Difference between revisions of "Benign endometrial polyp"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(tweak) |
|||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
| Micro = large blood vessels (muscular), fibrotic stroma, polypoid shape (epithelium on three sides), +/-gland dilation | | Micro = large blood vessels (muscular), fibrotic stroma, polypoid shape (epithelium on three sides), +/-gland dilation | ||
| Subtypes = | | Subtypes = | ||
| LMDDx = [[adenofibroma]], [[cervical polyp]] - have endocervical mucosa, lower uterine segment, [[endometrial carcinoma]] | | LMDDx = [[adenofibroma]], [[cervical polyp]] - have endocervical mucosa, lower uterine segment, [[endometrial carcinoma]], [[simple endometrial hyperplasia]], [[disordered proliferative endometrium]] | ||
| Stains = | | Stains = | ||
| IHC = | | IHC = | ||
| Line 66: | Line 66: | ||
*Lower uterine segment - have endocervical epithelium and lack the thick-walled blood vessels.<ref name=pmid16873562/> | *Lower uterine segment - have endocervical epithelium and lack the thick-walled blood vessels.<ref name=pmid16873562/> | ||
*[[Endometrial carcinoma]] - esp. [[serous carcinoma of the endometrium]]. | *[[Endometrial carcinoma]] - esp. [[serous carcinoma of the endometrium]]. | ||
*[[Simple endometrial hyperplasia]]. | |||
*[[Disordered proliferative endometrium]]. | |||
==Sign out== | ==Sign out== | ||
Revision as of 02:06, 3 November 2013
| Benign endometrial polyp | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
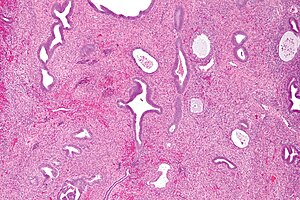 Endometrial polyp. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | large blood vessels (muscular), fibrotic stroma, polypoid shape (epithelium on three sides), +/-gland dilation |
| LM DDx | adenofibroma, cervical polyp - have endocervical mucosa, lower uterine segment, endometrial carcinoma, simple endometrial hyperplasia, disordered proliferative endometrium |
| Gross | polypoid mass in the endometrial cavity |
| Site | endometrium |
|
| |
| Associated Dx | invasive breast cancer - specifically assoc. with tamoxifen |
| Clinical history | bleeding |
| Prevalence | common |
| Prognosis | benign |
- Uterine polyp redirects here.
Benign endometrial polyp, abbreviated BEP, is a common diagnosis is endometrial specimens.
It is also simply known as endometrial polyp which is a somewhat ambiguous descriptor as not all endometrial polyps are benign.
General
- Very common.
- May be a cause of menorrhagia (heavy & long menses).
Gross
- Polypoid mass in the endometrial cavity.
Gross DDx:
- Secretory phase endometrium.[1]
- Pedunculated leiomyoma.
Microscopic
Features - diagnostic criteria:[1]
- Large blood vessels (muscular) - key feature.
- Fibrotic stroma - key feature.
- Polypoid shape - epithelium on three sides.
- May not be seen... as polyp is fragmented on removal.
Glandular changes common:[1]
- Endometrial glands may be out of phase with surrounding endometrium.
- Often proliferative.
- +/-Cystic dilation of glands/unusual shapes
- Simple endometrial hyperplasia should not be diagnosed in a polyp!
- +/-Focal gland crowding.
Notes:
- Apparently benign polyps should be examined closely at the surface for in situ & invasive malignancies.
- Stroma often cellular.
DDx:
- Adenofibroma.
- Cervical polyp - have endocervical mucosa.
- Lower uterine segment - have endocervical epithelium and lack the thick-walled blood vessels.[1]
- Endometrial carcinoma - esp. serous carcinoma of the endometrium.
- Simple endometrial hyperplasia.
- Disordered proliferative endometrium.
Sign out
Non-proliferative
ENDOMETRIUM, CURETTAGE: - BENIGN ENDOMETRIAL POLYP.
ENDOMETRIUM ("POLYPS"), REMOVAL:
- BENIGN ENDOMETRIAL POLYPS WITH CYSTIC GLANDULAR DILATION AND
WITHOUT APPARENT PROLIFERATIVE ACTIVITY.
Suggestive of polyp
ENDOMETRIUM, CURETTAGE: - POLYPOID NONPROLIFERATIVE ENDOMETRIUM WITH FOCALLY PROMINENT SMALL BLOOD VESSELS AND FIBROUS STROMA, SUGGESTIVE OF BENIGN POLYP. - NEGATIVE FOR HYPERPLASIA AND NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
Proliferative
ENDOMETRIUM, CURETTAGE: - BENIGN ENDOMETRIAL POLYP WITH PROLIFERATIVE ACTIVITY.
Note:
- It is useful to comment on whether non-polypoid endometrium is proliferative (if present), esp. in menopausal women.[1]
Polyp with disordered proliferative phase in the background
ENDOMETRIUM, BIOPSY: - BENIGN ENDOMETRIAL POLYP WITH PROLIFERATIVE GLANDS AND FOCAL GLAND DILATION. - SUSPICIOUS FOR A BACKGROUND OF DISORDERED PROLIFERATIVE PHASE ENDOMETRIUM, SEE COMMENT. - STRIPPED BENIGN ENDOCERVICAL EPITHELIUM. COMMENT: The endometrium sampled is proliferative with focal gland dilation throughout. The features of a polyp (large muscular blood vessels, fibrous stroma and polypoid fragments of endometrium) are only focally present, suggesting there is a background of disordered proliferative phase endometrium. Clinical correlation is suggested.
Clinically a polyp but not apparent on histology
UTERUS (POLYP), REMOVAL: - LARGE FRAGMENT OF SECRETORY PHASE ENDOMETRIUM WITH LARGE BLOOD VESSELS, A NON-FIBROUS STROMA AND NO DISCERNIBLE SURFACE EPITHELIUM.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 McCluggage, WG. (Aug 2006). "My approach to the interpretation of endometrial biopsies and curettings.". J Clin Pathol 59 (8): 801-12. doi:10.1136/jcp.2005.029702. PMC 1860448. PMID 16873562. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1860448/.