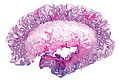
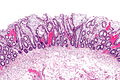
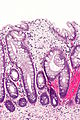
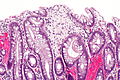
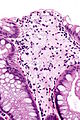
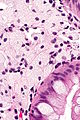
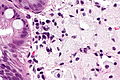
Colorectal xanthomatous polyp
(Redirected from Rectal xanthelasma)
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Colorectal xanthomatous polyp | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
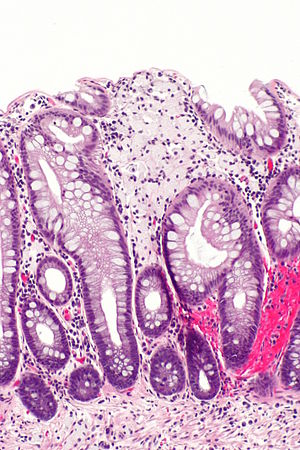 Colorectal xanthomatous polyp. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | abundant foamy histiocytes in the superficial lamina propria +/- superficial serrations (hyperplastic features) |
| LM DDx | hyperplastic polyp, signet ring cell carcinoma, others |
| IHC | CD68 +ve, pankeratin -ve |
| Site | colon, rectum |
|
| |
| Associated Dx | +/-hyperlipidemia |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Endoscopy | polyp - red or yellow colour |
| Prognosis | benign |
| Clin. DDx | other colorectal polyps |
The colorectal xanthomatous polyp, also colorectal xanthoma, is a rare benign intestinal polyp.
Rectal xanthoma, colonic xanthoma, rectal xanthelasma and colonic xanthelasma redirect here.
Colorectal xanthomatous polyp may be abbreviated CXP.
General
Gross
Microscopic
Features:
- Abundant foamy histiocytes in the superficial lamina propria.
- +/-Superficial serrations (hyperplastic features).
- Seen in ~80% of cases.[2]
DDx:
Images
Stains
IHC
- CD68 +ve (foamy histiocytes).[1]
- Pankeratin -ve.
Sign out
Polyp, Rectum, Polypectomy or Biopsy: - Xanthomatous polyp with hyperplastic features, see comment. - NEGATIVE for dysplasia. COMMENT: Xanthomatous polyps may be seen in the context of hyperlipidemia.[1] A lipid profile could be considered. 1. APMIS 112 (1): 3-10. PMID: 14961968.
Block letters
POLYP, SIGMOID COLON, POLYPECTOMY: - XANTHOMATOUS POLYP WITH HYPERPLASTIC FEATURES. - NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA. COMMENT: Xanthomatous polyps may be seen in the context of hyperlipidemia.[1] A lipid profile could be considered. 1. APMIS 112 (1): 3-10. PMID: 14961968.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Miliauskas, JR. (Apr 2002). "Rectosigmoid (colonic) xanthoma: a report of four cases and review of the literature.". Pathology 34 (2): 144-7. PMID 12009096.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Nakasono, M.; Hirokawa, M.; Muguruma, N.; Okahisa, T.; Okamura, S.; Ito, S.; Miyamoto, H.; Wada, S. et al. (Jan 2004). "Colorectal xanthomas with polypoid lesion: report of 25 cases.". APMIS 112 (1): 3-10. PMID 14961968.