Hibernoma
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
The printable version is no longer supported and may have rendering errors. Please update your browser bookmarks and please use the default browser print function instead.
Hibernoma, also tumour of brown fat,[1] is an uncommon adipocytic tumour.
| Hibernoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
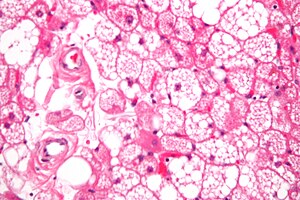 Hibernoma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | large polygonal/oval cells with central & small nucleus; nucleoli typically prominent; cytoplasm multivacuolated, oval, eosinophilic, granular |
| LM DDx | reaction to silicone implant |
| Gross | lobulated lesion, light-brown, usually extremities |
| Site | cervical-supraclavicular, periaortic - both thorax and the abdomen, perirenal; see soft tissue - adipocytic lesions |
|
| |
| Clinical history | typically young adults |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Prognosis | benign |
| Clin. DDx | Lipoma |
General
- Consists of brown fat (present in the infants to generate heat).[2]
- Benign.
- Usually asymptomatic.[3]
Epidemiology:
- Young adults - disappears with age.[4]
Gross
- Well-circumscribed.
- Lobulated and light-brown on sectioning.
Locations:[4]
- Cervical-supraclavicular.
- Periaortic - both thorax and the abdomen.
- Perirenal.
Microscopic
Features:[5]
- Large polygonal/oval cells:
- +/-Prominent blood vessels, central.[8]
DDx:
- Reaction to silicone implant.
Images
See also
References
- ↑ SHUTE, D. (Nov 1954). "Tumours of brown fat.". Can Med Assoc J 71 (5): 484-5. PMID 13209434.
- ↑ Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 605. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ Ahmed SA, Schuller I (December 2008). "Pediatric hibernoma: a case review". J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 30 (12): 900–1. doi:10.1097/MPH.0b013e318184e6dd. PMID 19131775.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Zoico E, Rubele S, De Caro A, Nori N, Mazzali G, Fantin F, Rossi A, Zamboni M (2019). "Brown and Beige Adipose Tissue and Aging". Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 10: 368. doi:10.3389/fendo.2019.00368. PMC 6595248. PMID 31281288. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6595248/.
- ↑ Chen DY, Wang CM, Chan HL (March 1998). "Hibernoma. Case report and literature review". Dermatol Surg 24 (3): 393–5. PMID 9537018.
- ↑ http://www.pathconsultddx.com/pathCon/diagnosis?pii=S1559-8675(06)70271-6
- ↑ http://surgpathcriteria.stanford.edu/softfat/hibernoma/
- ↑ URL: http://radiographics.rsna.org/content/24/5/1433.full. Accessed on: 11 February 2013.