Carcinoembryonic antigen
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
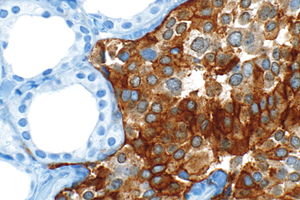

CEA immunostaining in C-cell hyperplasia. (WC)
Carcinoembryonic antigen, abbreviated CEA, is set of glycoproteins present during fetal development and associated with the gastrointestinal tract.
In pathology, they are associated with gastrointestinal tract tumours; however, may be seen in other tumours.
Monoclonal & polyclonal
- Several different types of CEA antibodies are available.
Broadly speaking they are divided into:
- CEA-p = polyclonal CEA antibody.
- CEA-m = monocloncal CEA antibody.
The staining is dependent on the specific antibody,[1] as is generally true.
Positive
- C-cell hyperplasia.
- Medullary thyroid carcinoma.
- Eccrine glands of the skin.
- Endocervical adenocarcinoma - CEA-m (25 +ve of 26 cases[2]).
See also
References
- ↑ Sheahan, K.; O'Brien, MJ.; Burke, B.; Dervan, PA.; O'Keane, JC.; Gottlieb, LS.; Zamcheck, N. (Aug 1990). "Differential reactivities of carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and CEA-related monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies in common epithelial malignancies.". Am J Clin Pathol 94 (2): 157-64. PMID 1695478.
- ↑ McCluggage, WG.; Sumathi, VP.; McBride, HA.; Patterson, A. (Jan 2002). "A panel of immunohistochemical stains, including carcinoembryonic antigen, vimentin, and estrogen receptor, aids the distinction between primary endometrial and endocervical adenocarcinomas.". Int J Gynecol Pathol 21 (1): 11-5. PMID 11781517.