Difference between revisions of "Cushing syndrome"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→See also: +CD) |
Jensflorian (talk | contribs) (→Microscopic: +pictures crooke cell adenoma) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Cushing syndrome''', also '''hypercortisolism''', is when there is too much glucocorticoids. | '''Cushing syndrome''', also '''hypercortisolism''', is when there is too much glucocorticoids. | ||
==Clinical== | |||
The features can be remembered with ''CUSHING'':<ref>URL: [http://www.usmletomd.com/smartmd/2007/09/remembering-clinical-features-of.html http://www.usmletomd.com/smartmd/2007/09/remembering-clinical-features-of.html]. Accessed on: 1 May 2012.</ref> | |||
*'''C'''entral obesity + '''C'''ervical fat pad + '''C'''omedones (acne). | |||
*'''U'''nusual brUising. | |||
*'''S'''triae. | |||
*'''H'''ypertension + '''H'''yperglycemia. | |||
*'''I'''mmunosuppression. | |||
*'''N'''eoplasia may cause it. | |||
*'''G'''rowth retardation. | |||
A shorter version is ''CUSH'': | |||
*'''C'''entral obesity with peripheral wasting, '''C'''ervical fat pad. | |||
*'''U'''nusual br'''U'''ising. | |||
*'''S'''traiae on Skin. | |||
*'''H'''ypertension + '''H'''yperglycemia. | |||
==Microscopic== | ==Microscopic== | ||
| Line 5: | Line 21: | ||
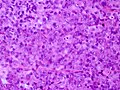
*Crooke-hyaline change:<ref>{{Ref PCPBoD8|581}}</ref> | *Crooke-hyaline change:<ref>{{Ref PCPBoD8|581}}</ref> | ||
**ACTH producing cell: basophilic granular cytoplasm becomes pale and homogenous. | **ACTH producing cell: basophilic granular cytoplasm becomes pale and homogenous. | ||
<gallery> | |||
File:Crooke HE 40x.jpg | Crooke´s cell adenoma showing various Crooke cells with hyalinzed cytoplasms. (WC/marvin101) | |||
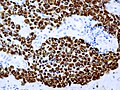
File:Crooke Cytokeratins.jpg | Ringlike perinuclear expression of cytokeratins in Crooke´s cell adenoma. (WC/marvin101) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Latest revision as of 12:30, 16 June 2015
Cushing syndrome, also hypercortisolism, is when there is too much glucocorticoids.
Clinical
The features can be remembered with CUSHING:[1]
- Central obesity + Cervical fat pad + Comedones (acne).
- Unusual brUising.
- Striae.
- Hypertension + Hyperglycemia.
- Immunosuppression.
- Neoplasia may cause it.
- Growth retardation.
A shorter version is CUSH:
- Central obesity with peripheral wasting, Cervical fat pad.
- Unusual brUising.
- Straiae on Skin.
- Hypertension + Hyperglycemia.
Microscopic
Features - pituitary gland:
- Crooke-hyaline change:[2]
- ACTH producing cell: basophilic granular cytoplasm becomes pale and homogenous.
See also
References
- ↑ URL: http://www.usmletomd.com/smartmd/2007/09/remembering-clinical-features-of.html. Accessed on: 1 May 2012.
- ↑ Mitchell, Richard; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Abbas, Abul K.; Aster, Jon (2011). Pocket Companion to Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 581. ISBN 978-1416054542.