Difference between revisions of "Steatocystoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(redirect) |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
# | {{ Infobox diagnosis | ||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | |||
| Image = Steatocystoma - very high mag.jpg | |||
| Width = | |||
| Caption = Steatocystoma. [[H&E stain]]. | |||
| Synonyms = | |||
| Micro = cyst lined by squamous epithelium with a corrugated eosinophilic lining, no granular cell layer | |||
| Subtypes = | |||
| LMDDx = | |||
| Stains = | |||
| IHC = | |||
| EM = | |||
| Molecular = | |||
| IF = | |||
| Gross = | |||
| Grossing = | |||
| Site = [[skin]] - see ''[[dermal cysts]]'' | |||
| Assdx = | |||
| Syndromes = steatocystoma multiplex | |||
| Clinicalhx = | |||
| Signs = | |||
| Symptoms = | |||
| Prevalence = rare | |||
| Bloodwork = | |||
| Rads = | |||
| Endoscopy = | |||
| Prognosis = benign | |||
| Other = | |||
| ClinDDx = | |||
| Tx = | |||
}} | |||
'''Steatocystoma''' is a rare benign [[dermal cyst]]. | |||
==General== | |||
*Benign. | |||
*Rare.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Gordon Spratt | first1 = EA. | last2 = Kaplan | first2 = J. | last3 = Patel | first3 = RR. | last4 = Kamino | first4 = H. | last5 = Ramachandran | first5 = SM. | title = Steatocystoma. | journal = Dermatol Online J | volume = 19 | issue = 12 | pages = 20721 | month = Dec | year = 2013 | doi = | PMID = 24365012 }}</ref> | |||
*Typically adults. | |||
*Usually on the trunk. | |||
*May be genetic; known as ''steatocystoma multiplex''.<ref name=omim184500>{{OMIM|184500}}</ref> | |||
**Classically autosomal dominant.<ref>URL: [http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case674/dx.html http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case674/dx.html]. Accessed on: 29 January 2012.</ref> | |||
==Microscopic== | |||
Features:<ref name=Ref_Derm312>{{Ref Derm|312}}</ref> | |||
*Cyst lined by squamous epithelium with: | |||
*#Corrugated eosinophilic lining - '''key feature'''. | |||
*#*Similar appearance to compact keratin (hyperkeratosis). | |||
*#*Described as a ''hyaline cuticle''.<ref>URL: [http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case674/dx.html http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case674/dx.html]. Accessed on: 29 January 2012.</ref> | |||
*#'''No''' granular cell layer. | |||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
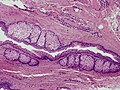
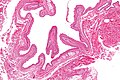
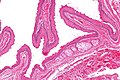
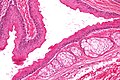
Image:SkinTumors-P6260388.JPG | Steatocystoma. (WC) | |||
Image:Steatocystoma_-_low_mag.jpg | Steatocystoma - low mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
Image:Steatocystoma_-_intermed_mag.jpg | Steatocystoma - intermed. mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
Image:Steatocystoma_-_high_mag.jpg | Steatocystoma - high mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
</gallery> | |||
www: | |||
*[http://www.flickr.com/photos/santoshpath/4788590105/in/photostream/ Steatocystoma - low mag. (flickr.com)]. | |||
**[http://www.flickr.com/photos/santoshpath/4788590109/ Steatocystoma - high mag. (flickr.com)]. | |||
*[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case674/images/fig03.jpg Steatocystoma (upmc.edu)].<ref>URL: [http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case674.html http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case674.html]. Accessed on: 29 January 2012.</ref> | |||
==See also== | |||
*[[Dermal cysts]]. | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|2}} | |||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | |||
[[Category:Dermal cysts]] | |||
Latest revision as of 22:53, 16 February 2014
| Steatocystoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
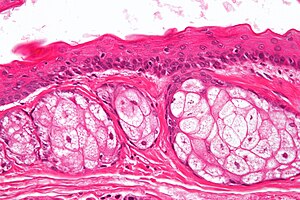 Steatocystoma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | cyst lined by squamous epithelium with a corrugated eosinophilic lining, no granular cell layer |
| Site | skin - see dermal cysts |
|
| |
| Syndromes | steatocystoma multiplex |
|
| |
| Prevalence | rare |
| Prognosis | benign |
Steatocystoma is a rare benign dermal cyst.
General
- Benign.
- Rare.[1]
- Typically adults.
- Usually on the trunk.
- May be genetic; known as steatocystoma multiplex.[2]
- Classically autosomal dominant.[3]
Microscopic
Features:[4]
- Cyst lined by squamous epithelium with:
- Corrugated eosinophilic lining - key feature.
- Similar appearance to compact keratin (hyperkeratosis).
- Described as a hyaline cuticle.[5]
- No granular cell layer.
- Corrugated eosinophilic lining - key feature.
Images
www:
See also
References
- ↑ Gordon Spratt, EA.; Kaplan, J.; Patel, RR.; Kamino, H.; Ramachandran, SM. (Dec 2013). "Steatocystoma.". Dermatol Online J 19 (12): 20721. PMID 24365012.
- ↑ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 184500
- ↑ URL: http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case674/dx.html. Accessed on: 29 January 2012.
- ↑ Busam, Klaus J. (2009). Dermatopathology: A Volume in the Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 312. ISBN 978-0443066542.
- ↑ URL: http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case674/dx.html. Accessed on: 29 January 2012.
- ↑ URL: http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case674.html. Accessed on: 29 January 2012.