Difference between revisions of "Squamous cell carcinoma of the uterine cervix"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(redirect) |
(split out) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Squamous cell carcinoma of the uterine cervix''', also '''cervical squamous cell carcinoma''', is the most common primary malignancy of the [[uterine cervix]]. | |||
==General== | |||
*Most common type of cervical cancer. | |||
Risk factors: | |||
*Low socioeconomic status. | |||
*Smoking. | |||
*Early first intercourse. | |||
*High risk partners. | |||
*[[Human papillomavirus]] (HPV) infection, esp. "high risk HPV". | |||
**HPV 16 closely assoc. with SCC.<ref name=pmid15551313>{{Cite journal | last1 = De Boer | first1 = MA. | last2 = Peters | first2 = LA. | last3 = Aziz | first3 = MF. | last4 = Siregar | first4 = B. | last5 = Cornain | first5 = S. | last6 = Vrede | first6 = MA. | last7 = Jordanova | first7 = ES. | last8 = Fleuren | first8 = GJ. | title = Human papillomavirus type 18 variants: histopathology and E6/E7 polymorphisms in three countries. | journal = Int J Cancer | volume = 114 | issue = 3 | pages = 422-5 | month = Apr | year = 2005 | doi = 10.1002/ijc.20727 | PMID = 15551313 }}</ref> | |||
==Microscopic== | |||
Features: | |||
*Squamous differentiation. | |||
**+/-Intracellular bridges. | |||
**Scant-to-moderate cytoplasm. | |||
*Penetration of basement membrane. | |||
**May be challenging to determine. | |||
*Nuclear atypia. | |||
SCC of the cervix versus CIN III: | |||
Invasive cancer look for: | |||
*Eosinophilia. | |||
*Extra large nuclei, i.e. nuclei 5x normal size. | |||
*Stromal inflammation (lymphocytes, plasma cells). | |||
*Long rete ridges. | |||
*Numerous beeds/blobs of epithelial cells that seem unlikely to be rete ridges. | |||
*[[Desmoplastic stroma]] - increased cellularity, spindle cell morphology. | |||
DDx: | |||
* [[Squamous metaplasia of the uterine cervix]] - if you can trace the squamous cells from a gland to the surface it is less likely to be invasive cancer.<ref>[http://www.nature.com/modpathol/journal/v15/n3/pdf/3880520a.pdf http://www.nature.com/modpathol/journal/v15/n3/pdf/3880520a.pdf]</ref> | |||
*[[CIN III]] +/- endocervical gland involvement. | |||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
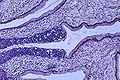
Image:Ca_in_situ,_cervix_2.jpg|SCC in situ. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
www: | |||
*[http://sunnybrook.ca/uploads/cx_microinv_scc_S10-5249_6.jpg Microinvasive cervical SCC - low mag. (sunnybrook.ca)].<ref name=sb_cx_scc/> | |||
*[http://sunnybrook.ca/uploads/cx_microinv_scc_S10-5249_7.jpg Microinvasive cervical SCC - high mag. (sunnybrook.ca)].<ref name=sb_cx_scc>URL: [http://sunnybrook.ca/content/?page=dept-labs-apath-gynpath-imgat-cvx-mal-microiscc http://sunnybrook.ca/content/?page=dept-labs-apath-gynpath-imgat-cvx-mal-microiscc]. Accessed on: 2 May 2013.</ref> | |||
*[http://missinglink.ucsf.edu/lm/IDS_107_Cervix_Ovary_Uterus/ASSETS/Slide329SCClp_small.JPG Cervical SCC - low mag. (ucsf.edu)].<ref name=uscf>URL: [http://missinglink.ucsf.edu/lm/IDS_107_Cervix_Ovary_Uterus/homepage.htm http://missinglink.ucsf.edu/lm/IDS_107_Cervix_Ovary_Uterus/homepage.htm]. Accessed on: 2 May 2013.</ref> | |||
*[http://missinglink.ucsf.edu/lm/IDS_107_Cervix_Ovary_Uterus/ASSETS/Slide329SCChp.JPG Cervical SCC - high mag. (uscf.edu)]. | |||
===Grading=== | |||
Divided into:<ref>{{Ref PBoD|1077}}</ref> | |||
#Well-differentiated (keratinizing). | |||
#Moderately differentiated (nonkeratinizing). | |||
#Poorly differentiated. | |||
===Depth measurement=== | |||
*Basement membrane (where it invades) to deepest point. | |||
Note: | |||
*Stage Ib - clinical diagnosis. | |||
**Definition of stage Ib: clinically visible. | |||
====FIGO==== | |||
Microinvasive SCC as per FIGO: | |||
*Depth < 5 mm. | |||
*Width < 7 mm. | |||
*+/-Vascular invasion. | |||
====SGO==== | |||
Microinvasive SCC as per The Society of Gynecologic Oncologists (SGO): | |||
*<= 3 mm. | |||
*Negative for [[vascular invasion]]. | |||
Note: | |||
*The SGO criteria the prefered by North American gynecologists. | |||
==IHC== | |||
*Factor VIII - to look for [[LVI]]. | |||
==Sign out== | |||
Early invasive SCC - things to report: | |||
*Depth of invasion. | |||
*Length of tumour. | |||
*Number of blocks with tumour. | |||
*LVI. | |||
*Margins. | |||
<pre> | |||
UTERINE CERVIX, BIOPSY: | |||
- FRAGMENTS OF INVASIVE SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA. | |||
-- DEPTH OF INVASION AND LENTH OF TUMOUR CANNOT BE ASSESSED. | |||
-- LYMPHOVASCULAR INVASION NOT APPARENT. | |||
</pre> | |||
==See also== | |||
*[[Uterine cervix]]. | |||
*[[Squamous cell carcinoma]]. | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|2}} | |||
[[Category:Uterine cervix]] | |||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | [[Category:Diagnosis]] | ||
Revision as of 14:00, 23 February 2014
Squamous cell carcinoma of the uterine cervix, also cervical squamous cell carcinoma, is the most common primary malignancy of the uterine cervix.
