Difference between revisions of "Neuroendocrine tumour of the appendix"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
*Classically subepithelial/mural. | *Classically subepithelial/mural. | ||
*Various growth patterns: | *Various growth patterns: | ||
**Nested (insular) | **Nested (insular). | ||
**Trabecular | **Trabecular. | ||
**Palisading | **Palisading. | ||
**Ribbons, | **Ribbons, [[rosette]]s. | ||
*Fibrous stroma in between cell groups. | *Fibrous stroma in between cell groups. | ||
*Cytomorphology | *Cytomorphology: | ||
**Monotonous appearance with scanty mitoses. | **Monotonous appearance with scanty mitoses. | ||
**Round central nuclei | **Round central nuclei. | ||
**Stippled chromatin [[AKA]] salt-and-pepper chromatin | **Stippled chromatin ([[AKA]] ''salt-and-pepper chromatin'' and ''coarse chromatin''). | ||
**Eosinophilic granular cytoplasm | **Eosinophilic granular cytoplasm. | ||
DDx: | |||
*[[Colorectal adenocarcinoma]]. | |||
*Adenocarcinoid. | |||
*[[Crypt cell carcinoma]], also known as ''goblet cell carcinoid''. | |||
*[[Metastasis|Metastatic]] [[adenocarcinoma]]. | |||
*Normal ganglion cells in the Meissner plexus (submucosa) and Auerbach plexus (located between the inner and outer layers of the muscularis propria). | |||
===Special Types=== | ===Special Types=== | ||
*Tubular carcinoid | *Tubular carcinoid. | ||
**Neuroendocrine cells forming tubules (no cell nests) | **Neuroendocrine cells forming tubules (no cell nests). | ||
**Some tubules can contain mucin | **Some tubules can contain mucin. | ||
**Can be confused with adenocarcinoma | **Can be confused with adenocarcinoma. | ||
**Features suggesting tubular carcinoid (over adenocarcinoma): | **Features suggesting tubular carcinoid (over adenocarcinoma): | ||
***Arises from base of crypts, with no disruption of surface epithelium. | ***Arises from base of crypts, with no disruption of surface epithelium. | ||
***No associated epithelial precursor (no adenomatous change). | ***No associated epithelial precursor (no adenomatous change). | ||
***Neuroendocrine cytologic features, without prominent atypia | ***Neuroendocrine cytologic features, without prominent atypia. | ||
***IHC (NE markers +ve) | ***IHC (NE markers +ve). | ||
*Goblet cell carcinoid - dealt with in the article ''[[crypt cell carcinoma]]''. | |||
*Goblet cell carcinoid | *Signet-ring cells forming glandular structures. | ||
*Signet-ring cells forming glandular structures | *Possibly also with extra-cellular mucin.{{fact}} | ||
*Possibly also with extra-cellular mucin | |||
===Images=== | ===Images=== | ||
| Line 86: | Line 85: | ||
*Chromogranin A -ve/+ve. | *Chromogranin A -ve/+ve. | ||
*Synaptophysin +ve. | *Synaptophysin +ve. | ||
*Keratin positive, but CK7/CK20 negative | *Keratin positive, but CK7/CK20 negative.{{fact}} | ||
*S100 positive for appendix | *S100 positive for appendix.{{fact}} | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Revision as of 07:35, 19 March 2015
Neuroendocrine tumour of the appendix is a common tumour of the vermiform appendix.
General
- Most common tumour of the appendix.[1]
- Not really common though - one is seen in approximately 300 appendectomies.[2]
Presentation
- Often found incidentally, may be microscopic.
- May cause obstruction leading to mucocele or acute appendicitis.
- May precipitate torsion.
Size matters in appendiceal NETs:[3]
- <1.0 cm - do not metastasize.
- 1.0-2.0 cm - rarely metastasize.
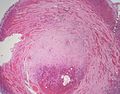
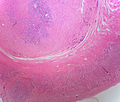
Gross
- Classically found in the tip of the appendix.
- Characteristic yellow cut surface (when fixed)
- Circumscribed but not encapsulated
- Firm (due to desmoplasia)
- Centred in the submucosa
- Nodules that do not usually cause erosion of the overlying mucosa.
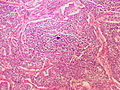
Image
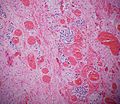
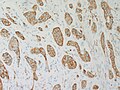
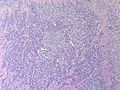
Microscopic
Features:
- Classically subepithelial/mural.
- Various growth patterns:
- Nested (insular).
- Trabecular.
- Palisading.
- Ribbons, rosettes.
- Fibrous stroma in between cell groups.
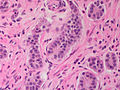
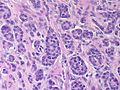
- Cytomorphology:
- Monotonous appearance with scanty mitoses.
- Round central nuclei.
- Stippled chromatin (AKA salt-and-pepper chromatin and coarse chromatin).
- Eosinophilic granular cytoplasm.
DDx:
- Colorectal adenocarcinoma.
- Adenocarcinoid.
- Crypt cell carcinoma, also known as goblet cell carcinoid.
- Metastatic adenocarcinoma.
- Normal ganglion cells in the Meissner plexus (submucosa) and Auerbach plexus (located between the inner and outer layers of the muscularis propria).
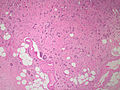
Special Types
- Tubular carcinoid.
- Neuroendocrine cells forming tubules (no cell nests).
- Some tubules can contain mucin.
- Can be confused with adenocarcinoma.
- Features suggesting tubular carcinoid (over adenocarcinoma):
- Arises from base of crypts, with no disruption of surface epithelium.
- No associated epithelial precursor (no adenomatous change).
- Neuroendocrine cytologic features, without prominent atypia.
- IHC (NE markers +ve).
- Goblet cell carcinoid - dealt with in the article crypt cell carcinoma.
- Signet-ring cells forming glandular structures.
- Possibly also with extra-cellular mucin.[citation needed]
Images
www:
- Appendiceal carcinoid (humpath.com).
- Carcinoid of the appendix (brown.edu).
- Appendiceal carcinoid (flickr.com/Qiao).
IHC
Features:
- Chromogranin A -ve/+ve.
- Synaptophysin +ve.
- Keratin positive, but CK7/CK20 negative.[citation needed]
- S100 positive for appendix.[citation needed]
See also
References
- ↑ Mitchell, Richard; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Abbas, Abul K.; Aster, Jon (2011). Pocket Companion to Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 435. ISBN 978-1416054542.
- ↑ Mitra, B.; Pal, M.; Paul, B.; Saha, TN.; Maiti, A. (2013). "Goblet cell carcinoid of appendix: A rare case with literature review.". Int J Surg Case Rep 4 (3): 334-7. doi:10.1016/j.ijscr.2013.01.007. PMID 23416502.
- ↑ Modlin, IM.; Lye, KD.; Kidd, M. (Feb 2003). "A 5-decade analysis of 13,715 carcinoid tumors.". Cancer 97 (4): 934-59. doi:10.1002/cncr.11105. PMID 12569593.