Difference between revisions of "Malakoplakia"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(+cat) |
|||
| Line 76: | Line 76: | ||
[[Category: Genitourinary pathology]] | [[Category: Genitourinary pathology]] | ||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | [[Category:Diagnosis]] | ||
[[Category:Urothelium]] | |||
Revision as of 20:47, 7 November 2013
| Malakoplakia | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
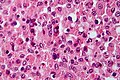
 Malakoplakia with numerous Michaelis-Gutmann bodies. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | basophilic calcified bodies approximately the size of a RBC (Michaelis-Gutmann body) - inside or outside of macrophages, large foamy macrophages with granular cytoplasm +/- multinucleation, lymphocytes |
| LM DDx | Xanthogranulomatous process (e.g. xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis, xanthogranulomatous cystitis), granulomatous inflammation, papillary renal cell carcinoma, infarction (prostate), granular cell tumour |
| Gross | yellow mass |
| Site | urinary bladder and elsewhere |
|
| |
| Prognosis | benign |
| Clin. DDx | renal cell carcinoma, other tumours |
Malakoplakia is a thingy that typically arises in the urinary bladder.
General
- Classically in the urinary bladder.
- May be outside of urinary tract.[1]
Gross
- Yellow mass.[2]
- May mimic renal cell carcinoma.
Microscopic
Features:[3]
- Basophilic calcified lysosomes (Michaelis-Gutmann bodies) -- key feature.
- May be inside or outside of macrophages - often size of RBC or larger.
- Large foamy macrophages with granular cytoplasm.
- Occasional multinucleated giant cell.
- Lymphocytes.
DDx:
- Xanthogranulomatous process.
- If you cannot find the Michaelis-Gutmann bodies... it is a xanthogranulomatous process, e.g. xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis, xanthogranulomatous cystitis.
- Granulomatous inflammation.
- Papillary renal cell carcinoma.
- Infarction (prostate).
- Granular cell tumour.[4]
Images
Stains
- PAS-D stain +ve.[1]
- Von Kossa stain +ve.[4]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Yousef, GM.; Naghibi, B.; Hamodat, MM. (Feb 2007). "Malakoplakia outside the urinary tract.". Arch Pathol Lab Med 131 (2): 297-300. doi:10.1043/1543-2165(2007)131[297:MOTUT]2.0.CO;2. PMID 17284117.
- ↑ URL: http://www.pathconsultddx.com/pathCon/diagnosis?pii=S1559-8675(06)70719-7. Accessed on: 9 September 2010.
- ↑ Cotran, Ramzi S.; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Nelso Fausto; Robbins, Stanley L.; Abbas, Abul K. (2005). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (7th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Elsevier Saunders. pp. 1027. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Diapera, MJ.; Lozon, CL.; Thompson, LD.. "Malacoplakia of the tongue: a case report and clinicopathologic review of 6 cases.". Am J Otolaryngol 30 (2): 101-5. doi:10.1016/j.amjoto.2008.02.014. PMID 19239951.