General
- Most common type of cervical cancer.
Risk factors:
- Low socioeconomic status.
- Smoking.
- Early first intercourse.
- High risk partners.
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, esp. "high risk HPV".
- HPV 16 closely assoc. with SCC.[1]
Microscopic
Features:
- Squamous differentiation.
- +/-Intracellular bridges.
- Scant-to-moderate cytoplasm.
- Penetration of basement membrane.
- May be challenging to determine.
- Nuclear atypia.
SCC of the cervix versus CIN III: Invasive cancer look for:
- Eosinophilia.
- Extra large nuclei, i.e. nuclei 5x normal size.
- Stromal inflammation (lymphocytes, plasma cells).
- Long rete ridges.
- Numerous beeds/blobs of epithelial cells that seem unlikely to be rete ridges.
- Desmoplastic stroma - increased cellularity, spindle cell morphology.
DDx:
- Squamous metaplasia of the uterine cervix - if you can trace the squamous cells from a gland to the surface it is less likely to be invasive cancer.[2]
- CIN III +/- endocervical gland involvement.
Images
www:
- Microinvasive cervical SCC - low mag. (sunnybrook.ca).[3]
- Microinvasive cervical SCC - high mag. (sunnybrook.ca).[3]
- Cervical SCC - low mag. (ucsf.edu).[4]
- Cervical SCC - high mag. (uscf.edu).
Grading
Divided into:[5]
- Well-differentiated (keratinizing).
- Moderately differentiated (nonkeratinizing).
- Poorly differentiated.
Depth measurement
- Basement membrane (where it invades) to deepest point.
Note:
- Stage Ib - clinical diagnosis.
- Definition of stage Ib: clinically visible.
FIGO
Microinvasive SCC as per FIGO:
- Depth < 5 mm.
- Width < 7 mm.
- +/-Vascular invasion.
SGO
Microinvasive SCC as per The Society of Gynecologic Oncologists (SGO):
- <= 3 mm.
- Negative for vascular invasion.
Note:
- The SGO criteria the prefered by North American gynecologists.
IHC
- Factor VIII - to look for LVI.
Sign out
Early invasive SCC - things to report:
- Depth of invasion.
- Length of tumour.
- Number of blocks with tumour.
- LVI.
- Margins.
UTERINE CERVIX, BIOPSY: - FRAGMENTS OF INVASIVE SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA. -- DEPTH OF INVASION AND LENTH OF TUMOUR CANNOT BE ASSESSED. -- LYMPHOVASCULAR INVASION NOT APPARENT.
See also
References
- ↑ De Boer, MA.; Peters, LA.; Aziz, MF.; Siregar, B.; Cornain, S.; Vrede, MA.; Jordanova, ES.; Fleuren, GJ. (Apr 2005). "Human papillomavirus type 18 variants: histopathology and E6/E7 polymorphisms in three countries.". Int J Cancer 114 (3): 422-5. doi:10.1002/ijc.20727. PMID 15551313.
- ↑ http://www.nature.com/modpathol/journal/v15/n3/pdf/3880520a.pdf
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 URL: http://sunnybrook.ca/content/?page=dept-labs-apath-gynpath-imgat-cvx-mal-microiscc. Accessed on: 2 May 2013.
- ↑ URL: http://missinglink.ucsf.edu/lm/IDS_107_Cervix_Ovary_Uterus/homepage.htm. Accessed on: 2 May 2013.
- ↑ Cotran, Ramzi S.; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Nelso Fausto; Robbins, Stanley L.; Abbas, Abul K. (2005). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (7th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. pp. 1077. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.