Lentigo simplex
(Redirected from Simple lentigo)
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Lentigo simplex | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
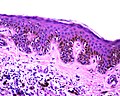
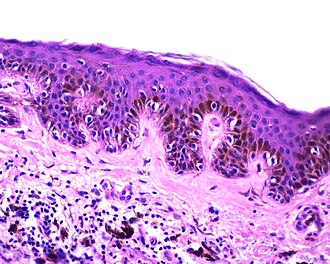 Simple lentigo. H&E stain. (WC) | |
|
| |
| Synonyms | simple lentigo |
|
| |
| LM | melanocytes in epidermis only - hyperpigmentation; no melanocytic nests; +/-mild/moderate elongation of the rete ridges |
| LM DDx | solar lentigo, ephelis (freckle), melanotic macule, lentiginous nevus, early seborrheic keratosis |
| Site | skin |
|
| |
| Clinical history | usu. older than 40 years |
| Prevalence | common |
| Prognosis | benign |
Lentigo simplex is a common benign melanocytic lesion.
It is also known as simple lentigo.[1]
General
- Benign.
- Usually <40 years old.
- May be precursor to seborrheic keratosis.[2]
Fits into the larger category of lentiginous melanocytic proliferations - these include:[3]
- Solar lentigo.
- Lentigo simplex.
- Lentiginous nevus.
- Lentiginous melanoma in situ.
Associated syndromes:[4]
Gross
- Small flat pigmented lesion.[5]
DDx - clinical:
Microscopic
Features:[5]
- Melanocytes in epidermis only.
- Melanocytes basally located (normal location) with hyperpigmentation.
- No melanocytic nests.
- +/-Mild/moderate elongation of the rete ridges.[6]
DDx:[7]
- Solar lentigo - solar elastosis, usu. in sun exposed areas.
- Ephelis (freckle) - change with UV light exposure.
- Melanotic macule.
- Lentiginous nevus - has melanocytic nests.
- Early seborrheic keratosis.
Images
Sign out
Left Hand Lesion, Radial, Biopsy:
- Simple lentigo/early seborrheic keratosis.
Block letters
SKIN LESION, LEFT ABDOMEN, BIOPSY: - SIMPLE LENTIGO, COMPLETELY EXCISED IN THE PLANE OF SECTION.
SKIN LESION, LEFT ABDOMEN, BIOPSY: - BENIGN SIMPLE LENTIGO.
Micro
The sections show skin with increased numbers of small pigmented melanocytes at the dermal-epidermal junction. The rete ridges are mildly elongated. No solar damage is apparent. No dermal melanocytes are identified. No melanocytic nests are identified. No nuclear atypia is apparent.
See also
References
- ↑ URL: http://www.dermnetnz.org/lesions/lentigo-simplex.html. Accessed on: 27 March 2013.
- ↑ Sahin, MT.; Oztürkcan, S.; Ermertcan, AT.; Güneş, AT. (Nov 2004). "A comparison of dermoscopic features among lentigo senilis/initial seborrheic keratosis, seborrheic keratosis, lentigo maligna and lentigo maligna melanoma on the face.". J Dermatol 31 (11): 884-9. PMID 15729860.
- ↑ Busam, Klaus J. (2009). Dermatopathology: A Volume in the Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 438. ISBN 978-0443066542.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 URL: http://dermaamin.com/site/histopathology-of-the-skin/64-l/1852-lentigo-simplex-.html. Accessed on: 17 December 2012.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 498. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Hafner, C.; Stoehr, R.; van Oers, JM.; Zwarthoff, EC.; Hofstaedter, F.; Klein, C.; Landthaler, M.; Hartmann, A. et al. (Nov 2009). "The absence of BRAF, FGFR3, and PIK3CA mutations differentiates lentigo simplex from melanocytic nevus and solar lentigo.". J Invest Dermatol 129 (11): 2730-5. doi:10.1038/jid.2009.146. PMID 19536147.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 URL: http://www.humpath.com/?lentigo-simplex. Accessed on: 17 December 2012.