–30. PMID 20819601.