Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis
(Redirected from XGC)
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
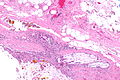
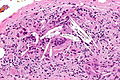
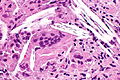
 Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | cholesterol clefts, granulomas |
| LM DDx | chronic cholecystitis, gallbladder cholesterolosis |
| Gross | thickened gallbladder wall, gallstones |
| Site | gallbladder |
|
| |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Radiology | hypo-attenuated nodules in gallbladder wall |
| Prognosis | benign |
| Clin. DDx | gallbladder carcinoma, acute cholecystitis |
| Treatment | cholecystectomy (surgical removal) |
Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis, abbreviated XGC,[1] is an uncommon pathology of the gallbladder.
General
- Uncommon ~ 1-9%.[2][3]
- Approximately 2% in one series of 724 gallbladders.[4]
- May be confused (clinically) with gallbladder carcinoma.[1][2][5]
Gross
Features:[6]
- Wall thickening ~ 90% of cases.
- Gallstones ~ 70% of cases.
- +/-Infiltration of surrounding tissues (liver, fat).
Imaging:
- Hypo-attenuated nodules in the gallbladder wall.[6]
Microscopic
Features:[4]
- Granulomas.
- Lipid-laden macrophages.
- +/-Cholesterol clefts.
- Inflammatory cells.
- Fibrosis.
DDx:
Images
www:
Sign out
Gallbladder, Cholecystectomy: - Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis. - Cholelithiasis.
Block letters
GALLBLADDER, CHOLECYSTECTOMY: - XANTHOGRANULOMATOUS CHOLECYSTITIS. - CHOLELITHIASIS.
Micro
The sections show a thickened gallbladder wall with cholesterol clefts, multinucleated giant cells, fibrosis and lymphoid aggregates. No metaplasia, nuclear atypia or dysplasia is apparent.
Alternate
The sections show a thickened gallbladder wall with cholesterol clefts, multinucleated giant cells, fibrosis and small lymphoid aggregates. No metaplasia, dysplasia or significant nuclear atypia is apparent.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Rammohan, A.; Cherukuri, SD.; Sathyanesan, J.; Palaniappan, R.; Govindan, M. (2014). "Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis masquerading as gallbladder cancer: can it be diagnosed preoperatively?". Gastroenterol Res Pract 2014: 253645. doi:10.1155/2014/253645. PMID 25404941.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Hale, MD.; Roberts, KJ.; Hodson, J.; Scott, N.; Sheridan, M.; Toogood, GJ. (Aug 2013). "Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis: a European and global perspective.". HPB (Oxford). doi:10.1111/hpb.12152. PMID 23991684.
- ↑ Alvi, AR.; Jalbani, I.; Murtaza, G.; Hameed, A. (Jul 2013). "Outcomes of Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis in laparoscopic era: A retrospective Cohort study.". J Minim Access Surg 9 (3): 109-15. doi:10.4103/0972-9941.115368. PMID 24019688.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Roberts, KM.; Parsons, MA. (Apr 1987). "Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis: clinicopathological study of 13 cases.". J Clin Pathol 40 (4): 412-7. PMC 1140974. PMID 3584484. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1140974/.
- ↑ Martins, PN.; Sheiner, P.; Facciuto, M. (Oct 2012). "Xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis mimicking gallbladder cancer and causing obstructive cholestasis.". Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int 11 (5): 549-52. PMID 23060404.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Zhao, F.; Lu, PX.; Yan, SX.; Wang, GF.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, SZ.; Wang, YX. (Sep 2013). "CT and MR features of xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis: an analysis of consecutive 49 cases.". Eur J Radiol 82 (9): 1391-7. doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2013.04.026. PMID 23726123.
- ↑ Cecava, ND.; Andrews, R. (2011). "Case report of xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis, review of its sonographic and magnetic resonance findings, and distinction from other gallbladder pathology.". J Radiol Case Rep 5 (4): 19-24. doi:10.3941/jrcr.v5i4.696. PMID 22470787.