B cell small lymphocytic lymphoma/chronic lymphocytic leukemia
(Redirected from CLL)
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| B cell small lymphocytic lymphoma/chronic lymphocytic leukemia | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
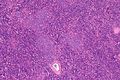
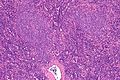
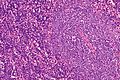
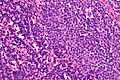
 Small lymphocytic lymphoma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | mixed population of lymphoid cells with "proliferation centers": (1) nodular collections of larger cells (~ 1.5x the size of resting lymphocyte ~ 12-15 micrometers) with nucleoli) - surrounded by (2) small dark cells (~ size of resting lymphocyte ~ 8-10 micrometers) - predominant population, lack nucleolus |
| LM DDx | other small cell lymphomas esp. mantle cell lymphoma (IHC similar) |
| IHC | CD20 +ve, CD23 +ve, CD5 +ve, cyclin D1 -ve, CD43 +ve |
| Site | blood + bone marrow/lymph nodes |
|
| |
| Prevalence | common |
| Blood work | elevated WBC (≥5 × 109/L) |
| Prognosis | good |
| Treatment | often followup |
B cell small lymphocytic lymphoma/chronic lymphocytic leukemia, often referred to as chronic lymphocytic leukemia (abbreviated CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma (abbreviated SLL), is a common low-grade hematologic malignancy. It typically afflicts older individuals.
General
- Very common.
- Good prognosis - treatment may be simply followup.[1]
- May transform to an aggressive lymphoma - see below.
- Older individuals.
- Elevated WBC ≥5 × 109/L - required for diagnosis (clinically).[2]
Richter's transformation
- CLL/SLL may under go a Richter's transformation into a high-grade non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL), e.g. DLBCL:[3]
- Incidence of transformation <5%.
- Prognosis < 1 year.
Microscopic
Features in a lymph node:[4]
- Mixed population of lymphoid cells with "proliferation centers" - key feature:
- Larger cells (~ 1.5x the size of resting lymphocyte ~ 12-15 micrometers):
- Nucleoli.
- Form (nodular) collections.
- Small dark cells (~ size of resting lymphocyte ~ 8-10 micrometers):
- Predominant population.
- Lack nucleolus.
- Larger cells (~ 1.5x the size of resting lymphocyte ~ 12-15 micrometers):
Images
www:
- CLL in the liver (pathologyatlas.ro).
- SLL in the parotid - several images (upmc.edu).
- CLL with Richter transformation - several images (upmc.edu).
IHC
Others:
- Cyclin D1 -ve.
- CD38 -ve/+ve.
- CD38 -ve suggests a good prognosis.[1]
Panel
A basic panel - based on Rizzo and Nassiri:[6]
- CD5, CD10, BCL6, CD23, cyclin D1.
Additional IHC:
- CD20, CD3, CD43, BCL2.
Molecular
- Lacks t(11;14) seen in mantle cell lymphoma.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Guarini A, Gaidano G, Mauro FR, et al. (August 2003). "Chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients with highly stable and indolent disease show distinctive phenotypic and genotypic features". Blood 102 (3): 1035–41. doi:10.1182/blood-2002-12-3639. PMID 12676780.
- ↑ Call TG, Norman AD, Hanson CA, et al. (April 2014). "Incidence of chronic lymphocytic leukemia and high-count monoclonal B-cell lymphocytosis using the 2008 guidelines". Cancer. doi:10.1002/cncr.28690. PMID 24711224.
- ↑ Tsimberidou AM, Keating MJ (April 2006). "Richter's transformation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia". Semin. Oncol. 33 (2): 250–6. doi:10.1053/j.seminoncol.2006.01.016. PMID 16616072.
- ↑ DG. 17 August 2010.
- ↑ URL: http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case296/dx.html. Accessed on: 14 January 2012.
- ↑ Rizzo, K.; Nassiri, M. (2012). "Diagnostic Workup of Small B Cell Lymphomas: A Laboratory Perspective.". Lymphoma. doi:doi:10.1155/2012/346084.