Vasitis nodosa
(Redirected from VN)
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Vasitis nodosa | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
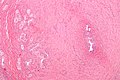
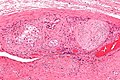
 Vasitis nodosa (left side of image). H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | tubules with sperm |
| LM DDx | prostate carcinoma, metastatic adenocarcinoma |
| IHC | PSA -ve, PSAP -ve |
| Site | vas deferens |
|
| |
| Clinical history | (usually) previous vasectomy |
| Prognosis | benign |
| Vasitis nodosa | |
|---|---|
| External resources | |
| EHVSC | 10185 |
Vasitis nodosa, abbreviated VN, is a common complication of vasectomy that is seldomly seen by pathologists. It is seen by pathologists in the context of vasovasostomy.
General
- Classically seen in a specimen from a vasovasostomy (vasectomy reversal).[1]
- Seen in association with other surgical procedures.
- May be seen in the context of infertility (without prior vasectomy).
- Some similarity to salpingitis isthmica nodosa.[1]
Gross
- Mass.
Microscopic
Features:[1]
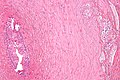
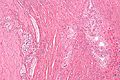
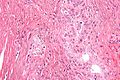
- Tubules in wall of vas deferens.
- Lined by columnar/cuboidal epithelium.
- May have mitotic activity.
- Nucleoli.
- Contain sperm - small, dark staining, teardrop-shaped (~1 micrometer) - key feature.
- The tail is rarely seen completely in the plane of section.
- Lined by columnar/cuboidal epithelium.
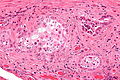
- +/-Sperm granulomas.
- Histocytes - abundant foamy cytoplasm.
- Sperm - small, dark staining, teardrop-shaped (~1 micrometer).
DDx:
- Metastatic carcinoma, especially prostate carcinoma.
Notes:
- Can be confused with prostatic adenocarcinoma:[2]
- May "invade" vascular spaces - associated with elastosis (breakdown of elastic fibres[3]).
Images
www:
IHC
Features:[4]
- PSA -ve.
- CK7 +ve
- CK34betaE12 +ve.
- Vimentin +ve.
- CK19 +ve.
Others:
- PSAP -ve.
Sign out
Right Vas Deferens, Excision:
- Vasitis nodosa.
Block letters
A. VAS DEFERENS WITH GRANULOMA, RIGHT, VASOVASOSTOMY: - VASITIS NODOSA AND SPERM GRANULOMAS. - COMPLETE CROSS SECTION OF VAS DEFERENS. B. VAS DEFERENS WITH GRANULOMA, LEFT, VASOVASOSTOMY: - VASITIS NODOSA AND SPERM GRANULOMAS. - COMPLETE CROSS SECTION OF VAS DEFERENS.
Micro
The sections show one unremarkable cross section of the vas deferens and several sections with a histocytic response at the external aspect of the vas deferens' muscle layers. The histocytes are aggregated and contains bland tubular structures with sperm.
The tubular structures are POSITIVE for CK7 and CK34betaE12, and NEGATIVE for PSA. CD68 marks the histiocytes.
See also
References
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.0 1.1 1.2 Hirschowitz, L.; Rode, J.; Guillebaud, J.; Bounds, W.; Moss, E. (Apr 1988). "Vasitis nodosa and associated clinical findings.". J Clin Pathol 41 (4): 419-23. PMC 1141468. PMID 3366928. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1141468/.
- ↑ Balogh, K.; Travis, WD. (Apr 1985). "Benign vascular invasion in vasitis nodosa.". Am J Clin Pathol 83 (4): 426-30. PMID 3984936.
- ↑ URL: http://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/elastosis. Accessed on: 26 September 2011.
- ↑ Sakaki, M.; Hirokawa, M.; Horiguchi, H.; Wakatsuki, S.; Sano, T. (Apr 2000). "Vasitis nodosa: immunohistochemical findings--case report.". APMIS 108 (4): 283-6. PMID 10843416.