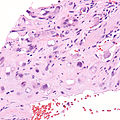
Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
The printable version is no longer supported and may have rendering errors. Please update your browser bookmarks and please use the default browser print function instead.
| Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
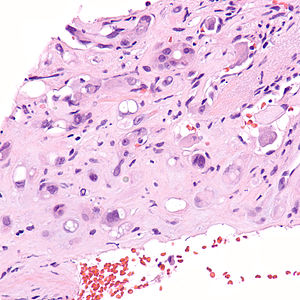 Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | large epithelioid perivascular cells with abundant pale eosinophilic cytoplasm and cytoplasmic vacuolation ("blister cells") - may form lumen and have RBC within, vesicular nucleus +/-prominent nucleolus; tuft-like projections into capillaries; cells may be in well-circumscribed paucicellular nodules or poorly formed cellular aggregates |
| LM DDx | epithelioid angiosarcoma, hemangioma, epithelioid sarcoma |
| IHC | CD31 +ve, CD34 +ve, factor VIII +ve, CAMTA1 +ve, TFE3 +ve/-ve |
| Molecular | gene fusions: WWTR1-CAMTA1 (approximately 90% of cases), YAP1-TFE3 (small number of cases) |
| Site | soft tissue - see vascular tumours, classically liver - but various sites reported |
|
| |
| Prevalence | rare |
| Prognosis | moderate |
| Treatment | resection |
Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma, abbreviated EHE, is rare malignant vascular tumour.
It should not be confused with epithelioid hemangioma.
General
- Malignant.[1]
- Adults - wide age range.
- Associated with oral contraceptives, vinyl chloride.[2]
- Rare.[3]
Treatment:
- Excision[4] if feasible.
- Chemotherapy - not standardized.[3]
- Liver transplantation.[5]
Prognosis - liver:
- ~55% five-year survival.[4]
- Better than other liver tumours.
Gross
- Classically, a liver lesion - but found elsewhere.[6][7]
- Case reports of EHE in a wide number of anatomical sites (bowel,[8], parotid[9] mediastinum[10]).
Microscopic
Features:[2]
- Large epithelioid perivascular cells with:
- Abundant pale eosinophilic cytoplasm.
- Cytoplasmic vacuolation (some cells) - AKA "blister cells" - key feature.
- May form lumen and have RBC within.
- Vesicular nucleus with prominent nucleolus in some cells.
- Tuft-like projections into capillaries.
- Tumour cells may be in well-circumscribed paucicellular nodules or more cellular poorly formed aggregates.
DDx:[11]
- Angiosarcoma, epithelioid.
- Hemangioma.
- Cholangiocarcinoma.
- Fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Epithelioid sarcoma.[12]
Images
www:
- Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma - low mag. (flickr.com/Rosen).
- Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma - high mag. (flickr.com/Rosen).
- Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma (surgicalpathologyatlas.com).
IHC
Features:[2]
- CD31 +ve.
- CD34 +ve.
- Factor VIII +ve.
- CAMTA1 +ve.[12]
- TFE3 +ve - minority of cases.
Molecular
Gene fusions:[12]
- WWTR1-CAMTA1 - seen in approximately 90% of cases.
- YAP1-TFE3 fusion gene - <5% of cases.
See also
References
- ↑ Humphrey, Peter A; Dehner, Louis P; Pfeifer, John D (2008). The Washington Manual of Surgical Pathology (1st ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 603. ISBN 978-0781765275.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Gupta, R.; Mathur, SR.; Gupta, SD.; Durgapal, P.; Iyer, VK.; Das, CJ.; Shalimar, SK.; Acharya, . (2010). "Hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: A diagnostic pitfall in aspiration cytology.". Cytojournal 6: 25. doi:10.4103/1742-6413.58951. PMID 20165548.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Chevreau, C.; Le Cesne, A.; Ray-Coquard, I.; Italiano, A.; Cioffi, A.; Isambert, N.; Robin, YM.; Fournier, C. et al. (Jul 2013). "Sorafenib in patients with progressive epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: a phase 2 study by the French Sarcoma Group (GSF/GETO).". Cancer 119 (14): 2639-44. doi:10.1002/cncr.28109. PMID 23589078.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Läuffer, JM.; Zimmermann, A.; Krähenbühl, L.; Triller, J.; Baer, HU. (Dec 1996). "Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of the liver. A rare hepatic tumor.". Cancer 78 (11): 2318-27. PMID 8941001.
- ↑ Nudo, CG.; Yoshida, EM.; Bain, VG.; Marleau, D.; Wong, P.; Marotta, PJ.; Renner, E.; Watt, KD. et al. (Oct 2008). "Liver transplantation for hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: the Canadian multicentre experience.". Can J Gastroenterol 22 (10): 821-4. PMID 18925305.
- ↑ Cardinal, J.; de Vera, ME.; Marsh, JW.; Steel, JL.; Geller, DA.; Fontes, P.; Nalesnik, M.; Gamblin, TC. (Nov 2009). "Treatment of hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: a single-institution experience with 25 cases.". Arch Surg 144 (11): 1035-9. doi:10.1001/archsurg.2009.121. PMID 19917940.
- ↑ Haughey AM, Moloney BM, O'Brien CM (October 2023). "Epithelioid Haemangioendothelioma; Not simply a hepatic pathology". Clin Imaging 102: 42–52. doi:10.1016/j.clinimag.2023.07.003. PMID 37541086.
- ↑ Spasic S, Brcic I, Freire R, Garcia-Buitrago MT, Rosenberg AE (June 2019). "Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma of the Bowel in Crohn's Disease: The First Reported Case". Int J Surg Pathol 27 (4): 423–426. doi:10.1177/1066896918801527. PMID 30238810.
- ↑ Suarez-Zamora DA, Rodriguez-Urrego PA, Hakim-Tawil JA, Palau-Lazaro MA (2019). "Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of the parotid gland: A case report in an unusual location with a review of the literature". Rev Esp Patol 52 (4): 260–264. doi:10.1016/j.patol.2019.04.002. PMID 31530411.
- ↑ Kim SH, Kim YS, Jang MH, Kwon HJ (2019). "Mediastinal Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma Invading Superior Vena Cava: A Case Report and Review of Literature". Curr Med Imaging Rev 15 (3): 349–352. doi:10.2174/1573405614666180124141817. PMID 31989887.
- ↑ Cardinal, J.; de Vera, ME.; Marsh, JW.; Steel, JL.; Geller, DA.; Fontes, P.; Nalesnik, M.; Gamblin, TC. (Nov 2009). "Treatment of hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: a single-institution experience with 25 cases.". Arch Surg 144 (11): 1035-9. doi:10.1001/archsurg.2009.121. PMID 19917940.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 Doyle LA, Fletcher CD, Hornick JL (January 2016). "Nuclear Expression of CAMTA1 Distinguishes Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma From Histologic Mimics". Am J Surg Pathol 40 (1): 94–102. doi:10.1097/PAS.0000000000000511. PMID 26414223.