Difference between revisions of "Leiomyoma"
| Line 81: | Line 81: | ||
*[[Myopericytoma]] / [[myofibroma]]. | *[[Myopericytoma]] / [[myofibroma]]. | ||
*[[Smooth muscle tumour of uncertain malignant potential]] (STUMP) - do not fulfill criteria for leiomyosarcoma. | *[[Smooth muscle tumour of uncertain malignant potential]] (STUMP) - do not fulfill criteria for leiomyosarcoma. | ||
*[[Epstein-Barr virus-associated smooth muscle tumour]] - very rare. | |||
===Variants=== | ===Variants=== | ||
Revision as of 17:38, 6 September 2014
| Leiomyoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
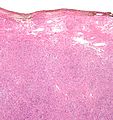
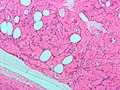
 Lipoleiomyoma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
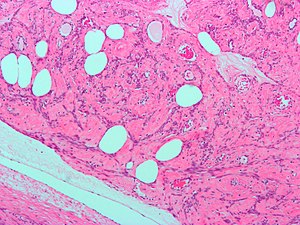
| LM | spindle cells arranged in fascicles, +/-nuclear atypia, rare mitoses (allowable mitotic rate dependent on specific site) |
| Subtypes | lipoleiomyoma, hypercellular leiomyoma, atypical leiomyoma (symplastic leiomyoma), benign metastasizing leiomyoma |
| LM DDx | leiomyosarcoma, STUMP, dermatomyofibroma |
| Gross | well-circumscribed, whorled appearance, firm |
| Site | skin, uterus, others |
|
| |
| Syndromes | hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell cancer (cutaneous & uterine leiomyomas) |
|
| |
| Symptoms | skin: pain, uterus: bulky |
| Prevalence | very common - esp. uterine |
| Prognosis | benign |
A leiomyoma is a very common benign tumour of smooth muscle. Leiomyomas fit into the soft tissue group of lesions. They are extremely common in the uterus. They may also be seen in the skin.
General
- Benign.
Cutaneous leiomyomas
- May be part of hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell cancer (HLRCC).[1][2]
- Painful skin lesion.
Uterine leiomyoma
- Often called "fibroids".
- Extremely common... 40% of women by age 40.
- Can be a cause of AUB (abnormal uterine bleeding).
- Large & multiple leiomyomas are associated with infertility.
- May be part of hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell cancer (HLRCC).
Colonic leiomyoma
Gross
- Sharply circumscribed.
- Gray-white.
- Whorled appearance.
Factors that raise concern for leiomyosarcoma:
- Haemorrhage.
- Cystic degeneration.
- Necrosis.
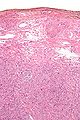
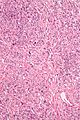
Microscopic
Features:
- Spindle cells arranged in fascicles.
- Fascicular appearance: adjacent groups of cells have their long axis perpendicular to one another; looks somewhat like a braided hair that was cut.
- Whorled arrangement of cells.
- +/-Medium-sized artery seen at the periphery of the lesion.
- Often arise from a muscular artery.
Uncommonly present - see note:
- Necrosis (low power) - suggestive of leiomyosarcoma.
- Hypercellularity.
- Nuclear atypia seen at low power.
- Few mitoses.
Note:
- Leiomyosarcoma is diagnosed if 2 of 3 are present: (1) high mitotic rate (dependent on site), (2) marked nuclear atypia (seen at low power), (3) necrosis.
DDx:
- Leiomyosarcoma.
- Lipoleiomyosarcoma - very rare.[3]
- Dermatomyofibroma.[4]
- Myopericytoma / myofibroma.
- Smooth muscle tumour of uncertain malignant potential (STUMP) - do not fulfill criteria for leiomyosarcoma.
- Epstein-Barr virus-associated smooth muscle tumour - very rare.
Variants
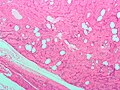
- Lipoleiomyoma - with adipose tissue.
- Hypercellular leiomyoma - hypercellularity assoc. with more mutations.[5]
- Atypical leiomyoma (AKA symplastic leiomyoma) - leiomyoma with nuclear atypia.
- Benign metastasizing leiomyoma.[6]
- This is just what it sounds like. Some believe these are low grade leiomyosarcomas.
IHC
Work-up of suspicious leiomyomas:[7]
- CD10 +ve.
- Ki-67 -ve.
- SMA +ve.
- Desmin +ve.
Other stains:
- H-caldesmon +ve.[8]
Sign out
SKIN LESION, RIGHT LEG, EXCISION: - LEIOMYOMA. - NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY. COMMENT: The lesion stains for desmin and SMA. It is negative for S-100 and has minimal staining with Ki-67.
Micro
The section shows unremarkable hair-bearing skin with a well-circumscribed subcutaneous lesion with a fascicular architecture. The lesion has no nuclear atypia and no mitotic activity is identified. At the periphery of the lesion is a medium-sized muscular artery from which the lesion appears to arise.
Alternate
The sections show a spindle cell lesion with a fascicular architecture. Focal hyaline change is seen. No nuclear atypia is apparent. Mitotic activity is not readily identified. No necrosis is identified. The lesion extends to the edge of the tissue fragments.
See also
References
- ↑ URL: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1252/. Accessed on: 2 September 2011.
- ↑ URL: http://ccr.cancer.gov/staff/gallery.asp?profileid=12822. Accessed on: 2 September 2011.
- ↑ Folpe, AL.; Weiss, SW. (Jun 2002). "Lipoleiomyosarcoma (well-differentiated liposarcoma with leiomyosarcomatous differentiation): a clinicopathologic study of nine cases including one with dedifferentiation.". Am J Surg Pathol 26 (6): 742-9. PMID 12023578.
- ↑ Busam, Klaus J. (2009). Dermatopathology: A Volume in the Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 533. ISBN 978-0443066542.
- ↑ http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/journal/119360394/abstract
- ↑ Patton, KT.; Cheng, L.; Papavero, V.; Blum, MG.; Yeldandi, AV.; Adley, BP.; Luan, C.; Diaz, LK. et al. (Jan 2006). "Benign metastasizing leiomyoma: clonality, telomere length and clinicopathologic analysis.". Mod Pathol 19 (1): 130-40. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3800504. PMID 16357844. http://www.nature.com/modpathol/journal/v19/n1/full/3800504a.html.
- ↑ STC. 25 February 2009.
- ↑ Zámecník, M.; Kascák, P. (Jul 2011). "Uterine leiomyoma with amianthoid-like fibers.". Cesk Patol 47 (3): 125-7. PMID 21887931.