Villous hypoplasia
(Redirected from Distal villous hypoplasia)
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Villous hypoplasia, also distal villous hypoplasia, is pathology of the placenta associated with intrauterine growth restriction.
| Villous hypoplasia | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
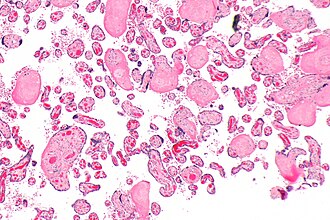 Distal villous hypoplasia. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| Synonyms | terminal villus deficiency, distal villous hypoplasia |
|
| |
| LM | small & round villi (30-60 micrometers), "long" villi (due to lack of branching), absence of syncytial knots, wide intervillous space |
| Gross | usu. small placenta |
| Site | placenta |
|
| |
| Associated Dx | IUGR, small placenta |
| Clinical history | small fetus |
| Prevalence | not common |
It is also known as terminal villus deficiency.[1]
General
Microscopic
Features:[1]
- Small, round villi (30-60 micrometers).
- "Long" villi (due to lack of branching).
- Absence of syncytial knots.
- Wide intervillous space.
Images
Sign out
PLACENTA AND MEMBRANES, BIRTH: - SMALL PLACENTA FOR GESTATIONAL AGE (265 GRAMS - TRIMMED , POST FIXATION). - FETAL MEMBRANES WITHIN NORMAL LIMITS. - THREE-VESSEL CORD WITHIN NORMAL LIMITS. - PLACENTAL DISC WITH VILLOUS HYPOPLASIA. COMMENT: THE PLACENTAL FINDINGS ARE COMPATIBLE WITH INTRAUTERINE GROWTH RESTRICTION.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Baergen, Rebecca N. (2011). Manual of Pathology of the Human Placenta (2nd ed.). Springer. pp. 346. ISBN 978-1441974938.
- ↑ Fitzgerald, B.; Kingdom, J.; Keating, S. (May 2012). "Distal villous hypoplasia.". Diagnostic Histopathology 18 (5): 195-200. doi:10.1016/j.mpdhp.2012.02.005.