Difference between revisions of "Eccrine spiradenoma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→IHC) |
|||
| (11 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
*Multiple lesions, early in life suggest a genetic syndrome. | *Multiple lesions, early in life suggest a genetic syndrome. | ||
**Brooke-Spiegler syndrome - spiradenomas, cylindromas and trichoepitheliomas | **Brooke-Spiegler syndrome - spiradenomas, cylindromas and trichoepitheliomas | ||
*Generally considered to be an 'eccrine' tumor but some hypothesize a pilar origin <ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Kazakov | first1 = DV. | last2 = Soukup | first2 = R. | last3 = Mukensnabl | first3 = P. | last4 = Boudova | first4 = L. | last5 = Michal | first5 = M. | title = Brooke-Spiegler syndrome: report of a case with combined lesions containing cylindromatous, spiradenomatous, trichoblastomatous, and sebaceous differentiation. | journal = Am J Dermatopathol | volume = 27 | issue = 1 | pages = 27-33 | month = Feb | year = 2005 | doi = | PMID = 15677973 }}</ref> | |||
==Microscopic== | ==Microscopic== | ||
Features:<ref name=dermatlas>URL: [http://www.dermatlas.com/derm/IndexDisplay.cfm?ImageID=-1193575448 http://www.dermatlas.com/derm/IndexDisplay.cfm?ImageID=-1193575448]. Accessed on: 29 November 2010.</ref><ref>URL: [http://www.pathconsultddx.com/pathCon/diagnosis?pii=S1559-8675%2806%2970191-7 http://www.pathconsultddx.com/pathCon/diagnosis?pii=S1559-8675%2806%2970191-7]. Accessed on: 10 May 2011.</ref> | Features:<ref name=dermatlas>URL: [http://www.dermatlas.com/derm/IndexDisplay.cfm?ImageID=-1193575448 http://www.dermatlas.com/derm/IndexDisplay.cfm?ImageID=-1193575448]. Accessed on: 29 November 2010.</ref><ref>URL: [http://www.pathconsultddx.com/pathCon/diagnosis?pii=S1559-8675%2806%2970191-7 http://www.pathconsultddx.com/pathCon/diagnosis?pii=S1559-8675%2806%2970191-7]. Accessed on: 10 May 2011.</ref> | ||
*Dense nests of cells in the dermis; "dermal blue balls". | *Dense nests of cells in the dermis; "dermal blue balls". | ||
* | *Biphasic cell population: | ||
** | **outer dark cells with small hyperchromatic nuclei and minimal cytoplasm. | ||
** | **inner larger cells with [[vesicular nuclei]] and more cytoplasm. | ||
**In some areas the two cell types mix together with dispersed hyaline droplets. | |||
*Ductal differentiation. | |||
*These cells form lobules that are surrounded by a hyaline or reticulin sheath. | |||
*+/-Lymphocytes. | *+/-Lymphocytes. | ||
*Vascular component - large and small blood vessels. | *Vascular component - large and small blood vessels. | ||
DDx: | DDx: | ||
*[[Dermal cylindroma]] | *[[Dermal cylindroma]]. | ||
**These two tumors are very closely related | **These two tumors are very closely related and overlap. | ||
**Many tumors have areas of both spiradenoma and cylindroma. | **Many tumors have areas of both spiradenoma and cylindroma. | ||
**The lobules of cylindroma are small | |||
***more consistently discrete, | |||
***show more a more consistent arrangement of the light and dark cells and are | |||
***often surrounded by prominent hyaline material. | |||
**Individual lobules of cylindroma fit together like pieces of a puzzle. | |||
**Lobules of spiradenoma are larger | |||
***may run together and fuse, | |||
***may not have a prominent hyaline surround and | |||
***may show more disorganization and mixing of the two cell types | |||
*[[Trichoepithelioma]]. | *[[Trichoepithelioma]]. | ||
*[[Glomus tumour]]. | **Trichoepithelioma will show | ||
**The location | ***attempts at hair bulbs, | ||
***areas with more eosinophilic cytoplasm and | |||
***characteristic peritumoral stroma | |||
*[[Glomus tumour]], hemangioma or hemangiopericytoma (vascular spiradenomas). | |||
**The location often speaks against glomus tumour. | |||
*Basal cell carcinoma | |||
**Spiradenoma is deeper, without connection to the epidermis | |||
**Spiradenoma lacks clefting artefact. | |||
**Spiradenoma lacks mitoses and prominent apoptosis. | |||
**BCC lacks ducts | |||
**BCC lobules lack a prominent surrounding hyaline membrane | |||
*Lymphoid aggregate (spiradenoma will be cytokeratin positive) | |||
===Images=== | ===Images=== | ||
| Line 69: | Line 93: | ||
Image:Skin Spiradenoma Thrombus HP 13PY174127.jpg|Spiradenoma - vascular channels within a basaloid tumor. (SKB) | Image:Skin Spiradenoma Thrombus HP 13PY174127.jpg|Spiradenoma - vascular channels within a basaloid tumor. (SKB) | ||
Image:Skin Spiradenoma Vascular Thrombus 14PY169268.jpg|Thrombosed blood vessel within a spiradenoma. (SKB) | Image:Skin Spiradenoma Vascular Thrombus 14PY169268.jpg|Thrombosed blood vessel within a spiradenoma. (SKB) | ||
Image:Skin Spiradenoma MP2 14PYSNP.jpg|Spiradenoma - dispersed hyaline pattern. (SKB) | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
www: | www: | ||
| Line 77: | Line 102: | ||
*S100 +ve. | *S100 +ve. | ||
*Keratins 7, 8, and 18 +ve. | *Keratins 7, 8, and 18 +ve. | ||
*Ductules are [[EMA]] and [[CEA]] positive. | |||
Notes: | Notes: | ||
*IHC profile essentially identical to dermal cylindroma.<ref name=pmid9129700/> | *IHC profile essentially identical to dermal cylindroma.<ref name=pmid9129700/> | ||
Latest revision as of 05:40, 2 January 2016
| Eccrine spiradenoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
 Eccrine spiradenoma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| Synonyms | spiradenoma |
|
| |
| LM | dense nests of cells in the dermis ("dermal blue balls"), mixed cell population (epithelial, myoepithelial, +/-lymphocytes) |
| LM DDx | dermal cylindroma, trichoepithelioma |
| IHC | S100 +ve, CK7 +ve, CK18 +ve |
| Site | skin |
|
| |
| Symptoms | pain - see painful skin lesions |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Prognosis | benign |
| Other | may be related to dermal cylindroma |
| Clin. DDx | painful skin lesions, others |
| Treatment | excision |
Eccrine spiradenoma, also spiradenoma,[1] is (usually) a benign, painful skin thingy. There is case series of malignant ones.[2]
General
- One of the ANGEL tumours:
- A painful skin lesion.
