Difference between revisions of "Pilocytic astrocytoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(+images) |
(→Images) |
||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
===Images=== | ===Images=== | ||
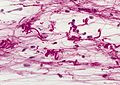
Smears | ====Smears==== | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
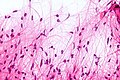
Image:Pilocytic_astrocytoma_-_smear_-_very_high_mag.jpg | Bipolar cells with hair-like processes - smear - very high mag. (WC) | Image:Pilocytic_astrocytoma_-_smear_-_very_high_mag.jpg | Bipolar cells with hair-like processes - smear - very high mag. (WC) | ||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
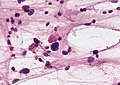
Image:Rosenthal_fibers.jpg | Rosenthal fibres - smear. (WC/AFIP) | Image:Rosenthal_fibers.jpg | Rosenthal fibres - smear. (WC/AFIP) | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Sections | ====Sections==== | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
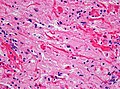
Image:Rosenthal_HE_40x.jpg | Rosenthal fibres. (WC) | Image:Rosenthal_HE_40x.jpg | Rosenthal fibres. (WC) | ||
Revision as of 02:14, 22 December 2013
Pilocytic astrocytoma is a low-grade astrocytoma. It the most common glioma in children.
General
- Low-grade astrocytoma - WHO Grade I by definition.
- Classically in the cerebellum in children; most common glioma in children.[1]
- The optic glioma associated with neurofibromatosis 1.
Gross
Features:[1]
- Usually well-circumscribed.
- Cystic or solid.
- Do not smear. (Ref. ?)
Microscopic
Features:[2]
- Classically biphasic (though either may be absent):
- Fibrillar.
- Microcystic/loose.
- Hair-like fibres ~ 1 micrometer; pilo- = hair.[3]
- Best seen on smear or with GFAP IHC.
- Rosenthal fibres - key feature.
- May be rare. Not pathognomonic (see below).
- Eosinophilic granular bodies.
- Low cellularity - when compared to medulloblastoma and ependymoma.
Notes:
- +/-Microvascular proliferation.
- +/-Focal necrosis.
- Necrosis with pseudopalisading more likely glioblastoma.
- +/-Mitoses - not significant in the context of the Dx.
DDx (of Rosenthal fibers):[4]
- Chronic reactive gliosis.
- Subependymoma.
- Ganglioma.
- Alexander's disease (rare leukodystrophy).
DDx of pilocystic astrocytoma (brief):
- Piloid gliosis.
- Oligodendroglioma.
- Glioblastoma (uncommon - but important).
Images
Smears
Sections
www:
- Rosenthal fibre (ouhsc.edu).
- Pilocytic astrocytoma (upmc.edu).
- Pilocytic astrocytoma - another case (upmc.edu).
- Pilocytic astrocytoma - pennies on a plate (upmc.edu).[5]
- Pilocytic astrocytoma (upmc.edu).
Stains
- PAS-D: eosinophilic granular bodies +ve.
IHC
Features:[6]
- GFAP +ve (fibres).
- CD68: may have a significant macrophage component.
- KI-67: may be "high" (~20% ???).
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Perry, Arie; Brat, Daniel J. (2010). Practical Surgical Neuropathology: A Diagnostic Approach: A Volume in the Pattern Recognition series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 82. ISBN 978-0443069826.
- ↑ Perry, Arie; Brat, Daniel J. (2010). Practical Surgical Neuropathology: A Diagnostic Approach: A Volume in the Pattern Recognition series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 82-4. ISBN 978-0443069826.
- ↑ URL: http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/pilo-. Accessed on: 24 November 2010.
- ↑ MUN. 9 Mar 2009.
- ↑ URL: http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case195.html. Accessed on: 8 January 2012.
- ↑ Perry, Arie; Brat, Daniel J. (2010). Practical Surgical Neuropathology: A Diagnostic Approach: A Volume in the Pattern Recognition series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 84. ISBN 978-0443069826.