Difference between revisions of "Intraductal papilloma of the breast"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→Images) |
(→Images) |
||
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
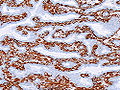
Image:Intraductal papilloma histopathology (2) smooth muscle actin.JPG | IP - SMA. (WC/KGH) | Image:Intraductal papilloma histopathology (2) smooth muscle actin.JPG | IP - SMA. (WC/KGH) | ||
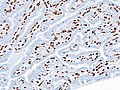
Image:Intraductal_papilloma_histopathology_(3)_p63.JPG | IP - p63 (WC/KGH) | Image:Intraductal_papilloma_histopathology_(3)_p63.JPG | IP - p63 (WC/KGH) | ||
Image:Breast IntraductalPapillomatosis LP CTR.jpg|Breast - Intraductal Papillomatosis - Low power (SKB) | |||
Image:Breast IntraductalPapillomatosis MP2 CTR.jpg|Breast - Intraductal Papillomatosis - Medium power (SKB) | |||
Image:Breast IntraductalPapilloma LP PA.JPG|Breast - Intraductal Papilloma - Low power (SKB) | |||
Image:Breast IntraductalPapilloma HP PA.JPG|Breast - Intraductal Papilloma - High power (SKB) | |||
Image:Breast IntraductalPapilloma LP (2) PA.JPG|Breast - Intraductal Papilloma - Low power (SKB) | |||
Image:Breast IntraductalPapilloma MP PA.JPG|Breast - Intraductal Papilloma - Medium power (SKB) | |||
Image:Breast IntraductalPapilloma Histiocytes MP PA.JPG|Breast - Intraductal Papilloma - Histiocytes - High power (SKB) | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 11:22, 29 April 2015
| Intraductal papilloma of the breast | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
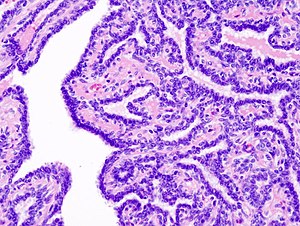 Intraductal papilloma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| Synonyms | breast papilloma |
|
| |
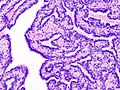
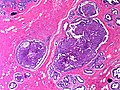
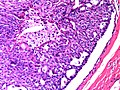
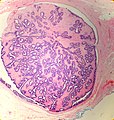
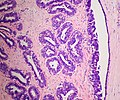
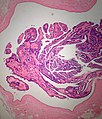
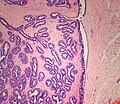
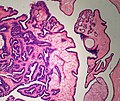
| LM | true papillae (nipple-shaped structures with fibrovascular cores), intraductal proliferation of epithelial and myoepithelial elements, +/-hyalinization |
| LM DDx | intraductal papilloma with florid epithelial hyperplasia, intraductal papilloma with atypical ductal hyperplasia, intraductal papilloma with ductal carcinoma in situ, invasive papillary carcinoma of the breast. |
| Site | breast |
|
| |
| Signs | +/-nipple discharge |
| Prevalence | common |
| Prognosis | benign |
| Treatment | usually excision |
Intraductal papilloma, also papilloma, is a relatively common benign pathology of the breast.
General
- May cause nipple discharge.[1]
- Similar to papillary hidradenoma of the vulva.
- Usually excised to exclude malignancy.
- Risk very low if not associated with a mass or suspicious radiologic findings - conservative management may be reasonable.[2]
Microscopic
Features:
- True papillae - nipple-shaped structures with fibrovascular cores.
- Intraductal proliferation of epithelial and myoepithelial elements.[3]
Notes:
- Lacks florid hyperplasia.[4]
- May degeneration and hyalinize to form a sclerosing papilloma.
DDx:
- Intraductal papilloma with florid epithelial hyperplasia.
- Intraductal papilloma with atypical ductal hyperplasia. †
- Intraductal papilloma with ductal carcinoma in situ. †
- Invasive papillary carcinoma of the breast.
† Size criteria are different in papillomas.
Images
IHC
Features:[5]
- CK5/6 +ve.
- p63 +ve.
- MUC3 weak.
- ER weak.
- Strong in DCIS.
See also
References
- ↑ Zervoudis, S.; Iatrakis, G.; Economides, P.; Polyzos, D.; Navrozoglou, I. (Jan 2010). "Nipple discharge screening.". Womens Health (Lond Engl) 6 (1): 135-51. doi:10.2217/whe.09.81. PMID 20050819.
- ↑ Weisman, PS.; Sutton, BJ.; Siziopikou, KP.; Hansen, N.; Khan, SA.; Neuschler, EI.; Rohan, SM.; Franz, JM. et al. (Nov 2013). "Non-mass-associated intraductal papillomas: is excision necessary?". Hum Pathol. doi:10.1016/j.humpath.2013.10.027. PMID 24444467.
- ↑ "Adenoma of Nipple.". Br Med J 1 (5330): 563. Mar 1963. PMC 2123505. PMID 20789667. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2123505/?page=1.
- ↑ URL: http://surgpathcriteria.stanford.edu/breast/nippleadenoma/printable.html. Accessed on: 6 August 2011.
- ↑ Furuya, C.; Kawano, H.; Yamanouchi, T.; Oga, A.; Ueda, J.; Takahashi, M. (Jun 2012). "Combined evaluation of CK5/6, ER, p63, and MUC3 for distinguishing breast intraductal papilloma from ductal carcinoma in situ.". Pathol Int 62 (6): 381-90. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1827.2012.02811.x. PMID 22612506.