- Many of these tumours have a prominent vascular component (think of blood vessels throbbing).
- Benign.
- Usually solitary, circumscribed and dermal.
- Most common on the head.
- Multiple lesions, early in life suggest a genetic syndrome.
- Brooke-Spiegler syndrome - spiradenomas, cylindromas and trichoepitheliomas
- Generally considered to be an 'eccrine' tumor but some hypothesize a pilar origin [3]
Microscopic
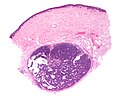
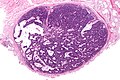
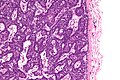
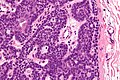
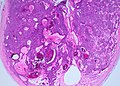
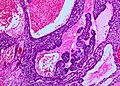
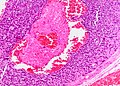
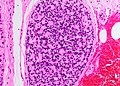
- Dense nests of cells in the dermis; "dermal blue balls".
- Biphasic cell population:
- outer dark cells with small hyperchromatic nuclei and minimal cytoplasm.
- inner larger cells with vesicular nuclei and more cytoplasm.
- In some areas the two cell types mix together with dispersed hyaline droplets.
- Ductal differentiation.
- These cells form lobules that are surrounded by a hyaline or reticulin sheath.
- +/-Lymphocytes.
- Vascular component - large and small blood vessels.
DDx:
- Dermal cylindroma.
- These two tumors are very closely related and overlap.
- Many tumors have areas of both spiradenoma and cylindroma.
- The lobules of cylindroma are small
- more consistently discrete,
- show more a more consistent arrangement of the light and dark cells and are
- often surrounded by prominent hyaline material.
- Individual lobules of cylindroma fit together like pieces of a puzzle.
- Lobules of spiradenoma are larger
- may run together and fuse,
- may not have a prominent hyaline surround and
- may show more disorganization and mixing of the two cell types
- Trichoepithelioma.
- Trichoepithelioma will show
- attempts at hair bulbs,
- areas with more eosinophilic cytoplasm and
- characteristic peritumoral stroma
- Trichoepithelioma will show
- Glomus tumour, hemangioma or hemangiopericytoma (vascular spiradenomas).
- The location often speaks against glomus tumour.
- Basal cell carcinoma
- Spiradenoma is deeper, without connection to the epidermis
- Spiradenoma lacks clefting artefact.
- Spiradenoma lacks mitoses and prominent apoptosis.
- BCC lacks ducts
- BCC lobules lack a prominent surrounding hyaline membrane
- Lymphoid aggregate (spiradenoma will be cytokeratin positive)
Images
www:
IHC
Features:[6]
Notes:
- IHC profile essentially identical to dermal cylindroma.[6]
See also
References
- ↑ URL: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1062079-overview. Accessed on: 9 May 2011.
- ↑ Andreoli, MT.; Itani, KM. (May 2011). "Malignant eccrine spiradenoma: a meta-analysis of reported cases.". Am J Surg 201 (5): 688-92. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2010.04.015. PMID 20851376.
- ↑ Kazakov, DV.; Soukup, R.; Mukensnabl, P.; Boudova, L.; Michal, M. (Feb 2005). "Brooke-Spiegler syndrome: report of a case with combined lesions containing cylindromatous, spiradenomatous, trichoblastomatous, and sebaceous differentiation.". Am J Dermatopathol 27 (1): 27-33. PMID 15677973.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 URL: http://www.dermatlas.com/derm/IndexDisplay.cfm?ImageID=-1193575448. Accessed on: 29 November 2010.
- ↑ URL: http://www.pathconsultddx.com/pathCon/diagnosis?pii=S1559-8675%2806%2970191-7. Accessed on: 10 May 2011.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Meybehm, M.; Fischer, HP. (Apr 1997). "Spiradenoma and dermal cylindroma: comparative immunohistochemical analysis and histogenetic considerations.". Am J Dermatopathol 19 (2): 154-61. PMID 9129700.